Abstract
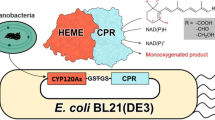
Cytochrome P450s are interesting biocatalysts due to their ability to hydroxylate non-activated hydrocarbons in a selective manner. However, to date only a few P450-catalyzed processes have been implemented in industry due to the difficulty of developing economically feasible processes. In this study, we have used the CYP153A heme domain from Marinobacter aquaeolei fused to the reductase domain of CYP102A1 from Bacillus megaterium (BM3) expressed in Escherichia coli. This self-sufficient protein chimera CYP153A-CPRBM3 G307A mutant is able to selectively hydroxylate medium and long chain length fatty acids at the terminal position. ω-Hydroxylated fatty acids can be used in the field of high-end polymers and in the cosmetic and fragrance industry. Here, we have identified the limitations for implementation of a whole-cell P450-catalyzed reaction by characterizing the chosen biocatalyst as well as the reaction system. Despite a well-studied whole-cell P450 catalyst, low activity and poor stability of the artificial fusion construct are the main identified limitations to reach sufficient biocatalyst yield (mass of product/mass of biocatalyst) and space-time yield (volumetric productivity) essential for an economically feasible process. Substrate and product inhibition are also challenges that need to be addressed, and the application of solid substrate is shown to be a promising option to improve the process.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe A, Sugiyama K (2005) Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of human melanoma cells by ω-hydroxy fatty acids. Anti-Cancer Drugs 16:543–549
Bernhardt R (2006) Cytochromes P450 as versatile biocatalysts. J Biotechnol 124:128–145
Bernhardt R, Urlacher VB (2014) Cytochromes P450 as promising catalysts for biotechnological application: chances and limitations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:6185–6203
Biermann U, Bornscheuer U, Meier MAR, Metzger JO, Schaefer HJ (2011) Oils and fats as renewable raw materials in chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:3854–3871
Bordeaux M, Galarneau A, Fajula F, Drone J (2011) A regioselective biocatalyst for alkane activation under mild conditions. Angew Chem Int Ed 123:2123–2127
ChemSpider (a) CSID:3756, http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.3756.html
ChemSpider (b) CSID:71366, http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.71366.html
Cirino PC, Arnold FH (2003) A self‐sufficient peroxide‐driven hydroxylation biocatalyst. Angew Chem Int Ed 115:3421–3423
Cornelissen S, Julsing MK, Volmer J, Riechert O, Schmid A, Bühler B (2013) Whole‐cell‐based CYP153A6‐catalyzed (S)‐limonene hydroxylation efficiency depends on host background and profits from monoterpene uptake via AlkL. Biotechnol Bioeng 110:1282–1292
Cornish-Bowden A (2012) Fundamentals of enzyme kinetics, 4th edn. Wiley-VCH Verlag & Co, Weinheim, Germany
Craft DL, Madduri KM, Eshoo M, Wilson CR (2003) Identification and characterization of the CYP52 family of Candida tropicalis ATCC 20336, important for the conversion of fatty acids and alkanes to α, ω-dicarboxylic acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5983–5991
Fujii T, Narikawa T, Sumisa F, Arisawa A, Takeda K, Kato J (2006) Production of α, ω-alkanediols using Escherichia coli expressing a cytochrome P450 from Acinetobacter sp. OC4. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:1379–1385
Gudiminchi RK, Randall C, Opperman DJ, Olaofe OA, Harrison STL, Albertyn J, Smit MS (2012) Whole-cell hydroxylation of n-octane by Escherichia coli strains expressing the CYP153A6 operon. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1507–1516
Huf S, Kruegener S, Hirth T, Rupp S, Zibek S (2011) Biotechnological synthesis of long-chain dicarboxylic acids as building blocks for polymers. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 113:548–561
Kiss FM, Lundemo MT, Zapp J, Woodley JM, Bernhardt R (2015) Process development for the production of 15β-hydroxycyproterone acetate using Bacillus megaterium expressing CYP106A2 as whole-cell biocatalyst. Microb Cell Fact 14
Kitazume T, Tanaka A, Takaya N, Nakamura A, Matsuyama S, Suzuki T, Shoun H (2002) Kinetic analysis of hydroxylation of saturated fatty acids by recombinant P450foxy produced by an Escherichia coli expression system. Eur J Biochem 269:2075–2082
Labinger JA (2004) Selective alkane oxidation: hot and cold approaches to a hot problem. J Mol Catal A Chem 220:27–35
Law HEM, Baldwin CVF, Chen BH, Woodley JM (2006) Process limitations in a whole-cell catalysed oxidation: sensitivity analysis. Chem Eng Sci 61:6646–6652
Lee W, Kim M, Jin Y, Seo J (2013) Engineering of NADPH regenerators in Escherichia coli for enhanced biotransformation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2761–2772
Liu C, Liu F, Cai J, Xie W, Long TE, Turner SR, Lyons A, Gross RA (2011) Polymers from fatty acids: poly (ω-hydroxyl tetradecanoic acid) synthesis and physico-mechanical studies. Biomacromolecules 12:3291–3298
Lu W, Ness JE, Xie W, Zhang X, Minshull J, Gross RA (2010) Biosynthesis of monomers for plastics from renewable oils. J Am Chem Soc 132:15451–15455
