Abstract
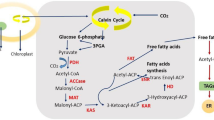
Microalgae are promising feedstock for renewable fuels. The accumulation of oils in microalgae can be enhanced by nanoparticle exposure. However, the nanoparticles employed in previous studies are mostly non-biodegradable, which hinders nanoparticles developing as promising approach for biofuel production. We recently reported the engineered resin nanoparticles (iBCA-NPs), which were found to be biodegradable in this study. When the cells of green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were exposed to the iBCA-NPs for 1 h, the cellular triacyclglycerols (TAG) and starch contents increased by 520% and 60% than that in the control. The TAG production improved by 1.8-fold compared to the control without compromised starch production. Additionally, the content of total fatty acids increased by 1.3-fold than that in control. Furthermore, we found that the iBCA-NPs addition resulted in increased cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) content and upregulated the activities of antioxidant enzymes. The relative expressions of the key genes involved in TAG and starch biosynthesis were also upregulated. Overall, our results showed that short exposure of the iBCA-NPs dramatically enhances TAG and starch accumulation in Chlamydomonas, which probably resulted from prompt upregulated expression of the key genes in lipid and starch metabolic pathways that were triggered by over-accumulated ROS. This study reported a useful approach to enhance energy-rich reserve accumulation in microalgae.
Key points
1. The first attempt to increase oil and starch in microalgae by biodegradable NPs.
2. The biodegradability of iBCA-NPs by the BOD test was more than 50% after 28 days.
3. The iBCA-NPs induce more energy reserves than that of previously reported NPs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Azab AJS, Widyaningrum D, Hirakawa H, Hayashi Y, Tanaka S, Ohama T (2021) A resin cyanoacrylate nanoparticle as an acute cell death inducer to broad spectrum of microalgae. Algal Res 54:102191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2021.102191
Alonso-López O, López-Ibáñez S, Beiras R (2021) Assessment of toxicity and biodegradability of poly(vinyl alcohol)-based materials in marine water. Polymers 13:3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213742
Cameron JL, Woodward SC, Pulaski EJ, Sleeman HK, Brandes G, Kulkarni RK, Leonard F (1965) The degradation of cyanoacrylate tissue adhesive. I. Surgery 58, 424–430. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14316507/
Chen R, Yang M, Li M, Zhang H, Lu H, Dou X, Feng S, Xue S, Zhu C, Chi Z, Kong F (2022) Enhanced accumulation of oil through co-expression of fatty acid and ABC transporters in Chlamydomonas under standard growth conditions. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod 15(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-022-02154-6
Cruz S, Serôdio J (2008) Relationship of rapid light curves of variable fluorescence to photoacclimation and non-photochemical quenching in a benthic diatom. Aquat Bot 88:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.11.001
Dev Sarkar R, Singh HB, Chandra Kalita M (2021) Enhanced lipid accumulation in microalgae through nanoparticle-mediated approach, for biodiesel production: a mini-review. Heliyon 7:e08057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08057
Du ZY, Benning C (2016) Triacylglycerol Accumulation in photosynthetic cells in plants and algae. Subcell Biochem 86:179–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25979-6_8
Freixa A, Acuña V, Sanchís J, Farré M, Barceló D, Sabater S (2018) Ecotoxicological effects of carbon-based nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Sci Total Environ 619–620:328–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.095
González-Fernández C, Le Grand F, Bideau A, Huvet A, Paul-Pont I, Soudant P (2020) Nanoplastics exposure modulate lipid and pigment compositions in diatoms. Environ Pollut 262:114274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114274
Han D, Wang J, Sommerfeld M, Hu Q (2012) Susceptibility and protective mechanisms of motile and non motile cells of haematococcus pluvialis (chlorophyceae) to photooxidative stress. J Phycol 48:693–705. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.2012.01147.x
He M, Yan Y, Pei F, Wu M, Gebreluel T, Zou S, Wang C (2017) Improvement on lipid production by Scenedesmus obliquus triggered by low-dose exposure to nanoparticles. Sci Rep 7:15526. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15667-0
Iwai M, Ikeda K, Shimojima M, Ohta H (2014) Enhancement of extraplastidic oil synthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using a type-2 diacylglycerol acyltransferase with a phosphorus starvation-inducible promoter. Plant Biotechnol J 12:808–819. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12210
Iwai M, Yamada-Oshima Y, Asami K, Kanamori T, Yuasa H, Shimojima M, Ohta H (2021) Recycling of the major thylakoid lipid MGDG and its role in lipid homeostasis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 187:1341–1356. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiab340
Jothibasu K, Muniraj I, Jayakumar T, Ray B, Dhar DW, Karthikeyan S, Rakesh S (2022) Impact of microalgal cell wall biology on downstream processing and nutrient removal for fuels and value-added products. Biochem Eng J 187:108642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2022.108642
Klein U, Betz A (1978) Fermentative metabolism of hydrogen-evolving Chlamydomonas moewusii. Plant Physiol 61:953–956. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.61.6.953
