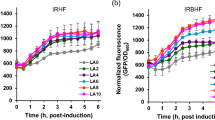
Abstract
Yarrowia lipolytica is an industrial yeast that has been used in the sustainable production of fatty acid-derived and lipid compounds due to its high growth capacity, genetic tractability, and oleaginous properties. This investigation examines the possibility of utilizing urea or urine as an alternative to ammonium sulfate as a nitrogen source to culture Y. lipolytica. The use of a stoichiometrically equivalent concentration of urea in lieu of ammonium sulfate significantly increased cell growth when glucose was used as the carbon source. Furthermore, Y. lipolytica growth was equally improved when grown with synthetic urine and real human urine. Equivalent or better lipid production was achieved when cells are grown on urea or urine. The successful use of urea and urine as nitrogen sources for Y. lipolytica growth highlights the potential of using cheaper media components as well as exploiting and recycling non-treated human waste streams for biotechnology processes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankar AV, Kumar AR, Zinjarde SS (2009) Environmental and industrial applications of Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84(5):847–865. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2156-8
Barth G, Gaillardin C (1996) Yarrowia lipolytica. In: Wolf K (ed) Non-conventional yeasts in biotechnology a handbook. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp 313–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-79856-6_10
Blazeck J, Hill A, Jamoussi M, Pan A, Miller J, Alper HS (2015) Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for itaconic acid production. Metab Eng 32:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.09.005
Blazeck J, Hill A, Liu LQ, Knight R, Miller J, Pan A, Otoupal P, Alper HS (2014) Harnessing Yarrowia lipolytica lipogenesis to create a platform for lipid and biofuel production. Nat Commun 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4131
Blazeck J, Liu LQ, Knight R, Alper HS (2013) Heterologous production of pentane in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J Biotechnol 165(3–4):184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.04.003
Blazeck J, Liu LQ, Redden H, Alper H (2011) Tuning gene expression in Yarrowia lipolytica by a hybrid promoter approach. Appl Environ Microb 77(22):7905–7914. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.05763-11
Bouatra S, Aziat F, Mandal R, Guo AC, Wilson MR, Knox C, Bjorndahl TC, Krishnamurthy R, Saleem F, Liu P, Dame ZT, Poelzer J, Huynh J, Yallou FS, Psychogios N, Dong E, Bogumil R, Roehring C, Wishart DS (2013) The human urine metabolome. PLoS One 8(9):e73076. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073076
Brigida AIS, Amaral PFF, Coelho MAZ, Goncalves LRB (2014) Lipase from Yarrowia lipolytica: production, characterization and application as an industrial biocatalyst. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 101:148–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2013.11.016
Corzo G, Revah S (1999) Production and characteristics of the lipase from Yarrowia lipolytica 681. Bioresour Technol 70(2):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(99)00024-3
Curran KA, Crook NC, Karim AS, Gupta A, Wagman AM, Alper HS (2014) Design of synthetic yeast promoters via tuning of nucleosome architecture. Nat Commun 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5002
D’Annibale A, Sermanni GG, Federici F, Petruccioli M (2006) Olive-mill wastewaters: a promising substrate for microbial lipase production. Bioresour Technol 97(15):1828–1833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.09.001
Darvishi F, Nahvi I, Zarkesh-Esfahani H, Momenbeik F (2009) Effect of plant oils upon lipase and citric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica yeast. J Biomed Biotechnol
Evans CT, Ratledge C (1984) Effect of nitrogen-source on lipid-accumulation in oleaginous yeasts. J Gen Microbiol 130(Jul):1693–1704
Fickers P, Benetti PH, Wache Y, Marty A, Mauersberger S, Smit MS, Nicaud JM (2005) Hydrophobic substrate utilisation by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, and its potential applications. FEMS Yeast Res 5(6–7):527–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsyr.2004.09.004
Fickers P, Nicaud JM, Gaillardin C, Destain J, Thonart P (2004) Carbon and nitrogen sources modulate lipase production in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. J Appl Microbiol 96(4):742–749. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02190.x
Godia F, Albiol J, Montesinos JL, Perez J, Creus N, Cabello F, Mengual X, Montras A, Lasseur C (2002) MELISSA: a loop of interconnected bioreactors to develop life support in space. J Biotechnol 99(3):319–330
