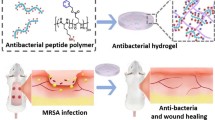
Abstract
Wound infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a great challenge which has caused significant burden and economic loss to the medical system. NZ2114, a plectasin-derived peptide, is an antibacterial agent for preventing and treating S. aureus infection, especially for methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) infection. Here, three-dimensional reticulated antimicrobial peptide (AMP) NZ2114 hydrogels were developed based on hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) and sodium alginate (SA); they displayed sustained and stable release properties (97.88 ± 1.79% and 91.1 ± 10.52% release rate in 72 h, respectively) and good short-term cytocompatibility and hemocompatibility. But the HPC-NZ2114 hydrogel had a smaller pore size (diameter 0.832 ± 0.420 μm vs. 3.912 ± 2.881 μm) and better mechanical properties than that of the SA-NZ2114 hydrogel. HPC/SA-NZ2114 hydrogels possess efficient antimicrobial activity in vitro and in vivo. In a full-thickness skin defect model, the wound closure of the 1.024 mg/g HPC-NZ2114 hydrogel group was superior to those of the SA-NZ2114 hydrogel and antibiotic groups on day 7. The HPC-NZ2114 hydrogel accelerated wound healing by reducing inflammation and promoting the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), endothelial growth factor (EGF) and angiogenesis (CD31) through histological and immunohistochemistry evaluation. These data indicated that the HPC-NZ2114 hydrogel is an excellent candidate for S. aureus infection wound dressing.
Key points
•NZ2114 hydrogels showed potential in vitro bactericidal activity against S. aureus
•NZ2114 hydrogels could release continuously for 72 h and had good biocompatibility
•NZ2114 hydrogels could effectively promote S. aureus-infected wound healing









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Agubata CO, Okereke C, Nzekwe IT, Onoja RI, Obitte NC (2016) Development and evaluation of wound healing hydrogels based on a quinolone, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and biodegradable microfibres. Eur J Pharm Sci 89:1–10
Ahmad S, Ahmad M, Manzoor K, Purwar R, Ikram S (2019) A review on latest innovations in natural gums based hydrogels: preparations & applications. Int J Biol Macromol 136:870–890
Algammal AM, Hetta HF, Elkelish A, Alkhalifah DHH, Hozzein WN, Batiha GE, El Nahhas N, Mabrok MA (2020) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): one health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors, antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect Drug Resist 13:3255–3265
Andes D, Craig W, Nielsen LA, Kristensen HH (2009) In vivo pharmacodynamic characterization of a novel plectasin antibiotic, NZ2114, in a murine infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(7):3003–3009
Barty-King CH, Chan C, Parker RM, Bay MM, Vadrucci R, De Volder M, Vignolini S (2021) Mechanochromic, structurally colored, and edible hydrogels prepared from hydroxypropyl cellulose and gelatin. Adv Mater 33:2102112
Bin Zaman S, Hussain MA, Nye R, Mehta V, Mamun KT, Hossain N (2017) A review on antibiotic resistance: alarm bells are ringing. Cureus 9(6):e1403
Boateng J, Catanzano O (2015) Advanced therapeutic dressings for effective wound healing–a review. J Pharm Sci 104(11):3653–3680
Bolton L, van Rijswijk L (1991) Wound dressings: meeting clinical and biological needs. Dermatol Nurs 3(3):146–161
Bouhadir KH, Lee KY, Alsberg E, Damm KL, Anderson KW, Mooney DJ (2001) Degradation of partially oxidized alginate and its potential application for tissue engineering. Biotechnol Progr 17(5):945–950
Bowler PG (2002) Wound pathophysiology, infection and therapeutic options. Ann Med 34(6):419–427
Brinch KS, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F, Frimodt-Møller N, Høiby N, Kristensen HH (2010) Intracellular activity of the peptide antibiotic NZ2114: studies with Staphylococcus aureus and human THP-1 monocytes, and comparison with daptomycin and vancomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother 65(8):1720–1724
Broughton G, 2nd, Janis JE and Attinger CE (2006) Wound healing: an overview. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(7 Suppl):1e-S-32e-S
Childs DR, Murthy AS (2017) Overview of wound healing and management. Surg Clin North Am 97(1):189–207
