Abstract
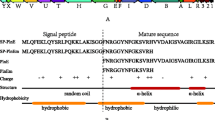
The proteinase-encoding prtB gene of Lactobacillus (Lb.) delbrueckii (d.) subsp. bulgaricus 92059 was cloned and sequenced. Two soluble, secreted, C-terminally His-tagged derivatives were constructed and expressed in Lactococcus lactis by means of the NICE® Expression System. In both obtained derivatives PrtBb and PrtB2, the C-terminal, cell wall-binding domain was deleted. In addition, in derivative PrtB2, the C-terminal part of the B domain was deleted and the signal sequence was replaced by a lactococcal export signal. The affinity-purified derivatives were both proteolytically active. Peptide hydrolysates produced from casein with each of the derivatives showed identical peptide composition, as determined by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Comparison of the peptides generated to those generated with living Lb. d. subsp. bulgaricus 92059 cells (Kliche et al. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:7621–7633, 2017) showed that β-casein was the casein fraction most susceptible to hydrolysis and that some significant differences were observed between the products obtained by either the derivatives or living Lb. d. subsp. bulgaricus 92059 cells. When tested for biological activity, the hydrolysate obtained with PrtBb showed 50% inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme at a concentration of 0.5 mg/ml and immunomodulation/anti-inflammation in an in vitro assay of TNF-α induced NFκB activation at concentrations of 5 and 2.5 mg/ml, respectively. The enzymatically obtained hydrolysate did not show any pro-inflammatory or cytotoxic activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann K, Wutkowski A, Klempt M, Clawin-Rädecker I, Meisel H, Lorenzen PC (2015) Generation and identification of anti-inflammatory peptides from bovine β-casein using enzyme preparations from cod and hog. J Sci Food Agric 96:868–877. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7159
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich A, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin V, Nikolenko S, Pham S, Prjibelski A, Pyshkin A, Sirotkin A, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Bertani G (1951) Studies on lysogenesis. I. the mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 62:293–300
Blanc B, Laloi P, Atlan D, Gilbert C, Portalier R (1993) Two cell-wall-associated aminopeptidases from Lactobacillus helveticus and the purification and characterization of APII from strain ITGL1. J Gen Microbiol 139:1441–1448. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-139-7-1441
de Man JD, Rogosa M, Sharpe ME (1960) A Medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J Appl Bacteriol 23:130–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1960.tb00188.x
de Ruyter PG, Kuipers OP, Beerthuyzen MM, van Alen-Boerrigter I, de Vos WM (1996) Functional analysis of promoters in the nisin gene cluster of Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol 178:3434–3439. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.178.12.3434-3439.1996
Dimitrov Z, Chorbadjiyska E, Gotova I, Pashova K, Ilieva S (2015) Selected adjunct cultures remarkably increase the content of bioactive peptides in Bulgarian white brined cheese. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.969918
Drouault S, Anba J, Bonneau S, Bolotin A, Ehrlich SD, Renault P (2002) The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase motif is lacking in PmpA, the PrsA-like protein involved in the secretion machinery of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3932–3942. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.8.3932-3942.2002
Ebner J, Arslan AA, Fedorova M, Hoffmann R, Kücükcetin A, Pischetsrieder M (2015) Peptide profiling of bovine kefir reveals 236 unique peptides released from caseins during its production by starter culture or kefir grains. J Proteome 117:41–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2015.01.005
Espeche Turbay MB, de Moreno de LeBlanc A, Perdigón G, Savoy de Giori G, Hebert EM (2012) β-Casein hydrolysate generated by the cell envelope-associated proteinase of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis CRL 581 protects against trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice. J Dairy Sci 95:1108–1118. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2011-4735
Fernandez-Espla MD, Garault P, Monnet V, Rul F (2000) Streptococcus thermophilus cell wall-anchored proteinase: release, purification, and biochemical and genetic characterization. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4772–4778. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.11.4772-4778.2000
Germond JE, Delley M, Gilbert C, Atlan D (2003) Determination of the domain of the Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus cell surface proteinase PrtB involved in attachment to the cell wall after heterologous expression of the prtB gene in Lc. lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(6):3377–3384. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.6.3377-3384.2003
Gilbert C, Atlan D, Blanc B, Portalier R, Germond JE, Lapierre L, Mollet B (1996) A new cell surface proteinase: sequencing and analysis of the prtB gene from Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. J Bacteriol 178:3059–3065. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.178.11.3059-3065.1996
Gobetti M, Ferranti P, Smachi E, Goffredi F, Addeo F (2000) Production of angiotensin-I-converting-enzyme-inhibitory peptides in fermented milks started by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus SS1 and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris FT4. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3898–3904. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.66.9.3898-3904.2000
Gomez-Ruiz JA, Ramos M, Recio I (2002) Angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides in Manchego cheeses manufactured with different starter cultures. Int Dairy J 12:697–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-6946(02)00059-6
Ha GE, Chang OK, Jo S-M, Han G-S, Park B-Y, Ham J-S, Jeong S-G (2015) Identification of antihypertensive peptides derived from low molecular weight casein hydrolysates generated during fermentation by Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour 35:738–747. https://doi.org/10.5851/kosfa.2015.35.6.738
Haft DH, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Brover V, Chetvernin V, O’Neill K, Li W, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Lu F, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Zheng C, Thibaud-Nissen F, Geer LY, Marchler-Bauer A, Pruitt KD (2018) RefSeq: an update on prokaryotic genome annotation and curation. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D851–D860. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1068
Hayes M, Stanton C, Slattery H, O'Sullivan O, Hill C, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP (2007) Casein fermentate of Lactobacillus animalis DPC6134 contains a range of novel propeptide angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4658–4667. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00096-07
