Abstract
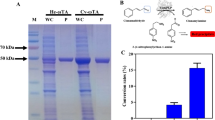
Vanillin is a popular flavoring compound and an important food additive. Owing to the consumer preference for inexpensive natural aroma flavors, vanillin production through a biotechnological pathway has become of great interest and commercial value in recent years. In this study, an enzymatic synthetic system for vanillin using a coenzyme-independent decarboxylase (FDC) and oxygenase (CSO2) cascade was reconstituted and optimized. This system produces a slightly higher production yield (40.20%) than the largest yield reported for immobilized FDC and CSO2 (35.00%) with ferulic acid as a substrate. It was previously reported that the low catalytic activity and thermal instability of CSO2 restrict the overall productivity of vanillin. In present study, site-directed mutagenesis was applied to rate-limiting oxygenase CSO2 to generate positive mutants. The production yields of mutants A49P (58.44%) and Q390A (65.29%) were 1.45- and 1.62-fold that of CSO2 wild type, respectively. The potential mechanism for enhanced vanillin production using A49P involved increased thermostability and catalytic efficiency, while that using Q390A was probably associated with a better thermostable performance and increased catalytic efficiency resulting from a larger entrance channel.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee G, Chattopadhyay P (2019) Vanillin biotechnology: the perspectives and future. J Sci Food Agric 99(2):499–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9303
Bonnina E, Brunel M, Gouy Y, Lesage-Meessen L, Asther M, Thibault J (2001) Aspergillus niger I-1472 and Pycnoporus cinnabarinus MUCL39533, selected for the biotransformation of ferulic acid to vanillin, are also able to produce cell wall polysaccharide-degrading enzymes and feruloyl esterases. Enzym Microb Technol 28(2001):70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(00)00277-5
Boone CD, Rasi V, Tu C, McKenna R (2015) Structural and catalytic effects of proline substitution and surface loop deletion in the extended active site of human carbonic anhydrase II. FEBS J 282(8):1445–1457. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13232
Chakraborty D, Selvam A, Kaur B, Wong JWC, Karthikeyan OP (2017) Application of recombinant Pediococcus acidilactici BD16 (fcs +/ech +) for bioconversion of agrowaste to vanillin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(14):5615–5626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8283-8
Chattopadhyay P, Banerjee G, Sen SK (2018) Cleaner production of vanillin through biotransformation of ferulic acid esters from agroresidue by Streptomyces sannanensis. J Clean Prod 182:272–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.043
Converti A, Aliakbarian B, Dominguez JM, Bustos Vázquez G, Perego P (2010) Microbial production of biovanillin. Braz J Microbiol 41(3):519–530. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-83822010000300001
Di Gioia D, Sciubba L, Setti L, Luziatelli F, Ruzzi M, Zanichelli D, Fava F (2007) Production of biovanillin from wheat bran. Enzym Microb Technol 41(4):498–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.04.003
Furuya T, Kuroiwa M, Kino K (2016) Biotechnological production of vanillin using immobilized enzymes. J Biotechnol 243:25–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.12.021
Furuya T, Miura M, Kino K (2014) A coenzyme-independent decarboxylase/oxygenase cascade for the efficient synthesis of vanillin. ChemBioChem 15(15):2248–2254. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201402215
Furuya T, Miura M, Kuroiwa M, Kino K (2015) High-yield production of vanillin from ferulic acid by a coenzyme-independent decarboxylase/oxygenase two-stage process. New Biotechnol 32(3):335–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.03.002
Gallage NJ, Møller BL (2015) Vanillin-bioconversion and bioengineering of the most popular plant flavor and its de novo biosynthesis in the vanilla orchid. Mol Plant 8(1):40–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.11.008
Gao X, Wu J, Wu D (2019) Rational design of the beta-galactosidase from Aspergillus oryzae to improve galactooligosaccharide production. Food Chem 286(0308–8146):362–367
García-Bofill M, Sutton PW, Guillén M, Álvaro G (2019) Enzymatic synthesis of vanillin catalysed by an eugenol oxidase. Appl Catal A-Gen 582:0926–860X. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2019.117117
