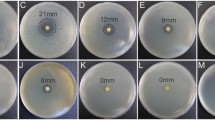
Abstract
Polyketide–terpenoid hybrid compounds are one of the largest families of meroterpenoids, with great potential for drug development for resistant pathogens. Genome sequence analysis of secondary metabolite gene clusters of a phytopathogenic fungus, Bipolaris sorokiniana 11134, revealed a type I polyketide gene cluster, consisting of highly reducing polyketide synthase, non-reducing polyketide synthase, and adjacent prenyltransferase. MS- and UV-guided isolations led to the isolation of ten meroterpenoids, including two new compounds: 19-dehydroxyl-3-epi-arthripenoid A (1) and 12-keto-cochlioquinone A (2). The structures of 1–10 were elucidated by the analysis of NMR and high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy data. Compounds 5–8 and 10 showed moderate activity against common Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus, with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 12.5–100 μg/mL. Compound 5 also exhibited activity against four clinical resistant S. aureus strains and synergistic antifungal activity against Candida albicans with MIC values of 12.5–25 μg/mL. The biosynthetic gene cluster of the isolated compounds and their putative biosynthetic pathway are also proposed.
Key Points
• Ten meroterpenoids were identified from B. sorokiniana, including two new compounds.
• Cochlioquinone B (5) showed activity against MRSA and synergistic activity against C. albicans.
• The biosynthetic gene cluster and biosynthetic pathway of meroterpenoids are proposed.
• Genome mining provided a new direction to uncover the diversity of meroterpenoids.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mageed WM, Bayoumi SA, Al-wahaibi LH, Li L, Sayed HM, Abdelkader MS, El-Gamal AA, Liu M, Zhang J, Zhang L, Liu X (2016) Noncyanogenic cyanoglucoside cyclooxygenase inhibitors from Simmondsia chinensis. Org Lett 18(8):1728–1731. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.6b00206
Bai C, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Hu Y, Xiang S, Miao J, Lou C, Zhang L (2015) Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(39):12181–12186. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511027112
Campos FF, Rosa LH, Cota BB, Caligiorne RB, Rabello ALT, Alves TMA, Rosa CA, Zani CL (2008) Leishmanicidal metabolites from Cochliobolus sp., an endophytic fungus isolated from Piptadenia adiantoides (Fabaceae). PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2(12):e348. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000348
Chooi Y-H, Tang Y (2012) Navigating the fungal polyketide chemical space: from genes to molecules. J Organomet Chem 77(22):9933–9953. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo301592k
Cricchio R (1980) Thiazo rifamycins II: mechanism of the reaction between rifamycin S and 2-amino ethanethiol derivatives. Tetrahedron 36(13):2009–2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-4020(80)80215-8
Dashti Y, Grkovic T, Abdelmohsen UR, Hentschel U, Quinn RJ (2017) Actinomycete metabolome induction/suppression with N-acetylglucosamine. J Nat Prod 80(4):828–836. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00673
Demain AL, Zhang L (2005) Natural products and drug discovery. Natural products. Springer, pp. 3–29
Geris R, Simpson TJ (2009) Meroterpenoids produced by fungi. Nat Prod Rep 26(8):1063–1094. https://doi.org/10.1039/b820413f
Han J, Zhang J, Song Z, Liu M, Hu J, Hou C, Zhu G, Jiang L, Xia X, Quinn RJ, Feng Y, Zhang L, Hsiang T, Liu X (2019) Genome-and MS-based mining of antibacterial chlorinated chromones and xanthones from the phytopathogenic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana strain 11134. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(13):5167–5181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09821-z
He W, Liu M, Huang P, Abdel-Mageed WM, Han J, Watrous JD, Nguyen DD, Wang W, Song F, Dai H, Zhang J, Quinn RJ, Grkovic T, Luo H, Zhang L, Liu X (2016a) Discovery of tanshinone derivatives with anti-MRSA activity via targeted bio-transformation. Synthetic Syst Biotechnol 1(3):187–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2016.05.002
