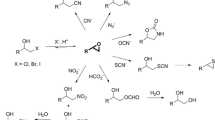
Abstract
Biocatalytic transformations in organic synthesis often require the use of organic solvents to improve substrate solubility and promote the product formation. Halohydrin dehalogenases (HHDHs) are enzymes that catalyze the formation and conversion of epoxides, important synthetic class of compounds that are often sparingly soluble in water and prone to hydrolysis. In this study, the activity, stability, and enantioselectivity of HHDH from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 (HheC) in form of cell-free extract were evaluated in various aqueous-organic media. A correlation was discovered between the enzyme activity in the ring-closure reaction and logP of the solvent. Knowledge of such a relationship makes biocatalysis with organic solvents more predictable, which may reduce the need to experiment with a variety of solvents in the future. The results revealed a high enzyme compatibility with hydrophobic solvents (e.g., n-heptane) in terms of activity and stability. Regarding the HHDH applicability in an organic medium, inhibitions by a number of solvents (e.g., THF, toluene, chloroform) proved to be a more challenging problem than the protein stability, especially in the ring-opening reaction, thus suggesting which solvents should be avoided. In addition, solvent tolerance of the thermostable variant ISM-4 was also evaluated, revealing increased stability and to a lesser extent enantioselectivity compared to the wild-type. This is the first time such a systematic analysis has been reported, giving insight into the behavior of HHDHs in nonconventional media and opening new opportunities for the future biocatalytic applications.
Key points
• HheC performs better in the presence of hydrophobic than hydrophilic solvents.
• Enzyme activity in the PNSHH ring-closure reaction is a function of the logP.
• Thermostability of ISM-4 variant is accompanied by superior solvent tolerance.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
References
Arabnejad H, Dal Lago M, Jekel PA, Floor RJ, Thunnissen A-MWH, Terwisscha van Scheltinga AC, Wijma HJ, Janssen DB (2016) A robust cosolvent-compatible halohydrin dehalogenase by computational library design. Protein Eng Des Sel 30:175–189. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzw068
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Calderini E, Süss P, Hollmann F, Wardenga R, Schallmey A (2021) Two (chemo)-enzymatic cascades for the production of opposite enantiomers of chiral azidoalcohols. Catalysts 11:982. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11080982
Cao C, Matsuda T (2016) Biocatalysis in organic solvents, supercritical fluids and ionic liquids. Organic Synthesis Using Biocatalysis. Elsevier, In, pp 67–97
Chen S-Y, Yang C-X, Wu J-P, Xu G, Yang L-R (2013) Multi-enzymatic biosynthesis of chiral β-hydroxy nitriles through co-expression of oxidoreductase and halohydrin dehalogenase. Adv Synth Catal 355:3179–3190. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201300549
Cui H, Zhang L, Eltoukhy L, Jiang Q, Korkunç SK, Jaeger K-E, Schwaneberg U, Davari MD (2020) Enzyme hydration determines resistance in organic cosolvents. ACS Catal 10:14847–14856. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.0c03233
Cui H-B, Xie L-Z, Wan N-W, He Q, Li Z, Chen Y-Z (2019) Cascade bio-hydroxylation and dehalogenation for one-pot enantioselective synthesis of optically active β-halohydrins from halohydrocarbons. Green Chem 21:4324–4328. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC01802F
de Jong RM (2003) Structure and mechanism of a bacterial haloalcohol dehalogenase: a new variation of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase fold without an NAD(P)H binding site. EMBO J 22:4933–4944. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg479
Dong F, Chen H, Malapit CA, Prater MB, Li M, Yuan M, Lim K, Minteer SD (2020) Biphasic bioelectrocatalytic synthesis of chiral β-hydroxy nitriles. J Am Chem Soc 142:8374–8382. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c01890
Doukyu N, Ogino H (2010) Organic solvent-tolerant enzymes. Biochem Eng J 48:270–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2009.09.009
Findrik Blažević Z, Milčić N, Sudar M, Majerić Elenkov M (2021) Halohydrin dehalogenases and their potential in industrial application – a viewpoint of enzyme reaction engineering. Adv Synth Catal 363:388–410. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.202000984
Floor RJ, Wijma HJ, Colpa DI, Ramos-Silva A, Jekel PA, Szymański W, Feringa BL, Marrink SJ, Janssen DB (2014) Computational library design for increasing haloalkane dehalogenase stability. ChemBioChem 15:1660–1672. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201402128
