Abstract
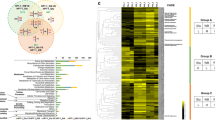
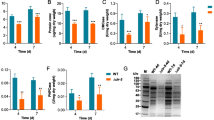
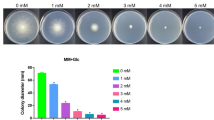
Cellulosic biomass represents a valuable potential substitute for fossil-based fuels. As such, there is a strong need to develop efficient biotechnological processes for the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic biomass via the optimization of cellulase production by fungi. Ambient pH is an important factor affecting the industrial production of cellulase. In the present study, we demonstrate that several Aspergillus nidulans genes encoding cellulolytic enzymes are regulated by Pal-PacC-mediated pH signaling, as evidenced by the decreased cellulase productivity of the palC mutant and pacC deletants of A. nidulans. The deletion of pacC was observed to result in delayed induction and decreased expression of the cellulase genes based on time course expression analysis. The genome-wide identification of PacC-regulated genes under cellobiose-induced conditions demonstrated that genes expressed in a PacC-dependent manner included 82 % of ClrB (a transcriptional activator of the cellulase genes)-regulated genes, including orthologs of various transporter and β-glucosidase genes considered to be involved in cellobiose uptake or production of stronger inducer molecules. Together with the significant overlap between ClrB- and PacC-regulated genes, the results suggest that PacC-mediated regulation of the cellulase genes involves not only direct regulation by binding to their promoter regions but also indirect regulation via modulation of the expression of genes involved in ClrB-dependent transcriptional activation. Our findings are expected to contribute to the development of more efficient industrial cellulase production methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coradetti ST, Craig JP, Xiong Y, Shock T, Tian C, Glass NL (2012) Conserved and essential transcription factors for cellulase gene expression in ascomycete fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:7397–7402
Coradetti ST, Xiong Y, Glass NL (2013) Analysis of a conserved cellulase transcriptional regulator reveals inducer-independent production of cellulolytic enzymes in Neurospora crassa. Microbiology Open 2:595–609
Eberhart BM, Beck RS, Goolsby KM (1977) Cellulase of Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol 130:181–186
Espeso EA, Arst HNJ (2000) On the mechanism by which alkaline pH prevents expression of an acid-expressed gene. Mol Cell Biol 20:3355–3363
Espeso EA, Peñalva MA (1996) Three binding sites for the Aspergillus nidulans PacC zinc-finger transcription factor are necessary and sufficient for regulation by ambient pH of the isopenicillin N synthase gene promoter. J Biol Chem 271:28825–28830
Espeso EA, Tilburn J, Sánchez-Pulido L, Brown CV, Valencia A, Arst HNJ, Peñalva MA (1997) Specific DNA recognition by the Aspergillus nidulans three zinc finger transcription factor PacC. J Mol Biol 274:466–480
Galazka JMC, Tian C, Beeson WT, Martinez B, Glass NL, Cate JH (2010) Cellodextrin transport in yeast for improved biofuel production. Science 330:84–86
Galindo A, Hervás-Aguilar A, Rodríguez-Galán O, Vincent O, Arst HNJ, Tilburn J, Peñalva MA (2007) PalC, one of two Bro1 domain proteins in the fungal pH signaling pathway, localizes to cortical structures and binds Vps32. Traffic 8:1346–1364
Galindo A, Calcagno-Pizarelli AM, Arst HNJ, Peñalva MÁ (2012) An ordered pathway for the assembly of fungal ESCRT-containing ambient pH signalling complexes at the plasma membrane. J Cell Sci 125:1784–1795
Gielkens M, González-Candelas L, Sánchez-Torres P, van de Vondervoort P, de Graaff L, Visser J, Ramón D (1999a) The abfB gene encoding the major α-L-arabinofuranosidase of Aspergillus nidulans: nucleotide sequence, regulation and construction of a disrupted strain. Microbiol 145:735–741
Gielkens MM, Dekkers E, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1999b) Two cellobiohydrolase-encoding genes from Aspergillus niger require D-xylose and the xylanolytic transcriptional activator XlnR for their expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4340–4345