He W, Liu M, Li X, Zhang X, Abdel-Mageed WM, Li L, Wang W, Zhang J, Han J, Dai H, Quinn RJ, H-w L, Luo H, Zhang L, Liu X (2016b) Fungal biotransformation of tanshinone results in [4+2] cycloaddition with sorbicillinol: evidence for enzyme catalysis and increased antibacterial activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(19):8349–8357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7488-6
He W, Li Y, Qin Y, Tong X, Song Z, Zhao Y, Wei R, Li L, Dai H, Wang W, Luo H, Ye X, Zhang L, Liu X (2017) New cryptotanshinone derivatives with anti-influenza A virus activities obtained via biotransformation by Mucor rouxii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(16):6365–6374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8351-0
Huang P, Xie F, Ren B, Wang Q, Wang J, Wang Q, Abdel-Mageed WM, Liu M, Han J, Oyeleye A, Shen J, Song F, Dai HQ, Liu X, Zhang L (2016) Anti-MRSA and anti-TB metabolites from marine-derived Verrucosispora sp. MS100047. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(17):7437–7447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7406-y
Itoh T, Tokunaga K, Matsuda Y, Fujii I, Abe I, Ebizuka Y, Kushiro T (2010) Reconstitution of a fungal meroterpenoid biosynthesis reveals the involvement of a novel family of terpene cyclases. Nat Chem 2(10):858–864. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.764
Johnson M, Zaretskaya I, Raytselis Y, Merezhuk Y, McGinnis S, Madden TL (2008) NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res 36(suppl_2):W5–W9. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn201
Johnson EO, LaVerriere E, Office E, Stanley M, Meyer E, Kawate T, Gomez JE, Audette RE, Bandyopadhyay N, Betancourt N, Hung DT (2019) Large-scale chemical–genetics yields new M. tuberculosis inhibitor classes. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1315-z
Kurtböke Dİ, French JR, Hayes RA, Quinn RJ (2014) Eco-taxonomic insights into actinomycete symbionts of termites for discovery of novel bioactive compounds. Biotechnological applications of biodiversity. Springer, pp. 111–135
Kwan DH, Leadlay PF (2010) Mutagenesis of a modular polyketide synthase enoylreductase domain reveals insights into catalysis and stereospecificity. ACS Chem Biol 5(9):829–838. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb100175a
Kwan DH, Schulz F (2011) The stereochemistry of complex polyketide biosynthesis by modular polyketide synthases. Molecules 16(7):6092–6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16076092
Kwan DH, Sun Y, Schulz F, Hong H, Popovic B, Sim-Stark JC, Haydock SF, Leadlay PF (2008) Prediction and manipulation of the stereochemistry of enoylreduction in modular polyketide synthases. Chem Biol 15(11):1231–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.09.012
Li C-S, Ren G, Yang B-J, Miklossy G, Turkson J, Fei P, Ding Y, Walker LA, Cao S (2016) Meroterpenoids with antiproliferative activity from a Hawaiian-plant associated fungus Peyronellaea coffeae-arabicae FT238. Org Lett 18(10):2335–2338. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.6b00685
Liang M, Li Z, Wang W, Liu J, Liu L, Zhu G, Karthik L, Wang M, Wang K-F, Wang Z, Yu J, Shuai Y, Yu J, Zhang L, Yang Z, Li C, Zhang Q, Shi T, Zhou L, Xie F, Dai HQ, Liu X, Zhang J, Liu G, Zhuo Y, Zhang B, Liu C, Li S, Xia X, Tong Y, Liu Y, Alterovitz G, Tan G, Zhang L (2019) A CRISPR-Cas12a-derived biosensing platform for the highly sensitive detection of diverse small molecules. Nat Commun 10(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11648-1
Lim C-H, Ueno H, Miyoshi H, Miyagawa H, Iwamura H, Ueno T (1996) Phytotoxic compounds cochlioquinones are inhibitors of mitochondrial NADH-ubiquinone reductase. J Pestic Sci 21(2):213–215. https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.21.213
Lim C-H, Miyagawa H, Akamatsu M, Nakagawa Y, Ueno T (1998) Structures and biological activities of phytotoxins produced by the plant pathogenic fungus Bipolaris cynodontis cynA. J Pestic Sci 23(3):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1584/jpestics.23.281
Liu M, Grkovic T, Liu X, Han J, Zhang L, Quinn RJ (2017a) A systems approach using OSMAC, log P and NMR fingerprinting: an approach to novelty. Synthetic Syst Biotechnol 2(4):276–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2017.10.001
Liu M, Huang P, Wang Q, Ren B, Oyeleye A, Liu M, Zhang J, Li X, Zhang X, Zhang L, Liu X (2017b) Synergistic antifungal indolecarbazoles from Streptomyces sp. CNS-42 associated with traditional Chinese medicine Alisma orientale. J Antibiot 70(5):715. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2016.160