Knothe G (2009) Improving biodiesel fuel properties by modifying fatty ester composition. Energy Environ Sci 2:759–766. https://doi.org/10.1039/B903941D
Kong F, Liang Y, Légeret B, Beyly-Adriano A, Blangy S, Haslam RP, Napier JA, Beisson F, Peltier G, Li-Beisson Y (2017) Chlamydomonas carries out fatty acid β-oxidation in ancestral peroxisomes using a bona fide acyl-CoA oxidase. Plant J 90(2):358–371. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13498
Kong F, Romero IT, Warakanont J, Li-Beisson Y (2018a) Lipid catabolism in microalgae. New Phytol 218:1340–1348. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15047
Kong F, Burlacot A, Liang Y, Légeret B, Alseekh S, Brotman Y, Fernie AR, Krieger-Liszkay A, Beisson F, Peltier G, Li-Beisson Y (2018b) Interorganelle communication: peroxisomal MALATE DEHYDROGENASE2 connects lipid catabolism to photosynthesis through redox coupling in Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell 30:1824–1847. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00361
Kou Y, Liu M, Sun P, Dong Z, Liu J (2020) High light boosts salinity stress-induced biosynthesis of astaxanthin and lipids in the green alga Chromochloris zofingiensis. Algal Res 50:101976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2020.101976
La Mantia FP, Morreale M, Botta L, Mistretta MC, Ceraulo M, Scaffaro R (2017) Degradation of polymer blends: a brief review. Polym Degrad Stab 145:79–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.07.011
La Russa M, Bogen C, Uhmeyer A, Doebbe A, Filippone E, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2012) Functional analysis of three type-2 DGAT homologue genes for triacylglycerol production in the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biotechnol 162:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.04.006
Lenaerts V, Couvreur P, Christiaens-Leyh D, Joiris E, Roland M, Rollman B, Speiser P (1984) Degradation of poly (isobutyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Biomaterials 5(2):65–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(84)90002-4
Li-Beisson Y, Beisson F, Riekhof W (2015) Metabolism of acyl-lipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 82(3):504–522. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj
Li-Beisson Y, Kong F, Wang P, Lee Y, Kang BH (2021) The disassembly of lipid droplets in Chlamydomonas. New Phytol 231:1359–1364. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17505
Liu J, Han D, Yoon K, Hu Q, Li Y (2016) Characterization of type 2 diacylglycerol acyltransferases in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii reveals their distinct substrate specificities and functions in triacylglycerol biosynthesis. Plant J 86:3–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13143
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
López-Serrano A, Muñoz Olivas R, Sanz Landaluze J, Cámara C (2014) Nanoparticles: a global vision. characterization, separation, and quantification methods. Potential environmental and health impact. Anal Methods 6:38–56. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AY40517F
Mallick N, Mohn FH (2000) Reactive oxygen species: response of algal cells. J Plant Physiol 157:183–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(00)80189-3
Mao X, Wu T, Sun D, Zhang Z, Chen F (2018) Differential responses of the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis to the starvation of various nutrients for oil and astaxanthin production. Bioresour Technol 249:791–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.090
Maurer-Jones MA, Gunsolus IL, Murphy CJ, Haynes CL (2013) Toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Anal Chem 85:3036–3049. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac303636s
Miazek K, Iwanek W, Remacle C, Richel A, Goffin D (2015) Effect of metals, metalloids and metallic nanoparticles on microalgae growth and industrial product biosynthesis: a review. Int J Mol Sci 16:23929–23969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161023929
Mumtaz M, Baqar Z, Hussain N, Afifa BM, Azam HMH, Baqir Q, Iqbal HMN (2022) Application of nanomaterials for enhanced production of biodiesel, biooil, biogas, bioethanol, and biohydrogen via lignocellulosic biomass transformation. Fuel 315:122840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122840
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao AJ, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg L (2008) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicol Lond Engl 17:372–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-008-0214-0
Pádrová K, Lukavský J, Nedbalová L, Čejková A, Cajthaml T, Sigler K, Vítová M, Řezanka T (2015) Trace concentrations of iron nanoparticles cause overproduction of biomass and lipids during cultivation of cyanobacteria and microalgae. J Appl Phycol 27:1443–1451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0477-1
Quigg A, Chin W-C, Chen C-S, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Miao AJ, Schwehr KA, Xu C, Santschi PH (2013) Direct and indirect toxic effects of engineered nanoparticles on algae: role of natural organic matter. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1:686–702. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400103x
Ravi Kumar MN (2000) Nano and microparticles as controlled drug delivery devices. J Pharm Pharm 3(2):234–258
Ren HY, Dai YQ, Kong F, Xing D, Zhao L, Ren NQ, Ma J, Liu BF (2020) Enhanced microalgal growth and lipid accumulation by addition of different nanoparticles under xenon lamp illumination. Bioresour Technol 297:122409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122409
