Abstract
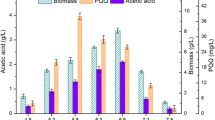
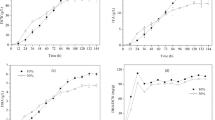
Oxygen is a vital parameter for pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) biosynthesis. In this study, the effects of oxygen supply on the biosynthesis of PQQ were first investigated systematically with Hyphomicrobium denitrificans FJNU-6. Following a kinetic analysis of the specific cell growth rate (μx) and specific PQQ formation rate (μp) in 5 L benchtop fermentation systems at various oxygen supply levels ranging from 0 to 60%, a novel, two-stage oxygen supply strategy was developed for enhancing PQQ production and productivity. Moreover, the transcription of genes involved in methanol oxidation and PQQ biosynthesis was analyzed throughout the process to outline the effect of oxygen supply on cell metabolism. Furthermore, with constant feeding of methanol at 0–1 g/L after the initial methanol was consumed completely, the PQQ concentration and productivity reached 1070 mg/L and 7.64 mg/L/h, respectively, after 140 h in a 5-L fermenter. The two-stage oxygen supply strategy developed in this study provides an effective and economical strategy for the industrial production of PQQ.
Key Points
• A novel, two-stage oxygen supply strategy was developed for enhancing PQQ production and productivity.
•The transcription of genes involved in methanol oxidation and PQQ biosynthesis was regulated by changes in oxygen supply.
• This study offers an effective and economical strategy for industrial or large-scale production of PQQ.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagawa M, Nakano M, Ikemoto K (2016) Recent progress in studies on the health benefits of pyrroloquinoline quinone. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 80(1):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2015.1062715
Barr I, Latham JA, Iavarone AT, Chantarojsiri T, Hwang JD, Klinman JP (2016) Demonstration that the radical S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) enzyme PqqE Catalyzes de novo carbon-carbon cross-linking within a peptide substrate PqqA in the presence of the peptide chaperone PqqD. J Biol Chem 291(17):8877–8884. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C115.699918
Bonnot F, Iavarone AT, Klinman JP (2013) Multistep, eight-electron oxidation catalyzed by the cofactorless oxidase, PqqC: identification of chemical intermediates and their dependence on molecular oxygen. Biochemistry 52(27):4667–4675. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi4003315
Broderick WE, Hoffman BM, Broderick JB (2018) Mechanism of radical initiation in the radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine superfamily. Acc Chem Res 51(11):2611–2619. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00356
Chi Z, Liu Y, Frear C, Chen S (2009) Study of a two-stage growth of DHA-producing marine algae Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 with shifting dissolved oxygen level. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(6):1141–1148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1740-7
Choi O, Kim J, Kim JG, Jeong Y, Moon JS, Park CS, Hwang I (2008) Pyrroloquinoline quinone is a plant growth promotion factor produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens B16. Plant Physiol 146(2):657–668. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.112748
Duine JA (1999) The PQQ story. J. Biosci. Bioeng 88(3):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-1723(00)80002-x
Duine JA, Jongejan JA (1989) Pyrroloquinoline quinone: a novel cofactor. Vitam Horm 45:223–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60396-9
Evans RL III, Latham JA, Xia Y, Klinman JP, Wilmot CM (2017) Nuclear magnetic resonance structure and binding studies of PqqD, a chaperone required in the biosynthesis of the bacterial dehydrogenase cofactor pyrroloquinoline quinone. Biochemistry 56(21):2735–2746. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00247
Frey PA, Hegeman AD, Ruzicka FJ (2008) The radical SAM superfamily. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 43(1):63–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409230701829169
Ge X, Wang W, Du B, Wang J, Xiong X, Zhang W (2015) Multiple pqqA genes respond differently to environment and one contributes dominantly to pyrroloquinoline quinone synthesis. J Basic Microbiol 55(3):312–323. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201300037
He K, Nukada H, Urakami T, Murphy MP (2003) Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ): implications for its function in biological systems. Biochem Pharmacol 65(1):67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(02)01453-3
Klinman JP, Bonnot F (2014) Intrigues and intricacies of the biosynthetic pathways for the enzymatic quinocofactors: PQQ, TTQ, CTQ, TPQ, and LTQ. Chem Rev 114(8):4343–4365. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400475g
Koehn EM, Latham JA, Armand T, Evans RL III, Tu X, Wilmot CM, Iavarone AT, Klinman JP (2019) Discovery of hydroxylase activity for PqqB provides a missing link in the pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthetic pathway. J Am Chem Soc 141(10):4398–4405. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b13453
Li Y, Hugenholtz J, Chen J, Lun SY (2002) Enhancement of pyruvate production by Torulopsis glabrata using a two-stage oxygen supply control strategy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60(1-2):101–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1064-y