Häkkinen M, Sivasiddarthan D, Aro N, Saloheimo M, Pakula TM (2015) The effects of extracellular pH and of the transcriptional regulator PACI on the transcriptome of Trichoderma reesei. Microb Cell Factories 14:63
He R, Ma L, Li C, Jia W, Li D, Zhang D, Chen S (2014) Trpac1, a pH response transcription regulator, is involved in cellulase gene expression in Trichoderma reesei. Enzym Microb Technol 67:17–26
Käfer E (1977) Meiotic and mitotic recombination in Aspergillus and its chromosomal aberrations. Adv Genet 19:33–131
Kato N, Murakoshi Y, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi N (2002a) Isomaltose formed by α-glucosidases triggers amylase induction in Aspergillus nidulans. Curr Genet 42:43–50
Kato N, Suyama S, Shirokane M, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi N (2002b) Novel α-glucosidase from Aspergillus nidulans with strong transglycosylation activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1250–1256
Kunitake E, Tani S, Sumitani J, Kawaguchi T (2013) A novel transcriptional regulator, ClbR, controls the cellobiose- and cellulose-responsive induction of cellulase and xylanase genes regulated by two distinct signaling pathways in Aspergillus aculeatus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2017–2028
Kurasawa T, Yachi M, Suto M, Kamagata Y, Takao S, Tomita F (1992) Induction of cellulase by gentiobiose and its sulfur-containing analog in Penicillium purpurogenum. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:106–110
Lockington RA, Rodbourn L, Barnett S, Carter CJ, Kelly JM (2002) Regulation by carbon and nitrogen sources of a family of cellulases in Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 37:190–196
MacCabe AP, Orejas M, Pérez-González CJ, Ramón D (1998) Opposite patterns of expression of two Aspergillus nidulans xylanase genes with respect to ambient pH. J Bacteriol 180:1331–1333
Mach RL, Seiboth B, Myasnikov A, Gonzalez R, Strauss J, Harkki AM, Kubicek CP (1995) The bgl1 gene of Trichoderma reesei QM9414 encodes an extracellular, cellulose-inducible β-glucosidase involved in cellulase induction by sophorose. Mol Microbiol 16:687–697
Makita T, Katsuyama Y, Tani S, Suzuki H, Kato N, Todd RB, Hynes MJ, Tsukagoshi N, Kato M, Kobayashi T (2009) Inducer-dependent nuclear localization of a Zn(II)2Cys6 transcriptional activator, AmyR, in Aspergillus nidulans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:391–399
Marui J, Kitamoto N, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi N (2002a) Transcriptional activator, AoXlnR, mediates cellulose-inductive expression of the xylanolytic and cellulolytic genes in Aspergillus oryzae. FEBS Lett 528:279–282
Marui J, Tanaka A, Mimura S, de Graaff LH, Visser J, Kitamoto N, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi N (2002b) A transcriptional activator, AoXlnR, controls the expression of genes encoding xylanolytic enzymes in Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 35:157–169
Mello-de-Sousa TM, Silva-Pereira I, Poças-Fonseca MJ (2011) Carbon source and pH-dependent transcriptional regulation of cellulase genes of Humicola grisea var. thermoidea grown on sugarcane bagasse. Enzym Microb Technol 48:19–26
Motoyama T, Fujiwara M, Kojima N, Horiuchi H, Ohta A, Takagi M (1997) The Aspergillus nidulans genes chsA and chsD encode chitin synthases which have redundant functions in conidia formation. Mol Gen Genet 253:520–528
Murakoshi Y, Makita T, Kato M, Kobayashi T (2012) Comparison and characterization of α-amylase inducers in Aspergillus nidulans based on nuclear localization of AmyR. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:1629–1635
Nakamura T, Makita T, Maeda Y, Tanoue N, Kato M, Kobayashi T (2006) Expression profile of amylolytic genes in Aspergillus nidulans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:2363–2370