Haak RM, Berthiol F, Jerphagnon T, Gayet AJA, Tarabiono C, Postema CP, Ritleng V, Pfeffer M, Janssen DB, Minnaard AJ, Feringa BL, de Vries JG (2008) Dynamic kinetic resolution of racemic β-haloalcohols: direct access to enantioenriched epoxides. J Am Chem Soc 130:13508–13509. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja805128x
Hasnaoui-Dijoux G, Majerić Elenkov M, Lutje Spelberg JH, Hauer B, Janssen DB (2008) Catalytic promiscuity of halohydrin dehalogenase and its application in enantioselective epoxide ring opening. ChemBioChem 9:1048–1051. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200700734
Jin H-X, Liu Z-Q, Hu Z-C, Zheng Y-G (2013) Production of (R)-epichlorohydrin from 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol by two-step biocatalysis using haloalcohol dehalogenase and epoxide hydrolase in two-phase system. Biochem Eng J 74:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.02.005
Klibanov AM (1997) Why are enzymes less active in organic solvents than in water? Trends Biotechnol 15:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7799(97)01013-5
Koudelakova T, Chaloupkova R, Brezovsky J, Prokop Z, Sebestova E, Hesseler M, Khabiri M, Plevaka M, Kulik D, Kuta Smatanova I, Rezacova P, Ettrich R, Bornscheuer UT, Damborsky J (2013) Engineering enzyme stability and resistance to an organic cosolvent by modification of residues in the access tunnel. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:1959–1963. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201206708
Liao Q, Du X, Jiang W, Tong Y, Zhao Z, Fang R, Feng J, Tang L (2018) Cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) of halohydrin dehalogenase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1: preparation, characterization and application as a biocatalyst. J Biotechnol 272–273:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.12.014
Lutje Spelberg JH, Tang L, Kellogg RM, Janssen DB (2004) Enzymatic dynamic kinetic resolution of epihalohydrins. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 15:1095–1102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetasy.2004.02.009
Lutje Spelberg JH, Tang L, van Gelder M, Kellogg RM, Janssen DB (2002) Exploration of the biocatalytic potential of a halohydrin dehalogenase using chromogenic substrates. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 13:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0957-4166(02)00222-7
Ma SK, Gruber J, Davis C, Newman L, Gray D, Wang A, Grate J, Huisman GW, Sheldon RA (2010) A green-by-design biocatalytic process for atorvastatin intermediate. Green Chem 12:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1039/B919115C
March D, Bianco V, Franzese G (2021) Protein unfolding and aggregation near a hydrophobic interface. Polymers 13:156. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010156
Mikleušević A, Hameršak Z, Salopek-Sondi B, Tang L, Janssen DB, Majerić Elenkov M (2015) Oxazolidinone synthesis through halohydrin dehalogenase- catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution. Adv Synth Catal 357:1709–1714. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201500111
Milčić N, Stepanić V, Crnolatac I, Findrik Blažević Z, Brkljača Z, Majerić Elenkov M (2022) Experimental and computational insights on the influence of organic co-solvent on structural and catalytic properties of a biocatalyst: inhibitory effect of DMSO on halohydrin dehalogenase. Chem Euro J 28:e202201923. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202201923
Nikfarjam S, Jouravleva EV, Anisimov MA, Woehl TJ (2020) Effects of protein unfolding on aggregation and gelation in lysozyme solutions. Biomolecules 10:1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091262
Roiban G-D, Sutton PW, Splain R, Morgan C, Fosberry A, Honicker K, Homes P, Boudet C, Dann A, Guo J, Brown KK, Ihnken LAF, Fuerst D (2017) Development of an enzymatic process for the production of (R)-2-butyl-2-ethyloxirane. Org Process Res Dev 21:1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00179
Sate D, Janssen MHA, Stephens G, Sheldon RA, Seddon KR, Lu JR (2007) Enzyme aggregation in ionic liquids studied by dynamic light scattering and small angle neutron scattering. Green Chem 9:859–886. https://doi.org/10.1039/b700437k
Schneider C (2006) Synthesis of 1,2-difunctionalized fine chemicals through catalytic, enantioselective ring-opening reactions of epoxides. Synthesis 23:3919–3944. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-950348