Costa F, Teixeira C, Gomes P, Martins MCL (2019) Clinical application of AMPs. Adv Exp Med Biol 1117:281–298
Dodero A, Vicini S, Alloisio M, Castellano M (2019) Sodium alginate solutions: correlation between rheological properties and spinnability. J Mater Sci 54(10):8034–8046
Ghobril C, Rodriguez EK, Nazarian A, Grinstaff MW (2016) Recent advances in dendritic macromonomers for hydrogel formation and their medical applications. Biomacromol 17(4):1235–1252
Golmohammadi R, Najar-Peerayeh S, Tohidi Moghadam T, Hosseini SMJ (2020) Synergistic antibacterial activity and wound healing properties of selenium-chitosan-mupirocin nanohybrid system: An in vivo study on rat diabetic Staphylococcus aureus wound infection model. Sci Rep 10(1):2854
Hong L, Shen M, Fang J, Wang Y, Bao Z, Bu S, Zhu Y (2018) Hyaluronic acid (HA)-based hydrogels for full-thickness wound repairing and skin regeneration. J Mater Sci-Mater Med 29(9):1–11
Huang H, Rajanbabu V, Pan C, Chan Y, Wu C, Chen J (2013) Use of the antimicrobial peptide EPINECIDIN-1 to protect against MRSA infection in mice with skin injuries. Biomaterials 34(38):10319–10327
Jiang Y, Chen Y, Song Z, Tan Z, Cheng J (2021) Recent advances in design of antimicrobial peptides and polypeptides toward clinical translation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 170:261–280
Justus CR, Leffler N, Ruiz-Echevarria M, Yang L (2014) In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J vis Exp 88:e51046
Kanikireddy V, Varaprasad K, Jayaramudu T, Karthikeyan C, Sadiku R (2020) Carboxymethyl cellulose-based materials for infection control and wound healing: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 164:963–975
Koh TJ, DiPietro LA (2011) Inflammation and wound healing: the role of the macrophage. Expert Rev Mol Med 13:e23
Kong Y, Hou Z, Zhou L, Zhang P, Ouyang Y, Wang P, Chen Y, Luo X (2021) Injectable self-healing hydrogels containing CuS nanoparticles with abilities of hemostasis, antibacterial activity, and promoting wound healing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 7(1):335–349
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2012) Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci 37(1):106–126
Leng X, Shang J, Gao D, Wu J (2018) Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes proliferation and migration of HaCaT keratinocytes through the PI3K/AKT and JNK pathways. Braz J Med Biol Res 51(12):e7862
Li H, Gong G (2010) Synthesis and characterization of temperature/pH-sensitive hydroxypropylcellulose/sodium alginate hydrogel. E-Polymers 10(1):125
Li J, Zhai D, Lv F, Yu Q, Ma H, Yin J, Yi Z, Liu M, Chang J, Wu C (2016) Preparation of copper-containing bioactive glass/eggshell membrane nanocomposites for improving angiogenesis, antibacterial activity and wound healing. Acta Biomater 36:254–266
Li YH, Wang C, Luan Y, Liu W, Chen T, Liu P, Liu Z (2022) Preparation of pH-responsive cellulose nanofibril/sodium alginate based hydrogels for drug release. J Appl Polym Sci 139(7):51647
Liu H, Yang N, Mao R, Teng D, Hao Y, Wang X, Wang J (2020) A new high-yielding antimicrobial peptide NZX and its antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus hyicus in vitro/vivo. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(4):1555–1568
Ma JZ, Li XL, Bao Y (2015) Advances in cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels. RSC Adv 5(73):59745–59757
Mahmood H, Khan IU, Asif M, Khan RU, Asghar S, Khalid I, Khalid SH, Irfan M, Rehman F, Shahzad Y, Yousaf AM, Younus A, Niazi ZR, Asim M (2021) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of gellan gum hydrogel films: assessing the co impact of therapeutic oils and ofloxacin on wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol 166:483–495
Mao Y, Ma J, Xia Y, Xie X (2020) The overexpression of epidermal growth factor (EGF) in HaCaT cells promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion and transdifferentiation to epidermal stem cell immunophenotyping of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs). Int J Stem Cells 13(1):93–103
Merkulova Y, Shen Y, Parkinson LG, Raithatha SA, Zhao H, Westendorf K, Sharma M, Bleackley RC, Granville DJ (2016) Granzyme B inhibits keratinocyte migration by disrupting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mediated signaling. Biol Chem 397(9):883–895