Rumeau D, Bécuwe-Linka N, Beyly A, Louwagie M, Garin J, Peltier G (2005) New subunits NDH-M, -N, and -O, encoded by nuclear genes, are essential for plastid Ndh complex functioning in higher plants. Plant Cell 17:219–232. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.028282
Sarma SJ, Das RK, Brar SK, Le Bihan Y, Buelna G, Verma M, Soccol CR (2014) Application of magnesium sulfate and its nanoparticles for enhanced lipid production by mixotrophic cultivation of algae using biodiesel waste. Energy 78:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.04.112
Schwab F, Bucheli TD, Lukhele LP, Magrez A, Nowack B, Sigg L, Knauer K (2011) Are carbon nanotube effects on green algae caused by shading and agglomeration? Environ Sci Technol 45:6136–6144. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200506b
Siaut M, Cuiné S, Cagnon C, Fessler B, Nguyen M, Carrier P, Beyly A, Beisson F, Triantaphylidès C, Li-Beisson Y, Peltier G (2011) Oil accumulation in the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: characterization, variability between common laboratory strains and relationship with starch reserves. BMC Biotechnol 11:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6750-11-7
Siddiqui MH, Al-Whaibi MH, Firoz M, Al-Khaishany MY (2015) Role of nanoparticles in plants. In Nanotechnology and plant sciences, in: Siddiqui, M.H. Al-Whaibi M.H., and Mohammad F. (Eds), Nanoparticles and their impact on plants cham: Springer International Publishing 19–35 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14502-0_2
Sulheim E, Baghirov H, von Haartman E, Bøe A, Åslund AK, Mørch Y, Davies Cde L (2016) Cellular uptake and intracellular degradation of poly(alkyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. J Nanobiotechnology 14:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-015-0156-7
Takeuchi T, Benning C (2019) Nitrogen-dependent coordination of cell cycle, quiescence and TAG accumulation in Chlamydomonas. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:292. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1635-0
Vonlanthen S, Dauvillée D, Purton S (2015) Evaluation of novel starch-deficient mutants of Chlorella sorokiniana for hyper-accumulation of lipids. Algal Res 12:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2015.08.008
Widyaningrum D, Iida D, Tanabe Y, Hayashi Y, Kurniasih SD, Ohama T (2019) Acutely induced cell mortality in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyceae) following exposure to acrylic resin nanoparticles. J Phycol 55:118–133. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpy.12798
Wu T, Yu L, Zhang Y, Liu J (2021) Characterization of fatty acid desaturases reveals stress-induced synthesis of C18 unsaturated fatty acids enriched in triacylglycerol in the oleaginous alga Chromochloris zofingiensis. Biotechnol Biofuels 14:184. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-021-02037-2
Xi Y, Kong F, Chi Z (2021) ROS induce β-Carotene biosynthesis caused by changes of photosynthesis efficiency and energy metabolism in Dunaliella salina under stress conditions. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:613768. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.613768
Xing H, Zhao Y, Li T, Han B, Zhao P, Yu X (2022) Enhancing astaxanthin and lipid coproduction in Haematococcus pluvialis by the combined induction of plant growth regulators and multiple stresses. Bioresour Technol 344:126225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126225
Yang J, Liu J, Pan Y, Maréchal E, Amato A, Liu M, Gong Y, Li Y, Hu H (2022) Less-unsaturated phosphatidylethanolamine, a PDAT substrate for oil biosynthesis, is a transient carbon reservoippr in Nannochloropsis. Plant Physiol 189(3):1345–1362
Yang M, Kong F, Xie X, Wu P, Chu Y, Cao X, Xue S (2020) Galactolipid DGDG and betaine lipid DGTS direct de novo synthesized linolenate into triacylglycerol in a stress-induced starchless mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Physiol 61:851–862. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcaa012
Yoon K, Han D, Li Y, Sommerfeld M, Hu Q (2012) Phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferase is a multifunctional enzyme involved in membrane lipid turnover and degradation while synthesizing triacylglycerol in the unicellular green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell 24:3708–3724. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.100701
Zabawinski C, Van Den Koornhuyse N, D’Hulst C, Schlichting R, Giersch C, Delrue B, Lacroix JM, Preiss J, Ball S (2001) Starchless mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii lack the small subunit of a heterotetrameric ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. J Bacteriol 183:1069–1077. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.3.1069-1077.2001
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900221), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (2020-MS-102), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DUT21LK14), and Japan Science, Sports and Culture, Grant-in Aid for Scientific Research (C) (19K12422).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FK designed and conceived the project. HL, ML, HZ, and KL performed lipid and starch analysis; HL, ML, HZ, and YG carried out RT-qPCR and enzyme activity analysis; HL, KL, YG, and XX carried out photosynthesis activities and physiological analysis; TO synthesized the NPs; FK wrote the paper with comments from TO, CZ, and SX. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Liu, K., Zhang, H. et al. Enhanced triacyclglycerols and starch synthesis in Chlamydomonas stimulated by the engineered biodegradable nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 971–983 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12366-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12366-x