Hebert EM, Mamone G, Picariello G, Raya RR, Savoy G, Ferranti P, Addeo F (2008) Characterization of the pattern of alphas1- and beta-casein breakdown and release of a bioactive peptide by a cell envelope proteinase from Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis CRL 581. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3682–3689. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00247-08
Kliche T, Li B, Bockelmann W, Meske D, Klempt M, deVrese M, Wutkowski A, Clawin-Rädecker I, Heller KJ (2017) Screening for proteolytically active lactic acid bacteria and bioactivity of peptide hydrolysates obtained with selected strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:7621–7633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8369-3
Kok J, Leenhouts KJ, Haandrikman AJ, Ledeboer AM, Venema G (1988) Nucleotide-sequence of the cell-wall proteinase gene of Streptococcus cremoris WG2. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:231–238
Kuipers OP, Beerthuyzen MM, de Ruyter PG, Luesink EJ, de Vos WM (1995) Autoregulation of nisin biosynthesis in Lc. lactis by signal transduction. J Biol Chem 270(45):27299–27304. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.45.27299
Kuipers OP, de Ruyter PG, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM (1997) Controlled overproduction of proteins by lactic acid bacteria. Trends Biotechnol 15:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7799(97)01029-9
Kuipers OP, de Ruyter PGGA, Kleerebezem M, de Vos WM (1998) Quorum sensing controlled gene expression in lactic acid bacteria. J Biotechnol 64(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(98)00100-X
Kunji ERS, Mierau I, Hagting A, Poolman B, Konings WN (1996) The proteolytic system of lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 70:187–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395933
Laloi P, Atlan D, Blanc B, Gilbert C, Portalier R (1991) Cell-wall-associated proteinase of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus CNRZ 397: differential extraction, purification and properties of the enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164419
Maeno M, Yamamoto N, Takano T (1996) Identification of an antihypertensive peptide from casein hydrolysate produced by a proteinase from Lactobacillus helveticus CP790. J Dairy Sci 79:1316–1321. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(96)76487-1
Malinowski J, Klempt M, Clawin-Rädecker I, Meisel H, Lorenzen PC (2014) Identification of NFκB inhibitory peptide from tryptic β-casein hydrolysate. Food Chem 165:129–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.075
Matagne A, Joris B, Frére JM (1991) Anomalous behaviour of a protein during SDS/PAGE corrected by chemical modification of carboxyclic groups. Biochem J 280:553–556. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2800553
Meisel H, Bockelmann W (1999) Bioactive peptides encrypted in milk proteins: proteolytic activation and tropho-functional properties. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 76:207–2015. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1002063805780
Mierau I, Kleerebezem M (2005) 10 years of the nisin-controlled gene expression system (NICE) in Lc. lactis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:705–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0107-6
Minervini F, Algaron F, Rizello CG, Fox PF, Monnet V, Gobetti M (2003) Angiotensin I-converting-enzyme-inhibitory and antibacterial peptides from Lactobacillus helveticus PR4 proteinase-hydrolyzed caseins of milk from six species. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5297–5305. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.9.5297-5305.2003
Minkiewicz P, Dziuba J, Iwaniak A, Dziuba M, Darewicz M (2008) BIOPEP database and other programs for processing bioactive peptide sequences. J AOAC Int 91:965–980
Ohkita M, Takaoka M, Shiota Y, Nojiri R, Sugii M, Matsumura Y (2002) A nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 suppresses endothelin-1 production in cultured vascular endothelial cells. Jpn J Pharmacol 89:81–84. https://doi.org/10.1254/jjp.89.81
Pastar I, Tonic I, Golic N, Kojic M, van Kranenburg R, Kleerebezem M, Topisirovic L, Jovanovic G (2003) Identification and genetic characterization of a novel proteinase, PrtR, from the human isolate Lactobacillus rhamnosus BGT10. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5802–5811. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.10.5802-5811.2003
Pederson JA, Mileski GJ, Weimer BC, Steele JL (1999) Genetic characterization of a cell envelope-associated proteinase from Lactobacillus helveticus CNRZ32. J Bacteriol 181:4592–4597
Pessione EAND, Cirrincione S (2016) Bioactive molecules released in food by lactic acid bacteria: encrypted peptides and biogenic amines. Front Microbiol 7:876. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00876
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York
Savijoki K, Ingmer H, Varmanen P (2006) Proteolytic systems of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:394–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0427-1
Siezen RJ (1999) Multi-domain, cell-envelope proteinases of lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 76:139–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-2027-4_6
Stefanitsi D, Garel J-R (1997) A zinc-dependent proteinase from the cell wall of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Lett Appl Microbiol 24:180–184. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-765X.1997.00376.x
Terzaghi BE, Sandine WE (1975) Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 29:807–813
Vos P, van Asseldonk M, van Jeveren F, Siezen R, Simons G, de Vos WM (1989) A maturation protein is essential for production of active forms of Lc. lactis SK11 serine proteinase located in or secreted from the cell envelope. J Bacteriol 171:2795–2802. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.171.5.2795-2802.1989
Yamamoto N, Akino A, Takano T (1994) Antihypertensive effect of peptides derived from casein by an extracellular proteinase from Lactobacillus helveticus CP790. J Dairy Sci 77:917–922. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(94)77026-0
Acknowledgements
Expert technical assistance by G. Gerke, R. Miller, F. Repenning and M. Steinke is gratefully acknowledged. T. Koudelka and A. Tholey were supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), within SFB877, project Z2.
Funding
The study was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (Support Code 0315539B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 205 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Habermann, D., Kliche, T. et al. Soluble Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus 92059 PrtB proteinase derivatives for production of bioactive peptide hydrolysates from casein. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 2731–2743 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-09586-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-09586-x