Nagaraja S, Wallqvist A, Reifman J, Mitrophanov AY (2014) Computational approach to characterize causative factors and molecular indicators of chronic wound inflammation. J Immunol 192(4):1824–1834
Ogawa A, Nakayama S, Uehara M, Mori Y, Takahashi M, Aiba T, Kurosaki Y (2014) Pharmaceutical properties of a low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose (L-HPC) hydrogel as a novel external dressing. Int J Pharm 477:546–552
Park JY, Lee DS, Kim CE, Shin MS, Seo CS, Shin HK, Hwang GS, An JM, Kim SN, Kang KS (2018) Effects of fermented black ginseng on wound healing mediated by angiogenesis through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Ginseng Res 42(4):524–531
Powers JG, Higham C, Broussard K, Phillips TJ (2016) Wound healing and treating wounds: chronic wound care and management. J Am Acad Dermatol 74(4):607–625
Preethi GU, Unnikrishnan BS, Sreekutty J, Archana MG, Anupama MS, Shiji R, Pillai KR, Joseph MM, Syama HP, Sreelekha TT (2020) Semi-interpenetrating nanosilver doped polysaccharide hydrogel scaffolds for cutaneous wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol 142:712–723
Puthia M, Butrym M, Petrlova J, Strömdahl AC, Andersson M, Kjellström S, Schmidtchen A (2020) A dual-action peptide-containing hydrogel targets wound infection and inflammation. Sci Transl Med 12(524):eaax6601
Ramachandran S, Chen S, Etzler F (1999) Rheological characterization of hydroxypropylcellulose gels. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 25(2):153–161
Rios AC, Moutinho CG, Pinto FC, Del Fiol FS, Jozala A, Chaud MV, Vila MM, Teixeira JA, Balcão VM (2016) Alternatives to overcoming bacterial resistances: state-of-the-art. Microbiol Res 191:51–80
Roy S, Santra S, Das A, Dixith S, Sinha M, Ghatak S, Ghosh N, Banerjee P, Khanna S, Mathew-Steiner S, Ghatak PD, Blackstone BN, Powell HM, Bergdall VK, Wozniak DJ, Sen CK (2020) Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infection compromises wound healing by causing deficiencies in granulation tissue collagen. Ann Surg 271(6):1174–1185
Saaristo A, Tammela T, Farkkilā A, Kärkkäinen M, Suominen E, Yla-Herttuala S, Alitalo K (2006) Vascular endothelial growth factor-C accelerates diabetic wound healing. Am J Pathol 169(3):1080–1087
Serra R, Grande R, Butrico L, Rossi A, Settimio UF, Caroleo B, Amato B, Gallelli L, de Franciscis S (2015) Chronic wound infections: the role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 13(5):605–613
Shahbazian JH, Hahn PD, Ludwig S, Ferguson J, Baron P, Christ A, Spicer K, Tolomeo P, Torrie AM, Bilker WB, Cluzet VC, Hu B, Julian K, Nachamkin I, Rankin SC, Morris DO, Lautenbach E, Davis MF (2017) Multidrug and mupirocin resistance in environmental methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates from homes of people diagnosed with community-onset MRSA infection. Appl Environ Microbiol 83(22):e01369-e1417
Shanmugapriya K, Kim H, Kang HW (2021) EGFR-conjugated hydrogel accelerates wound healing on ulcer-induced burn wounds by targeting collagen and inflammatory cells using photoimmunomodulatory inhibition. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 118:111541
Shaykhiev R, Beisswenger C, Kandler K, Senske J, Puchner A, Damm T, Behr J, Bals R (2005) Human endogenous antibiotic LL-37 stimulates airway epithelial cell proliferation and wound closure. Am J Physiol-Lung Cellul Molecul Physiol 289(5):L842-848
Shukla A, Choudhury S, Chaudhary G, Singh V, Prabhu SN, Pandey S, Garg SK (2021) Chitosan and gelatin biopolymer supplemented with mesenchymal stem cells (Velgraft®) enhanced wound healing in goats (Capra hircus): Involvement of VEGF, TGF and CD31. J Tissue Viabil 30(1):59–66
Sorg H, Tilkorn DJ, Hager S, Hauser J, Mirastschijski U (2017) Skin wound healing: an update on the current knowledge and concepts. Eur Surg Res 58(1–2):81–94
Tan P, Fu H, Ma X (2021) Design, optimization, and nanotechnology of antimicrobial peptides: from exploration to applications. Nano Today 39:101229
Teller P, White TK (2009) The physiology of wound healing: injury through maturation. Surg Clin North Am 89(3):599–610
Wang X, Wang X, Teng D, Mao R, Hao Y, Yang N, Li Z, Wang J (2018) Increased intracellular activity of MP1102 and NZ2114 against Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep 8(1):4204