Goncalves FAG, Colen G, Takahashi JA (2014) Yarrowia lipolytica and its multiple applications in the biotechnological industry. Sci World J
Haddouche R, Delessert S, Sabirova J, Neuveglise C, Poirier Y, Nicaud JM (2010) Roles of multiple acyl-CoA oxidases in the routing of carbon flow towards beta-oxidation and polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica. FEMS Yeast Res 10(7):917–927. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2010.00670.x
Hofman-Bang J (1999) Nitrogen catabolite repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biotechnol 12(1):35–73. https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:12:1:35
Imandi SB, Bandaru VVR, Somalanka SR, Bandaru SR, Garapati HR (2008) Application of statistical experimental designs for the optimization of medium constituents for the production of citric acid from pineapple waste. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4445–4450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.071
Karakaya A, Laleli Y, Takac S (2012) Development of process conditions for biodegradation of raw olive mill wastewater by Rhodotorula glutinis. Int Biodeter Biodegr 75:75–82
Kunze M, Pracharoenwattana I, Smith SM, Hartig A (2006) A central role for the peroxisomal membrane in glyoxylate cycle function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763(12):1441–1452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.09.009
Lanciotti R, Gianotti A, Baldi D, Angrisani R, Suzzi G, Mastrocola D, Guerzoni ME (2005) Use of Yarrowia lipolytica strains for the treatment of olive mill wastewater. Bioresour Technol 96(3):317–322
Ledesma-Amaro R, Dulermo R, Niehus X, Nicaud JM (2016) Combining metabolic engineering and process optimization to improve production and secretion of fatty acids. Metab Eng 38:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.06.004
Liu XY, Wang XF, Xu JX, Xia J, Lv JS, Zhang T, Wu Z, Deng YF, He JL (2015) Citric acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica SWJ-1b using corn steep liquor as a source of organic nitrogen and vitamins. Ind Crop Prod 78:154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.10.029
Menezes AA, Cumbers J, Hogan JA, Arkin AP (2015) Towards synthetic biological approaches to resource utilization on space missions. J R Soc Interface 12(102)
Moftah OAS, Grbavcic SZ, Moftah WAS, Lukovic ND, Prodanovic OL, Jakovetic SM, Knezevic-Jugovic ZD (2013) Lipase production by Yarrowia lipolytica using olive oil processing wastes as substrates. J Serb Chem Soc 78(6):781–794. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC120905005M
Oswal N, Sarma PM, Zinjarde SS, Pant A (2002) Palm oil mill effluent treatment by a tropical marine yeast. Bioresour Technol 85(1):35–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00063-9
Papanikolaou S, Aggelis G (2002) Lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica growing on industrial glycerol in a single-stage continuous culture. Bioresour Technol 82(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00149-3
Papanikolaou S, Chevalot I, Galiotou-Panayotou M, Komaitis M, Marc I, Aggelis G (2007) Industrial derivative of tallow: a promising renewable substrate for microbial lipid, single-cell protein and lipase production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Electron J Biotechnol 10(3):425–435
Prinz S, Avila-Campillo I, Aldridge C, Srinivasan A, Dimitrov K, Siegel AF, Galitski T (2004) Control of yeast filamentous-form growth by modules in an integrated molecular network. Genome Res 14(3):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.2020604
Qian WF, Liao BY, Chang AYF, Zhang JZ (2010) Maintenance of duplicate genes and their functional redundancy by reduced expression. Trends Genet 26(10):425–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2010.07.002
Qiao K, Imam Abidi SH, Liu H, Zhang H, Chakraborty S, Watson N, Kumaran Ajikumar P, Stephanopoulos G (2015) Engineering lipid overproduction in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab Eng 29:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.02.005
Rigouin C, Gueroult M, Croux C, Dubois G, Borsenberger V, Barbe S, Marty A, Daboussi F, Andre I, Bordes F (2017) Production of medium chain fatty acids by Yarrowia lipolytica: combining molecular design and TALEN to engineer the fatty acid synthase. ACS Synth Biol 6(10):1870–1879. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00034
Rodriguez GM, Hussain MS, Gambill L, Gao D, Yaguchi A, Blenner M (2016) Engineering xylose utilization in Yarrowia lipolytica by understanding its cryptic xylose pathway. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:149