Noguchi Y, Sano M, Kanamaru K, Ko T, Takeuchi M, Kato M, Kobayashi T (2009) Genes regulated by AoXlnR, the xylanolytic and cellulolytic transcriptional regulator, in Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:141–154
Ogawa M, Kobayashi T, Koyama Y (2012) ManR, a novel Zn(II)2Cys6 transcriptional activator, controls the β-mannan utilization system in Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 49:987–995
Ogawa M, Kobayashi T, Koyama Y (2013) ManR, a transcriptional regulator of the β-mannan utilization system, controls the cellulose utilization system in Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:426–429
Peñalva MA, Lucena-Agell D, Arst HNJ (2014) Liaison alcaline: Pals entice non-endosomal ESCRTs to the plasma membrane for pH signaling. Curr Opin Microbiol 22:49–59
Rowlands RT, Turner G (1973) Nuclear and extranuclear inheritance of oligomycin resistance in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 126:201–216
Saloheimo M, Kuja-Panula J, Ylösmäki E, Ward M, Penttilä M (2002) Enzymatic properties and intracellular localization of the novel Trichoderma reesei β-glucosidase BGLII (cel1A). Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4546–4553
Sternberg D, Mandels GR (1979) Induction of cellulolytic enzymes in Trichoderma reesei by sophorose. J Bacteriol 139:761–769
Sternberg D, Mandels GR (1980) Regulation of the cellulolytic system in Trichoderma reesei by sophorose: induction of cellulase and repression of β-glucosidase. J Bacteriol 144:1197–1199
Stewart JC, Parry JB (1981) Factors influencing the production of cellulase by Aspergillus fumigatus (Fresenius). J Gen Microbiol 125:33–39
Stricker AR, Grosstessner-Hain K, Würleitner E, Mach RL (2006) Xyr1 (xylanase regulator 1) regulates both the hydrolytic enzyme system and D-xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina. Eukaryot Cell 5:2128–2137
Sun J, Nishiyama T, Shimizu K, Kadota K (2013) TCC: an R package for comparing tag count data with robust normalization strategies. BMC Bioinformatics 14:219
Thomas-Chollier M, Sand O, Turatsinze JV, Janky R, Defrance M, Vervisch E, Brohée S, van Helden J (2008) RSAT: regulatory sequence analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 36:W119–W127
van Peij NN, Gielkens MM, de Vries RP, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1998a) The transcriptional activator XlnR regulates both xylanolytic and endoglucanase gene expression in Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3615–3619
van Peij NN, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1998b) Isolation and analysis of xlnR, encoding a transcriptional activator co-ordinating xylanolytic expression in Aspergillus niger. Mol Microbiol 27:131–142
Yamakawa Y, Endo Y, Li N, Yoshizawa M, Aoyama M, Watanabe A, Kanamaru K, Kato M, Kobayashi T (2013) Regulation of cellulolytic genes by McmA, the SRF-MADS box protein in Aspergillus nidulans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431:777–782
Zhang W, Kou Y, Xu J, Cao Y, Zhao G, Shao J, Wang H, Wang Z, Bao X, Chen G, Liu W (2013) Two major facilitator superfamily sugar transporters from Trichoderma reesei and their roles in induction of cellulase biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 288:32861–32872
Znameroski EA, Li X, Tsai JC, Galazka JM, Glass NL, Cate JH (2014) Evidence for transceptor function of cellodextrin transporters in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem 289:2610–2619
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for Promotion of Basic and Applied Researches for Innovations in Bio-oriented Industry and by the Science and Technology Research Promotion Program for Agriculture, Forestry, Fisheries, and Food Industry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 823 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunitake, E., Hagiwara, D., Miyamoto, K. et al. Regulation of genes encoding cellulolytic enzymes by Pal-PacC signaling in Aspergillus nidulans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 3621–3635 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7409-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7409-8