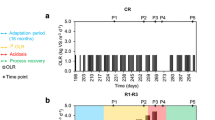
Abstract
In natural settings, anaerobic digestion can take place in a wide temperature range, but industrial digesters are usually operated under either mesophilic (~35 °C) or thermophilic (~55 °C) conditions. The ability of anaerobic digestion microbiota to switch from one operating temperature to the other remains poorly documented. We therefore studied the effect of sudden temperature changes (35 °C/55 °C) in lab-scale bioreactors degrading 13C-labelled cellulose. An asymmetric behaviour was observed. In terms of methane production, after an adaptation period, mesophilic inoculum exhibited a functional resistance to temperature increase but no functional resilience when temperature was reset to 35 °C, while thermophilic inoculum methanogenic activity strongly decreased under mesophilic conditions but partially recovered when temperature was reset to 55 °C. Automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis community fingerprints evidenced a strong influence of temperature on microbial diversity, particularly pronounced and persistent for Archaea. Key phylotypes involved in 13C-cellulose degradation were identified with a coupled stable isotope probing (SIP)-16S rDNA pyrotag sequencing approach, suggesting that the hydrolytic and fermentative metabolic functions could be maintained thanks to functional redundancy between members of the class Clostridia, whereas methanogenic activity primarily relied on specialized groups affiliated either to genus Methanosarcina (mesophilic conditions), Methanothermobacter or Methanoculleus (thermophilic conditions) that were irreversibly modified by temperature increase.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagge E, Sahlstrom L, Albihn A (2005) The effect of hygienic treatment on the microbial flora of biowaste at biogas plants. Water Res 39(20):4879–4886
Bouskova A, Dohanyos M, Schmidt JE, Angelidaki I (2005) Strategies for changing temperature from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions in anaerobic CSTR reactors treating sewage sludge. Water Res 39(8):1481–1488
Cabirol N, Fernandez FJ, Mendoza L, Noyola A (2003) Acclimation of mesophilic anaerobic sludge to thermophilic conditions: PCR genera detection methodology. Water Sci Technol 48:81–86
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010a) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 26(2):266–267
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pẽa AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010b) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Meth 7(5):335–336
Cardinale M, Brusetti L, Quatrini P, Borin S, Puglia AM, Rizzi A, Zanardini E, Sorlini C, Corselli C, Daffonchio D (2004) Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(10):6147–6156
Chapleur O, Bize A, Serain T, Mazeas L, Bouchez T (2014) Co-inoculating ruminal content neither provides active hydrolytic microbes nor improves methanization of (1)(3)C-cellulose in batch digesters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87(3):616–629. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12249
Chin KJ, Lukow T, Conrad R (1999) Effect of temperature on structure and function of the methanogenic archaeal community in an anoxic rice field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(6):2341–2349
Choorit W, Wisarnwan P (2007) Effect of temperature on the anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent. Electron J Biotechnol 10(3):376–385
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37(SUPPL. 1):141–145
Conrad R, Klose M, Noll M (2009) Functional and structural response of the methanogenic microbial community in rice field soil to temperature change. Environ Microbiol 11(7):1844–1853
Donoso-Bravo A, Retamal C, Carballa M, Ruiz-Filippi G, Chamy R (2009) Influence of temperature on the hydrolysis, acidogenesis and methanogenesis in mesophilic anaerobic digestion: parameter identification and modeling application. Water Sci Technol 60(1):9–17. doi:10.2166/wst.2009.316
Fisher MM, Triplett EW (1999) Automated approach for ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of microbial diversity and its application to freshwater bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(10):4630–4636
Gagnaire DY, Taravel FR (1980) Biosynthesis of bacterial cellulose from D-glucose uniformly enriched in 13C. Eur J Biochem 103(1):133–143
García-Martínez J, Rodríguez-Valera F (2000) Microdiversity of uncultured marine prokaryotes: the SAR11 cluster and the marine Archaea of group I. Mol Ecol 9(7):935–948. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2000.00953.x