Lundemo MT, Woodley JM (2015) Guidelines for development and implementation of biocatalytic P450 processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:2465–2483
Maier T, Forster H, Asperger O, Hahn U (2001) Molecular characterization of the 56-kDa CYP153 from Acinetobacter sp. EB104. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:652–658
Malca SH, Scheps D, Kühnel L, Venegas-Venegas E, Seifert A, Nestl BM, Hauer B (2012) Bacterial CYP153A monooxygenases for the synthesis of omega-hydroxylated fatty acids. Chem Commun 48:5115–5117
Marisch K, Bayer K, Cserjan-Puschmann M, Luchner M, Striedner G (2013) Evaluation of three industrial Escherichia coli strains in fed-batch cultivations during high-level SOD protein production. Microb Cell Fact 12
Narhi LO, Fulco AJ (1987) Identification and characterization of two functional domains in cytochrome P-450BM-3, a catalytically self-sufficient monooxygenase induced by barbiturates in Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem 262:6683–6690
Nelson DR (2009) The cytochrome P450 homepage. Hum Genomics 4:59–65
Olaofe OA, Fenner CJ, Gudiminchi RK, Smit MS, Harrison STL (2013) The influence of microbial physiology on biocatalyst activity and efficiency in the terminal hydroxylation of n-octane using Escherichia coli expressing the alkane hydroxylase, CYP153A6. Microb Cell Fact 12:8
Omura T, Sato R (1964) The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J Biol Chem 239:2370–2378
O’Reilly E, Köhler V, Flitsch SL, Turner NJ (2011) Cytochromes P450 as useful biocatalysts: addressing the limitations. Chem Commun 47:2490–2501
Paul CE, Gargiulo S, Opperman DJ, Lavandera I, Gotor-Fernandez V, Gotor V, Taglieber A, Arends IWCE, Hollmann F (2013) Mimicking nature: synthetic nicotinamide cofactors for C = C bioreduction using enoate reductases. Org Lett 15:180–183
Rammler DH (1967) The effect of DMSO on several enzyme systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci 141:291–299
Royce LA, Liu P, Stebbins MJ, Hanson BC, Jarboe LR (2013) The damaging effects of short chain fatty acids on Escherichia coli membranes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:8317–8327
Sadeghi SJ, Fantuzzi A, Gilardi G (2011) Breakthrough in P 450 bioelectrochemistry and future perspectives. BBA-Protein Proteomics 1814:237–248
Salazar O, Cirino PC, Arnold FH (2003) Thermostabilization of a cytochrome P450 peroxygenase. Chembiochem 4:891–893
Scheps D, Malca SH, Hoffmann H, Nestl BM, Hauer B (2011) Regioselective ω-hydroxylation of medium-chain n-alkanes and primary alcohols by CYP153 enzymes from Mycobacterium marinum and Polaromonas sp. strain JS666. Org Biomol Chem 9:6727–6733
Scheps D, Honda Malca S, Richter SM, Marisch K, Nestl BM, Hauer B (2013) Synthesis of ω-hydroxy dodecanoic acid based on an engineered CYP153A fusion construct. Microb Biotechnol 6:694–707
Schrewe M, Julsing MK, Bühler B, Schmid A (2013) Whole-cell biocatalysis for selective and productive C–O functional group introduction and modification. Chem Soc Rev 42:6346–6377
Siriphongphaew A, Pisnupong P, Wongkongkatep J, Inprakhon P, Vangnai AS, Honda K, Ohtake H, Kato J, Ogawa J, Shimizu S (2012) Development of a whole-cell biocatalyst co-expressing P450 monooxygenase and glucose dehydrogenase for synthesis of epoxyhexane. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:357–367
Sligar SG, Cinti DL, Gibson GG, Schenkman JB (1979) Spin state control of the hepatic cytochrome P450 redox potential. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 90:925–932
Stumpp T, Wilms B, Altenbuchner J (2000) Ein neues L-rhamnose-induzierbares expressionssystem für Escherichia coli. Biospektrum 6:33–36
Tran N, Nguyen D, Dwaraknath S, Mahadevan S, Chavez G, Nguyen A, Dao T, Mullen S, Nguyen T, Cheruzel LE (2013) An efficient light-driven P450 BM3 biocatalyst. J Am Chem Soc 135:14484–14487
Vallon T, Glemser M, Honda Malca S, Scheps D, Schmid J, Siemann-Herzberg M, Hauer B, Takors R (2013) Production of 1-octanol from n-octane by Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Chem Ing Tech 85:841–848
van Beilen JB, Smits THM, Whyte LG, Schorcht S, Roethlisberger M, Plaggemeier T, Engesser K, Witholt B (2002) Alkane hydroxylase homologues in gram-positive strains. Environ Microbiol 4:676–682
van Beilen JB, Duetz WA, Schmid A, Witholt B (2003) Practical issues in the application of oxygenases. Trends Biotechnol 21:170–177
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the funding from the People Programme (Marie Curie Actions) of the European Union’s 7th Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under REA Grant Agreement 289217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
We dedicate this work to Prof. Dr. Bernard Witholt.
M. T. Lundemo and S. Notonier contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lundemo, M.T., Notonier, S., Striedner, G. et al. Process limitations of a whole-cell P450 catalyzed reaction using a CYP153A-CPR fusion construct expressed in Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 1197–1208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6999-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6999-x