Abstract
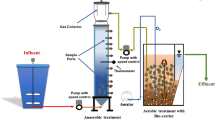
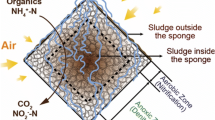
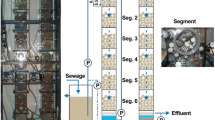
A stand-alone down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) system with a two-stage configuration was operated for 700 days to treat synthetic soft drink wastewater at 3000 mg/L chemical oxygen demand (COD). Throughout the operation, >90% COD and total organic carbon (TOC) removal efficiency was obtained by the first stage, and a final effluent of COD <60 mg/L (TOC <20 mg/L) was consistently maintained with the second stage. Lower organic removal efficiency was observed to closely correlate with lower pH, higher volatile fatty acid (VFA) concentration, and higher suspended solid (SS) in the effluent. Occasionally, biomass sloughing was observed as a cause to unstable reactor performance in the first stage. The microbial community of the retained biomass on the sponges differed significantly based on spatial locations of sponges, sampling time points, and loading shocks. In general, Proteobacteria were found to be more abundant in the reactor at an organic removal efficiency >80% than that at <50%. Specifically, operational taxonomic units closely related to Tolumonas auensis and Rivicola pingtungensis were identified as important populations that were responsible for degrading the major substrate in the soft drink wastewater toward to the end of the reactor operation. In addition, high abundance of Bacteroidetes in the reactor was speculated to be responsible for the VFA accumulation in the effluent. This study demonstrated that stand-alone DHS reactor could be used in treating high-strength wastewater efficiently.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal LK, Ohashi Y, Mochida E, Okui H, Ueki Y, Harada H, Ohashi A (1997) Treatment of raw sewage in a temperate climate using a UASB reactor and the hanging sponge cubes process. Wat Sci Tech 36:433–440
Ait Hsine E, Benhammou A, Pons M (2005) Water resources management in soft drink industry-water use and wastewater generation. Environ Technol 26:1309–1316
Anderson MJ (2005) Permutational multivariate analysis of variance. Department of Statistics, University of Auckland, Auckland
American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association, Water Pollution Control Federation, Water Environment Federation (1915) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (Vol. 2). American Public Health Association
Bal A, Dhagat N (2001) Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor: a review. Indian J Environ Health 43:1–82
Bandara WM, Satoh H, Sasakawa M, Nakahara Y, Takahashi M, Okabe S (2011) Removal of residual dissolved methane gas in an upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor treating low-strength wastewater at low temperature with degassing membrane. Water Res 45:3533–3540
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010a) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26:266–267
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010b) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chen JP, Seng S-S, Hung Y-T (2005) Soft drink waste treatment. Wastewater Treatment 255–269
Chuang H-P, Ohashi A, Imachi H, Tandukar M, Harada H (2007) Effective partial nitrification to nitrite by down-flow hanging sponge reactor under limited oxygen condition. Water Res 41:295–302
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
El-Kamah H, Mahmoud M, Tawfik A (2011) Performance of down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor coupled with up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor for treatment of onion dehydration wastewater. Bioresour Technol 102:7029–7035
Fischer-Romero C, Tindall BJ, Jüttner F (1996) Tolumonas auensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a toluene-producing bacterium from anoxic sediments of a freshwater lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 46(1):183–188
Fleifle A, Tawfik A, Saavedra O, Yoshimura C, Elzeir M (2013a) Modeling and profile analysis of a down-flow hanging sponge system treating agricultural drainage water. Sep Purif Technol 116:87–94
Fleifle A, Tawfik A, Saavedra OC, Elzeir M (2013b) Treatment of agricultural drainage water via downflow hanging sponge system for reuse in agriculture. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 13:403–412
Garny K, Neu TR, Horn H (2009) Sloughing and limited substrate conditions trigger filamentous growth in heterotrophic biofilms—measurements in flow-through tube reactor. Chem Eng Sci 64:2723–2732
Gonzalez-Martinez A, Rodriguez-Sanchez A, van Loosdrecht MM, Gonzalez-Lopez J, Vahala R (2016) Detection of comammox bacteria in full-scale wastewater treatment bioreactors using tag-454-pyrosequencing. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–11
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504
Kalyuzhnyi S, Saucedo JV, Martinez JR (1997) The anaerobic treatment of soft drink wastewater in UASB and hybrid reactors. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 66:291–301
Kawai F (2002) Microbial degradation of polyethers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:30–38. doi:10.1007/s00253-001-0850-2
Kruskal WH, Wallis WA (1952) Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. JASA 47:583–621
Kubota K, Hayashi M, Matsunaga K, Iguchi A, Ohashi A, Li Y-Y, Yamaguchi T, Harada H (2014) Microbial community composition of a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor combined with an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor for the treatment of municipal sewage. Bioresour Technol 151:144–150
Le-Clech P, Chen V, Fane TAG (2006) Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J Membr Sci 284:17–53. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2006.08.019
Lesjean B, Rosenberger S, Laabs C, Jekel M, Gnirss R, Amy G (2005) Correlation between membrane fouling and soluble/colloidal organic substances in membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment. Wat Sci Tech 51:1–8