Rodriguez-Vargas S, Sanchez-Garcia A, Martinez-Rivas JM, Prieto JA, Randez-Gil F (2007) Fluidization of membrane lipids enhances the tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to freezing and salt stress. Appl Environ Microb 73(1):110–116. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01360-06
Roon RJ, Levenberg B, Hampshire J (1972) Urea amidolyase—involvement of biotin in urea cleavage. J Biol Chem 247(23):7539
Sarris D, Galiotou-Panayotou M, Koutinas AA, Komaitis M, Papanikolaou S (2011) Citric acid, biomass and cellular lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica strains cultivated on olive mill wastewater-based media. J Chem Technol Biot 86(11):1439–1448
Schwartz C, Shabbir-Hussain M, Frogue K, Blenner M, Wheeldon I (2017) Standardized markerless gene integration for pathway engineering in Yarrowia lipolytica. ACS Synth Biol 6(3):402–409
Schwartz CM, Hussain MS, Blenner M, Wheeldon I (2016) Synthetic RNA polymerase III promoters facilitate high-efficiency CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing in Yarrowia lipolytica. ACS Synth Biol 5(4):356–359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5b00162
Shabbir Hussain M, Gambill L, Smith S, Blenner MA (2016a) Engineering promoter architecture in oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. ACS Synth Biol 5(3):213–223. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5b00100
Shabbir Hussain M, Rodriguez G, Gao D, Spagnaulo M, Gambill L, Blenner M (2016b) Recent advances in metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica. AIMS Bioeng 3(4):493–514. https://doi.org/10.3934/bioeng.2016.4.493
Shaw AJ, Lam FH, Hamilton M, Consiglio A, MacEwen K, Brevnova EE, Greenhagen E, LaTouf WG, South CR, van Dijken H, Stephanopoulos G (2016) Metabolic engineering of microbial competitive advantage for industrial fermentation processes. Science 353(6299):583–586. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf6159
Szabo R (1999) Dimorphism in Yarrowia lipolytica: filament formation is suppressed by nitrogen starvation and inhibition of respiration. Folia Microbiol 44(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02816215
Tsigie YA, Wang CY, Truong CT, Ju YH (2011) Lipid production from Yarrowia lipolytica Po1g grown in sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Bioresour Technol 102(19):9216–9222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.06.047
Vavouri T, Semple JI, Lehner B (2008) Widespread conservation of genetic redundancy during a billion years of eukaryotic evolution. Trends Genet 24(10):485–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2008.08.005
Wang GK, Xiong XC, Ghogare R, Wang PD, Meng YH, Chen SL (2016) Exploring fatty alcohol-producing capability of Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Biofuels 9
Xue Z, Sharpe PL, Hong SP, Yadav NS, Xie D, Short DR, Damude HG, Rupert RA, Seip JE, Wang J, Pollak DW, Bostick MW, Bosak MD, Macool DJ, Hollerbach DH, Zhang H, Arcilla DM, Bledsoe SA, Croker K, McCord EF, Tyreus BD, Jackson EN, Zhu Q (2013) Production of omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid by metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica. Nat Biotechnol 31(8):734–740. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2622
Yano Y, Oikawa H, Satomi M (2008) Reduction of lipids in fish meal prepared from fish waste by a yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Int J Food Microbiol 121(3):302–307
Zhao MX, Chi Z, Chi ZM, Madzak C (2013) The simultaneous production of single-cell protein and a recombinant antibacterial peptide by expression of an antibacterial peptide gene in Yarrowia lipolytica. Process Biochem 48(2):212–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.01.003
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. David Bruce for access to GC-FID and Dr. Rodrigo Martinez Duarte for access to BSL-2 biosafety cabinet for human urine experiments. The authors would also like to acknowledge Dr. Difeng Gao for creating the ∆pex10 strain that was used in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by an Early Career Faculty Award from NASA’s Space Technology Research Grants Program (#NNX15AU46G) to MAB, the US National Science Foundation (CBET-1403099) to MAB, an Undergraduate Research Fellowship from the SC Space Grant Consortium, and Clemson University Creative Inquiry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 94 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brabender, M., Hussain, M.S., Rodriguez, G. et al. Urea and urine are a viable and cost-effective nitrogen source for Yarrowia lipolytica biomass and lipid accumulation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 2313–2322 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8769-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8769-z