Liu X, Xie F, Doughty LB, Wang Q, Zhang L, Liu X, Cheng Y-Q (2018) Genomics-guided discovery of a new and significantly better source of anticancer natural drug FK228. Synthetic Syst Biotechnol 3(4):268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2018.10.011
Liu M, El-Hossary EM, Oelschlaeger TA, Donia MS, Quinn RJ, Abdelmohsen UR (2019) Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant bacterial infections. Lancet Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30711-4
Long Y, Tang T, Wang L-Y, He B, Gao K (2019) Absolute configuration and biological activities of meroterpenoids from an endophytic fungus of Lycium barbarum. J Nat Prod 82(8):2229–2237. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00288
Lv Q, Fan Y, Tao G, Fu P, Zhai J, Ye B-P, Zhu W (2019) Sekgranaticin, a SEK34b-granaticin hybrid polyketide from Streptomyces sp. 166#. J Organomet Chem. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.9b01022
Machida T, Higashi K, Ogawara H (1995) Cochlioquinone A, an inhibitor of diacylglycerol kinase. J Antibiot 48(10):1076–1080. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.48.1076
Matsuda Y, Abe I (2016) Biosynthesis of fungal meroterpenoids. Nat Prod Rep 33(1):26–53. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NP00090D
Matsuda Y, Awakawa T, Abe I (2013) Reconstituted biosynthesis of fungal meroterpenoid andrastin A. Tetrahedron 69(38):8199–8204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2013.07.029
Miyagawa H, Nagai S, Tsurushima T, Sato M, Ueno T, Fukami H (1994) Phytotoxins produced by the plant pathogenic fungus Bipolaris bicolor El-1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58(6):1143–1145. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.58.1143
Osterhage C, König GM, Höller U, Wright AD (2002) Rare sesquiterpenes from the algicolous fungus Drechslera d ematioidea. J Nat Prod 65(3):306–313. https://doi.org/10.1021/np010092l
Smith SG, Goodman JM (2010) Assigning stereochemistry to single diastereoisomers by GIAO NMR calculation: the DP4 probability. J Am Chem Soc 132(37):12946–12959. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja105035r
Song F, Ren B, Yu K, Chen C, Guo H, Yang N, Gao H, Liu X, Liu M, Tong Y, Dai HQ, Bai H, Wang J, Zhang L (2012) Quinazolin-4-one coupled with pyrrolidin-2-iminium alkaloids from marine-derived fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum. Mar Drugs 10(6):1297–1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061297
Stryjewski ME, Corey GR (2014) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an evolving pathogen. Clin Infect Dis 58(suppl_1):S10–S19. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cit613
Wang Y, Wang Y, Chu J, Zhuang Y, Zhang L, Zhang S (2007) Improved production of erythromycin A by expression of a heterologous gene encoding S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75(4):837–842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0894-z
Wang JF, Dai HQ, Wei YL, Zhu HJ, Yan YM, Wang YH, Long CL, Zhong HM, Zhang LX, Cheng YX (2010) Antituberculosis agents and an inhibitor of the para-aminobenzoic acid biosynthetic pathway from Hydnocarpus anthelminthica seeds. Chem Biodivers 7(8):2046–2053. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201000072
Wang Q, Song F, Xiao X, Huang P, Li L, Monte A, Abdel-Mageed WM, Wang J, Guo H, He W, Xie F, Dai HQ, Liu M, Chen C, Xu H, Liu M, Piggott AM, Liu X, Capon RJ, Zhang L (2013) Abyssomicins from the South China Sea deep-sea sediment Verrucosispora sp.: natural thioether Michael addition adducts as antitubercular prodrugs. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(4):1231–1234. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201208801
Wang M, Sun Z-H, Chen Y-C, Liu H-X, Li H-H, Tan G-H, Li S-N, Guo X-L, Zhang W-M (2016) Cytotoxic cochlioquinone derivatives from the endophytic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana derived from Pogostemon cablin. Fitoterapia 110:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2016.02.005
Wang W-G, Du L-Q, Sheng S-L, Li A, Li Y-P, Cheng G-G, Li G-P, Sun G, Hu Q-F, Matsuda Y (2019) Genome mining for fungal polyketide-diterpenoid hybrids: discovery of key terpene cyclases and multifunctional P450s for structural diversification. Org Chem Front 6(5):571–578. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8QO01124A