Liu DH, Liptak BG (1999) Environmental engineers’ handbook on CD-ROM. CRC press
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Buchner A, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G, Förster W (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1363–1371
Machdar I, Harada H, Ohashi A, Sekiguchi Y, Okui H, Ueki K (1997) A novel and cost-effective sewage treatment system consisting of UASB pre-treatment and aerobic post-treatment units for developing countries. Wat Sci Tech 36:189–197. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(97)00739-7
Machdar I, Sekiguchi Y, Sumino H, Ohashi A, Harada H (2000) Combination of a UASB reactor and a curtain type DHS (downflow hanging sponge) reactor as a cost-effective sewage treatment system for developing countries. Wat Sci Tech 42(3–4):83–88
Madigan MT, Martinko JM, Parker J (1997) Brock biology of microorganisms, vol 11. Prentice hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Mahmoud M, Tawfik A, Samhan F, El-Gohary F (2009) Sewage treatment using an integrated system consisting of anaerobic hybrid reactor (AHR) and downflow hanging sponge (DHS). Desalin Water Treat 4:168–176
Mei R, Narihiro T, Nobu MK, Liu WT (2016) Effects of heat shocks on microbial community structure and microbial activity of a methanogenic enrichment degrading benzoate. Lett Appl Microbiol 63(5):356–362
Narihiro T, Kim N-K, Mei R, Nobu MK, Liu W-T (2015) Microbial community analysis of anaerobic reactors treating soft drink wastewater. PLoS One 10:e0119131
Onodera T, Matsunaga K, Kubota K, Taniguchi R, Harada H, Syutsubo K, Okubo T, Uemura S, Araki N, Yamada M (2013) Characterization of the retained sludge in a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor with emphasis on its low excess sludge production. Bioresour Technol 136:169–175
Purdue University (2007) Clean Water Act (CWA). Food Processing Environmental Assistance Center. http://www.fpeac.org/cwa.html. Accessed 1 Oct 2016
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Shapiro S, Wilk M (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality. Biometrika 52:591–611
Sheu S-Y, Chen J-C, Young C-C, Chen W-M (2014) Rivicola pingtungensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Neisseriaceae isolated from a freshwater river. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2009–2016
Spearman C (1904) The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am J Psychol 15:72–101
Statista (2015) Per capita consumption of soft drinks in the United States from 2010 to 2014 (in gallons). https://www.statista.com/statistics/306836/us-per-capita-consumption-of-soft-drinks/. Accessed Sep. 2016
Takahashi M, Yamaguchi T, Kuramoto Y, Nagano A, Shimozaki S, Sumino H, Araki N, Yamazaki S, Kawakami S, Harada H (2011) Performance of a pilot-scale sewage treatment: an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) and a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactors combined system by sulfur-redox reaction process under low-temperature conditions. Bioresour Technol 102:753–757
Tandukar M, Uemura S, Machdar I, Ohashi A, Harada H (2005) A low-cost municipal sewage treatment system with a combination of UASB and the “fourth-generation” downflow hanging sponge reactors. Water Sci Technol 52:323–329
Tandukar M, Machdar I, Uemura S, Ohashi A, Harada H (2006) Potential of a combination of UASB and DHS reactor as a novel sewage treatment system for developing countries: long-term evaluation. J Environ Eng 132:166–172. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2006)132:2(166)
Tawfik A (2012) Polyurethane trickling filter in combination with anaerobic hybrid reactor for treatment of tomato industry wastewater. In: Zafar F, Sharmin E (eds) Polyurethane. INTECH, Chapter 16. doi:10.5772/47982
Tawfik A, Wahab RA, Al-Asmer A, Matary F (2011) Effect of hydraulic retention time on the performance of down-flow hanging sponge system treating grey wastewater. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 34:767–776
Tebai L, Hadjivassilis I (1992) Soft drinks industry wastewater treatment. Wat Sci Tech 25(1):45–51
Ueki A, Akasaka H, Suzuki D, Ueki K (2006) Paludibacter propionicigenes gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel strictly anaerobic, Gram-negative, propionate-producing bacterium isolated from plant residue in irrigated rice-field soil in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:39–44
Uemura S, Suzuki S, Abe K, Kubota K, Yamaguchi T, Ohashi A, Takemura Y, Harada H (2010) Removal of organic substances and oxidation of ammonium nitrogen by a down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor under high salinity conditions. Bioresour Technol 101:5180–5185
Wang Y, Qian P-Y (2009) Conservative fragments in bacterial 16S rRNA genes and primer design for 16S ribosomal DNA amplicons in metagenomic studies. PLoS One 4:e7401
Wichitsathian B, Racho P (2010) Quantification of organic and nitrogen removal in downflow hanging sponge (DHS) systems as a post-treatment of UASB effluent. Water Sci Technol 62(9):2121–2127
Acknowledgements
We thank Kyohei Kuroda, Na-Kyung Kim, and Ran Mei at the University of Illinois at Champaign-Urbana for the valuable advice. The opinion expressed here is the authors’ perspective and does not represent PepsiCo Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JY, AS, and WTL designed the experiment, JL and CF conducted the experiment, and all authors contributed to the manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by PepsiCo Inc. to Dr. Wen-tso Liu.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 5504 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, J., Fang, C., Yu, J. et al. Direct treatment of high-strength soft drink wastewater using a down-flow hanging sponge reactor: performance and microbial community dynamics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 5925–5936 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8326-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8326-1