Abstract.
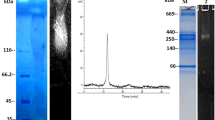
The thermostable β-glycosidase from Thermus thermophilus, cloned and overexpressed in Escherichia coli was used to catalyze the transfer of β-D-glucosyl and β-D-fucosyl from the corresponding p-nitrophenyl-β-D-glycopyranosides to a hydroxyl group of glucose in the synthesis of β-D-glucosyl-D-glucopyranoses and β-D-fucosyl-D-glucopyranoses. The yields in disaccharides produced under conditions of non-initial velocity were very attractive and the formation of the β(1–3) linked disaccharides was largely favored. The enzyme could constitute a valuable biocatalyst for the synthesis of disaccharides involving such structures as, for example, Bifidus factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received revision: 27 December 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fourage, .L., Colas, .B. Synthesis of β-D-glucosyl- and β-D-fucosyl-glucoses using β-glycosidase from Thermus thermophilus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56, 406–410 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100627
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100627