Schrittwieser JH, Lavandera I, Seisser B, Mautner B, Kroutil W (2009) Biocatalytic cascade for the synthesis of enantiopure β-azidoalcohols and β-hydroxynitriles. Eur J Org Chem 2009:2293–2298. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.200900091
SCIENTIST handbook (1986–1995) Micromath. City, Salt Lake
Seisser B, Lavandera I, Faber K, Lutje Spelberg JH, Kroutil W (2007) Stereo-complementary two-step cascades using a two-enzyme system leading to enantiopure epoxides. Adv Synth Catal 349:1399–1404. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.200700027
Solarczek J, Klünemann T, Brandt F, Schrepfer P, Wolter M, Jacob CR, Blankenfeldt W, Schallmey A (2019) Position 123 of halohydrin dehalogenase HheG plays an important role in stability, activity, and enantioselectivity. Sci Rep 9:5106. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41498-2
Staar M, Henke S, Blankenfeldt W, Schallmey A (2022) Biocatalytically active and stable cross-linked enzyme crystals of halohydrin dehalogenase HheG by protein engineering. ChemCatChem 14:e202200145. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202200145
Stepankova V, Bidmanova S, Koudelakova T, Prokop Z, Chaloupkova R, Damborsky J (2013) Strategies for stabilization of enzymes in organic solvents. ACS Catal 3:2823–2836. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs400684x
Szymanski W, Postema CP, Tarabiono C, Berthiol F, Campbell-Verduyn L, de Wildeman S, de Vries JG, Feringa BL, Janssen DB (2010) Combining designer cells and click chemistry for a one-pot four-step preparation of enantiopure β-hydroxytriazoles. Adv Synth Catal 352:2111–2115. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201000502
Tang L, van Hylckama Vlieg JET, Lutje Spelberg JH, Fraaije MW, Janssen DB (2002) Improved stability of halohydrin dehalogenase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 by replacement of cysteine residues. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(01)00488-4
van Schie MMCH, Spöring J-D, Bocola M, Domínguez de María P, Rother D (2021) Applied biocatalysis beyond just buffers – from aqueous to unconventional media. Options Guidel. Green Chem 23:3191–3206. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC00561H
Wang S, Meng X, Zhou H, Liu Y, Secundo F, Liu Y (2016) Enzyme stability and activity in non-aqueous reaction systems: a mini review. Catalysts 6:32. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6020032
Wang W, Nema S, Teagarden D (2010) Protein aggregation—pathways and influencing factors. Int J Pharm 390:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.02.025
Wessel J, Petrillo G, Estevez-Gay M, Bosch S, Seeger M, Dijkman WP, Iglesias-Fernández J, Hidalgo A, Uson I, Osuna S, Schallmey A (2021) Insights into the molecular determinants of thermal stability in halohydrin dehalogenase HheD2. FEBS J 288:4683–4701. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15777
Wu Z, Deng W, Tong Y, Liao Q, Xin D, Yu H, Feng J, Tang L (2017) Exploring the thermostable properties of halohydrin dehalogenase from Agrobacterium radiobacter AD1 by a combinatorial directed evolution strategy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:3201–3211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8090-2
Zhang X-J, Shi P-X, Deng H-Z, Wang X-X, Liu Z-Q, Zheng Y-G (2018) Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin using an immobilized halohydrin dehalogenase in aqueous and non-aqueous phase. Bioresour Technol 263:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.027
Zou S-P, Zheng Y-G, Du E-H, Hu Z-C (2014) Enhancement of (S)-2,3-dichloro-1-propanol production by recombinant whole-cell biocatalyst in n-heptane–aqueous biphasic system. J Biotechnol 188:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.08.014
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Croatian Science Foundation (HrZZ, IP-2018-01-4493). A part of the presented materials is the work supported by the Chinese-Croatian bilateral collaboration (2019-2021). N.M. is supported by a PhD scholarship from the Croatian Science Foundation through the Career Development Project for Young Researchers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NM, PŠ, and MME conducted experiments. NM, MS, and MME designed the research. MS, ZFB, and MME supervised the research. ZFB, LT, and MME acquired resources. MME acquired funding. All authors wrote, read, and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Milčić, N., Švaco, P., Sudar, M. et al. Impact of organic solvents on the catalytic performance of halohydrin dehalogenase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 2351–2361 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12450-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12450-2