Gasson MJ, Kitamura Y, McLauchlan WR, Narbad A, Parr AJ, Parsons EL, Payne J, Rhodes MJ, Walton NJ (1998) Metabolism of ferulic acid to vanillin. A bacterial gene of the enoyl-SCoA hydratase/isomerase superfamily encodes an enzyme for the hydration and cleavage of a hydroxycinnamic acid SCoA thioester. J Biol Chem 273(7):4163–4170. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.7.4163
Goihberg E, Dym O, Tel-Or S, Levin I, Peretz M, Burstein Y (2007) A single proline substitution is critical for the thermostabilization of Clostridium beijerinckii alcohol dehydrogenase. Proteins 66(1):196–204. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21170
Klaus T, Seifert A, Häbe T, Nestl B, Hauer B (2019) An enzyme cascade synthesis of vanillin. Catal 9(3):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9030252
Lesage-Meessen L, Lomascolo A, Bonnin E, Thibault JF, Buleon A, Roller M, Asther M, Record E, Ceccaldi BC, Asther M (2002) A biotechnological process involving filamentous fungi to produce natural crystalline vanillin from maize bran. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 102-103(1–6):141–153. https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:102-103:1-6:141
Liu HM, Zou Y, Yao CY, Yang Z (2019) Enzymatic synthesis of vanillin and related catalytic mechanism. Flavour Fragr J. https://doi.org/10.1002/ffj.3528
Ni J, Wu YT, Tao F, Peng Y, Xu P (2018) A coenzyme-free biocatalyst for the value-added utilization of lignin-derived aromatics. J Am Chem Soc 140(47):16001–16005. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b08177
Perálvarez-Marín A, Lórenz-Fonfría VA, Simón-Vázquez R, Gomariz M, Meseguer I, Querol E, Padrós E (2008) Influence of proline on the thermostability of the active site and membrane arrangement of transmembrane proteins. Biophys J 95(9):4384–4395. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.108.136747
Rao SR, Ravishankar GA (2000) Vanilla flavour: production by conventional and biotechnological routes. J Sci Food Agric 80(3):289–304. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0010(200002)80:3<289::aid-jsfa543>3.0.co;2-2
Schwartz SH, Tan BC, Gage DA, Zeevaart JA, McCarty DR (1997) Specific oxidative cleavage of carotenoids by VP14 of maize. Science 276(5320):1872–1874. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5320.1872
Serra S, Fuganti C, Brenna E (2005) Biocatalytic preparation of natural flavours and fragrances. Trends Biotechnol 23(4):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.02.003
Wang K, Luo H, Tian J, Turunen O, Huang H, Shi P, Hua H, Wang C, Wang S, Yao B (2014) Thermostability improvement of a Streptomyces xylanase by introducing proline and glutamic acid residues. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(7):2158–2165. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03458-13
Yang W, Yang Y, Zhang L, Xu H, Guo X, Yang X, Dong B, Cao Y (2017) Improved thermostability of an acidic xylanase from Aspergillus sulphureus by combined disulphide bridge introduction and proline residue substitution. Sci Rep 7(1):1587. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01758-5
Zamzuri NA, Abd-Aziz S (2013) Biovanillin from agro wastes as an alternative food flavour. J Sci Food Agric 93(3):429–438. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.5962
Zhao Z, Moghadasian MH (2008) Chemistry, natural sources, dietary intake and pharmacokinetic properties of ferulic acid: a review. Food Chem 109(4):691–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.039
Zhu F, Jiang T, Wu B, He B (2018) Enhancement of Z-aspartame synthesis by rational engineering of metalloprotease. Food Chem 253(0308–8146):30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.108
Supplementary data
Supplementary data of this work can be found in online version of the paper.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31700701) and Open Funding Project of the State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering (2018OPEN13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 319 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, X., Lv, Y., Yu, H. et al. Site-directed mutagenesis of coenzyme-independent carotenoid oxygenase CSO2 to enhance the enzymatic synthesis of vanillin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 3897–3907 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10433-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10433-1