Wang W, Li S, Li Z, Zhang J, Fan K, Tan G, Ai G, Lam SM, Shui G, Yang Z, Liu H, Jin P, Li Y, Chen X, Xia X, Liu X, Dannelly HK, Yang C, Yang Y, Zhang S, Alterovitz G, Xiang W, Zhang L (2020) Harnessing the intracellular triacylglycerols for titer improvement of polyketides in Streptomyces. Nat Biotechnol 38(1):76–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0335-4
Weber T, Blin K, Duddela S, Krug D, Kim HU, Bruccoleri R, Lee SY, Fischbach MA, Müller R, Wohlleben W, Breitling R, Takano E, Medema MH (2015) antiSMASH 3.0—a comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res 43(W1):W237–W243. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv437
WHO (2014) Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/112642/9789241564748_eng.pdf
Yan W, Song H, Song F, Guo Y, Wu C-H, Her AS, Pu Y, Wang S, Naowarojna N, Weitz A, Hendrich MP, Costello CE, Zhang L, Liu P, Zhang YJ (2015) Endoperoxide formation by an α-ketoglutarate-dependent mononuclear non-haem iron enzyme. Nature 527(7579):539–543. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15519
Zhang L, An R, Wang J, Sun N, Zhang S, Hu J, Kuai J (2005) Exploring novel bioactive compounds from marine microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 8(3):276–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2005.04.008
Zhang L, Yan K, Zhang Y, Huang R, Bian J, Zheng C, Sun H, Chen Z, Sun N, An R (2007) High-throughput synergy screening identifies microbial metabolites as combination agents for the treatment of fungal infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(11):4606–4611. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0609370104
Zhang J, Abdel-Mageed WM, Liu M, Huang P, He W, Li L, Song F, Dai H, Liu X, Liang J, Zhang L (2013) Caesanines A–D, new cassane diterpenes with unprecedented N bridge from Caesalpinia sappan. Org Lett 15(18):4726–4729. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol402058z
Zhang X, Wang TT, Xu QL, Xiong Y, Zhang L, Han H, Xu K, Guo WJ, Xu Q, Tan RX, Ge HM (2018) Genome mining and comparative biosynthesis of meroterpenoids from two phylogenetically distinct fungi. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(27):8184–8188. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201804317
Zhuo Y, Zhang W, Chen D, Gao H, Tao J, Liu M, Gou Z, Zhou X, Ye B-C, Zhang Q, Zhang S, Zhang L (2010) Reverse biological engineering of hrdB to enhance the production of avermectins in an industrial strain of Streptomyces avermitilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(25):11250–11254. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1006085107
Acknowledgments
J. Han thanks Griffith University for the provision of the Ph.D. scholarships (GUPRS and GUIPRS).
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81573341, 31720103901, and 21877038). This work was partially supported by the Open Project Funding of the State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, the 111 Project (B18022), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (22221818014), and Taishan Scholarship. This work was also supported by the Australian Research Council (ARC) (DP160101429, LE140100119, and LE120100170). The genome sequencing and assembly of BS11134 was supported by funding from the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada to T. Hsiang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.F. and R.Q. conceived and designed the research. T.H. sequenced and assembled the genomic data. J.H., J.Z., and Z.S. carried out the fermentation, compound purification, and structural elucidation. J.H. and H.D. evaluated the antimicrobial activity. J.H., J.Z., G.Z., and M.L. analyzed the data, and J.H. wrote the manuscript. Y.F., R.Q., L.Z., X.L., and T.H. reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 2570 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Zhang, J., Song, Z. et al. Genome-based mining of new antimicrobial meroterpenoids from the phytopathogenic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana strain 11134. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 3835–3846 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10522-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10522-1