Levén L, Eriksson ARB, Schnürer A (2007) Effect of process temperature on bacterial and archaeal communities in two methanogenic bioreactors treating organic household waste. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59(3):683–693
Li T, Mazéas L, Sghir A, Leblon G, Bouchez T (2009) Insights into networks of functional microbes catalysing methanization of cellulose under mesophilic conditions. Environ Microbiol 11(4):889–904. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01810.x
Lindorfer H, Waltenberger R, Kollner K, Braun R, Kirchmayr R (2008) New data on temperature optimum and temperature changes in energy crop digesters. Bioresour Technol 99(15):7011–7019
Loy A, Lehner A, Lee N, Adamczyk J, Meier H, Ernst J, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (2002) Oligonucleotide microarray for 16S rRNA gene-based detection of all recognized lineages of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(10):5064–5081. doi:10.1128/aem.68.10.5064-5081.2002
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66(3):506–577
McHugh S, Carton M, Collins G, O’Flaherty V (2004) Reactor performance and microbial community dynamics during anaerobic biological treatment of wastewaters at 16–37 °C. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48(3):369–378
Michelland RJ, Dejean S, Combes S, Fortun-Lamothe L, Cauquil L (2009) StatFingerprints: a friendly graphical interface program for processing and analysis of microbial fingerprint profiles. Mol Ecol Resour 9(5):1359–1363
Noll M, Klose M, Conrad R (2010) Effect of temperature change on the composition of the bacterial and archaeal community potentially involved in the turnover of acetate and propionate in methanogenic rice field soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73(2):215–225
Pap B, Györkei Á, Boboescu IZ, Nagy IK, Bíró T, Kondorosi É, Maróti G (2015) Temperature-dependent transformation of biogas-producing microbial communities points to the increased importance of hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis under thermophilic operation. Bioresour Technol 177:375–380. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.021
Pender S, Toomey M, Carton M, Eardly D, Patching JW, Colleran E, O’Flaherty V (2004) Long-term effects of operating temperature and sulphate addition on the methanogenic community structure of anaerobic hybrid reactors. Water Res 38(3):619–630
Prosser JI (2010) Replicate or lie. Environ Microbiol 12(7):1806–1810. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02201.x
Radajewski S, Ineson P, Parekh NR, Murrell JC (2000) Stable-isotope probing as a tool in microbial ecology. Nature 403(6770):646–649
Schnürer A, Zellner G, Svensson BH (1999) Mesophilic syntrophic acetate oxidation during methane formation in biogas reactors. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 29(3):249–261
Smith DM, Snow DE, Rees E, Zischkau AM, Hanson JD, Wolcott RD, Sun Y, White J, Kumar S, Dowd SE (2010) Evaluation of the bacterial diversity of pressure ulcers using bTEFAP pyrosequencing. BMC Med Genet 3(41):1
Thioulouse J, Chessel D, Dole’dec S, Olivier J-M (1997) ADE-4: a multivariate analysis and graphical display software. Stat Comput 7(1):75–83. doi:10.1023/A:1018513530268
Van Lier JB, Rebac S, Lettinga G (1997) High-rate anaerobic wastewater treatment under psychrophilic and thermophilic conditions. Water Sci Technol 35:199–206
Van Lier JB, Tilche A, Ahring BK, Macarie H, Moletta R, Dohanyos M, Hulshoff Pol LW, Lens P, Verstraete W (2001) New perspectives in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol 43:1–18
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267
Wu XL, Friedrich MW, Conrad R (2006) Diversity and ubiquity of thermophilic methanogenic archaea in temperate anoxic soils. Environ Microbiol 8(3):394–404
Zinder SH (1994) Syntrophic acetate oxidation and “reversible acetogenesis.” In: “Acetogenesis”. Chapman & Hall, New York:386–415
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Céline Madigou for precious support in achieving this work. All data are available in the supplementary material and on request from the authors. The experiments were conducted on the LABE experimental platform funded by DRRT in the framework of the CPER 2007–2014 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 751 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chapleur, O., Mazeas, L., Godon, JJ. et al. Asymmetrical response of anaerobic digestion microbiota to temperature changes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 1445–1457 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7046-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7046-7