Liu MS, Zhong LF, Ke CR, Gao M, Xia HP, Ren Y, Huang JZ (2019) Screening and validation of reference genes in Hyphomicrobium denitrificans. Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology 11:8–16. https://doi.org/10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2019.11.002
Mao XB, Zhong JJ (2004) Hyperproduction of cordycepin by two-stage dissolved oxygen control in submerged cultivation of medicinal mushroom Cordyceps militaris in bioreactors. Biotechnol Prog 20(5):1408–1413. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp049765r
Misra HS, Rajpurohit YS, Khairnar NP (2012) Pyrroloquinoline-quinone and its versatile roles in biological processes. J Biosci 37(2):313–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-012-9195-5
Puehringer S, Metlitzky M, Schwarzenbacher R (2008) The pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthesis pathway revisited: a structural approach. BMC Biochem 9:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2091-9-8
Shen YQ, Bonnot F, Imsand EM, RoseFigura JM, Sjolander K, Klinman JP (2012) Distribution and properties of the genes encoding the biosynthesis of the bacterial cofactor, pyrroloquinoline quinone. Biochemistry 51(11):2265–2275. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi201763d
Si Z, Zhu J, Wang W, Huang L, Wei P, Cai J, Xu Z (2016) Novel and efficient screening of PQQ high-yielding strains and subsequent cultivation optimization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(24):10321–10330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7739-6
Si Z, Machaku D, Wei P, Huang L, Cai J, Xu Z (2017) Enhanced fed-batch production of pyrroloquinoline quinine in Methylobacillus sp. CCTCC M2016079 with a two-stage pH control strategy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(12):4915–4922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8259-8
Song P, Chen C, Tian Q, Lin M, Huang H, Li S (2013) Two-stage oxygen supply strategy for enhanced lipase production by Bacillus subtilis based on metabolic flux analysis. Biochem Eng J 71:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2012.11.011
Urakami T, Yashima K, Kobayashi H, Yoshida A, Ito-Yoshida C (1992) Production of pyrroloquinoline quinone by using methanol-utilizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(12):3970–3976
Wang F, Du G-C, Li Y, Chen J (2005) Effects of dissolved oxygen concentration and two-stage oxygen supply strategy on the production of γ-CGTase by Bacillus macorous. Process Biochem 45:3468–3473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.02.019
Wecksler SR, Stoll S, Tran H, Magnusson OT, Wu SP, King D, Britt RD, Klinman JP (2009) Pyrroloquinoline quinone biogenesis: demonstration that PqqE from Klebsiella pneumoniae is a radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine enzyme. Biochemistry 48(42):10151–10161. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi900918b
Wei P, Si Z, Lu Y, Yu Q, Huang L, Xu Z (2017) Medium optimization for pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) production by Methylobacillus sp. zju323 using response surface methodology and artificial neural network-genetic algorithm. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47(7):709–719. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2017.1315596
Williams PA, Coates L, Mohammed F, Gill R, Erskine PT, Coker A, Wood SP, Anthony C, Cooper JB (2005) The atomic resolution structure of methanol dehydrogenase from Methylobacterium extorquens. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444904026964
Xiong XH, Zhao Y, Ge X, Yuan SJ, Wang JH, Zhi JJ, Yang YX, Du BH, Guo WJ, Wang SS, Yang DX, Zhang WC (2011) Production and radioprotective effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone. Int J Mol Sci 12(12):8913–8923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128913
Yang SY, Chen J, Ke CR, Huang JZ (2014) Screening and fermentation optimization for a pyrroloquinoline quinone producing strain. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 21(5):429–432. https://doi.org/10.19526/j.cnki.1005-8915.2014.05.011
Zheng Y, Chang Y, Zhang R, Song J, Xu Y, Liu J, Wang M (2018) Two-stage oxygen supply strategy based on energy metabolism analysis for improving acetic acid production by Acetobacter pasteurianus. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45(9):781–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2060-2
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21807011), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Grant No. 2018J01673), and the Special Scientific Research Fund of the Higher Education Institutions of Fujian Province (Grant No. JK2017012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KCR and HJZ conceived and designed the research. LMS, RY, and XHP conducted the experiments. YXW, LMS, and KCR analyzed the data. LMS and YXW wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 259 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Yang, X., Ren, Y. et al. Two-stage oxygen supply strategy for enhancing fed-batch production of pyrroloquinoline quinone in Hyphomicrobium denitrificans FJNU-6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 6615–6622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10690-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10690-0