Wang X, Teng D, Wang X, Hao Y, Chen H, Mao R, Wang J (2019) Internalization, distribution, and activity of peptide H2 against the intracellular multidrug-resistant bovine mastitis-causing bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep 9(1):7968
Werner S, Grose R (2003) Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev 83(3):835–870
Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock RE (2008) Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc 3(2):163–175
Xiong YQ, Hady WA, Deslandes A, Rey A, Fraisse L, Kristensen HH, Yeaman MR, Bayer AS (2011) Efficacy of NZ2114, a novel plectasin-derived cationic antimicrobial peptide antibiotic, in experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(11):5325–5330
Xu F, Zhu Y, Liu F, Nie J, Ma J, Yang W (2010) Comb-shaped conjugates comprising hydroxypropyl cellulose backbones and low-molecular-weight poly(N-isopropylacryamide) side chains for smart hydrogels: synthesis, characterization, and biomedical applications. Bioconjug Chem 21(3):456–464
Xu Z, Han S, Gu Z, Wu J (2020) Advances and impact of antioxidant hydrogel in chronic wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater 9(5):e1901502
Xue F, He XR, Cai SW, Nie J, Shi ZR, Wang X (2019) Synergistic effect of graphene oxide and sodium carboxymethylcellulose on the properties of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 136(24):47644
Zhang Y, Teng D, Mao R, Wang X, Xi D, Hu X, Wang J (2014) High expression of a plectasin-derived peptide NZ2114 in Pichia pastoris and its pharmacodynamics, postantibiotic and synergy against Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(2):681–694
Zhang Y, Chen H, Lü Y, Liu Y, Tang X, Shen X (2016) Effects of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose on adhesion properties of soybean protein isolate onto porcine bones. Sci Agric Sin 49:1550–1558
Zhang M, Qiao X, Han W, Jiang T, Liu F, Zhao X (2021) Alginate-chitosan oligosaccharide-ZnO composite hydrogel for accelerating wound healing. Carbohydr Polymers 266(21–22):118100
Zhao R, Liang H, Clarke E, Jackson C, Xue M (2016) Inflammation in chronic wounds. Int J Mol Sci 17(12):2085
Zhao Y, Wang Z, Zhang Q, Chen F, Yue Z, Zhang T, Deng H, Huselstein C, Anderson DP, Chang PR, Li Y, Chen Y (2018) Accelerated skin wound healing by soy protein isolate-modified hydroxypropyl chitosan composite films. Int J Biol Macromol 118:1293–1302
Zhou J, Yao D, Qian Z, Hou S, Li L, Jenkins ATA, Fan Y (2018) Bacteria-responsive intelligent wound dressing: Simultaneous in situ detection and inhibition of bacterial infection for accelerated wound healing. Biomaterials 161:11–23
Zubair M, Ahmad J (2019) Role of growth factors and cytokines in diabetic foot ulcer healing: a detailed review. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 20(2):207–217
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Chunli Li from the Core Facility at the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) for the technical support with SEM.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31872393), the Key Projects of Alternatives to Antibiotic for Animal (Grant No. CAAS-ZDRW202111), and Feed (Grant No. CAAS-ZDXT2018008) Usages of the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (ASTIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW and NY conceived and designed the study; YH carried out all experiments. YH and DT conducted the data analysis; YH wrote the first draft; RM, XM, and LW contributed to the writing, review, and editing of the manuscript. All the authors gave final approval. JW contributed in funding acquisition. YH contributed to materials and reagents.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The mouse experiment was performed according to the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Feed Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) and approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethical Committee and its Inspection of the Feed Research Institute of CAAS (AEC-CAAS-20090609).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Yang, N., Teng, D. et al. Antibacterial peptide NZ2114-loaded hydrogel accelerates Staphylococcus aureus-infected wound healing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106, 3639–3656 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11943-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11943-w