Abstract
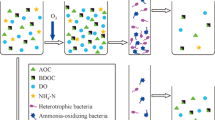
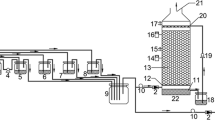
Currently, a novel chemical absorption-biological reduction (CABR) integrated process, employing Fe(II)EDTA as a solvent, is being under development to reduce the cost of NOx removal from flue gas. In this work, the NO removal profile, re-acclimation performance, and microbial characteristics in a thermophilic biofilter were investigated at the conditions typical to CABR process. The biofilter comprised of four layers of packing material with a surface area of 1200 m2 m−3. Experimental results revealed that the biofilter could remove 95 % of the fed NO at typical flue gas conditions. As the gas residence time varied from 90 to 15 s, the NO removal efficiency decreased from 100 to 56.5 % due to the NO mass transfer limitation. The longer period of the biofilter shutdown required more time for its re-acclimation. For example, after 8-day shutdown, the biofilter was re-acclimated in 32 h. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of PCR-amplified product showed that Pseudomonas, a group of denitrifier, was dominant in the biofilter. Because the Pseudomonas was abundant at the bottom layer of packed-bed, the bottom layer contributed to 60–70 % of the total NO removal. In addition, Pseudomonas gradually faded away along the gas flow path from the bottom to the top of biofilter, resulting in a significant decrease in NO removal at the other three packed-bed layers. These observed results will provide the process engineering and scale-up data with respect to the biofilter operations to help advance the CABR process to pilot-scale testing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen YX, Yin J, Wang KX, Fang S (2005) Effects of periods of nonuse and fluctuating ammonia concentration on biofilter performance. J Environ Sci Heal A 39:2447–2463
Coker AK (2007) Ludwig’s applied process design for chemical and petrochemical plants. 4th edition, Gulf Professional Publishing
Deshusses MA, Hamer G, Dunn IJ (1996) Transient state behavior of a biofilter removing mixtures of vapors of MEK and MIBK from air. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:587–598
Dilmore R, Neufeld RD, Hammack RW (2006) Laboratory-scale iron EDTA-based NOx scrubbing process with biological treatment and regeneration of spent scrubber water. Environ Eng Sci 23:788–802
Foerter D, Jozewicz W (2001) Cost of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) application for NOx control on coal-fired boilers. EPA/600/R-01/087
Ho K, Chung Y, Tseng C (2008) Continuous deodorization and bacterial community analysis of a biofilter treating nitrogen-containing gases from swine waste storage pits. Bioresour Technol 99:2757–2765
Jang JH, Hirai M, Shoda M (2006) Effect of shutdown on styrene removal in a biofilter inoculated with Pseudomonas sp. SR-5. J Hazard Mater B129:223–227
Kinney KA, Loehr RC, Corsi RL (1999) Vapor-phase bioreactors: avoiding problems through better design and operation. Environ Prog 18:222–229
Li W, Wu CZ, Shi Y (2006) Metal chelate absorption coupled with microbial reduction for the removal of NOx from flue gas. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:306–311
Li W, Wu CZ, Zhang SH, Shao K, Shi Y (2007) Evaluation of microbial reduction of Fe(III)EDTA in a chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated NOx removal system. Environ Sci Technol 41:639–644
Lin T, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Wang X, Jing G (2014) Evaluation of Fe(III)EDTA and Fe(II)EDTA-NO reduction in a NOx scrubber solution by magnetic Fe3O4-Chitosam microspheres immobilized microorganisms. Biotechnol Bioproc Eng 19:175–182
Martin FJ (1996) Effect of periods of non-use on biofilter performance. J Air Waste Manage Assoc 46(6):539–546
Mauzerall DL, Sultan B, Kim N, Bradford DF (2005) NOx emission from large point sources: variability in ozone production, resulting health damages and economic costs. Atmos Environ 39:2851–2866
Moe WM, Qi B (2004) Performance of a fungal biofilter treating gas-phase solvent mixtures during intermittent loading. Water Res 38:2259–2268
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Steele JA, Ozis F, Fuhrman JA, Devinny JS (2005) Structure of microbial communities in ethanol biofilters. Chem Eng J 113:135–143
Straub KL, Benz M, Schink B, Widdel F (1996) Anaerobic, nitrate-dependent microbial oxidation of ferrous iron. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1458–1460
Swanson WJ, Loehr RC (1997) Biofiltration: fundamentals, design and operations principles, and applications. J Environ Eng 123:538–546
van der Maas P, van de Sandt T, Klapwijk B, Lens P (2003) Biological reduction of nitric oxide in aqueous Fe(II)EDTA solutions. Biotechnol Prog 19:1323–1328
van der Maas P, van den Brink P, Klapwijk B, Lens P (2009) Acceleration of the Fe(III)EDTA- reduction rate in BioDeNOx reactors by dosing electron mediating compounds. Chemosphere 75:243–249
Xia YF, Lu BH, Liu N, Chen QL, Li SJ, Li W (2013) NOx removal in chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated system: process rate and rate-limiting step. Bioresour Technol 149:184–190
Zhang SH, Li W, Wu CZ, Chen H, Shi Y (2007) Reduction of Fe(II)EDTA-NO by a newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. strain DN-2 in NOx scrubber solution. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1181–1187
Zhang SH, Cai LL, Mi XH, Jiang JL, Li W (2008) NOx removal from simulated flue gas by chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated approach in a biofilter. Environ Sci Technol 42:3814–3820
Zhang SH, Cai LL, Liu Y, Shi Y, Li W (2009) Effects of NO2 - and NO3 - on the Fe(III)EDTA reduction in a chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated NOx removal system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:557–563
Zhang SH, Shi Y, Li W (2012) Biological and chemical interaction of oxygen on the reduction of Fe(III)EDTA in a chemical absorption-biological reduction integrated NOx removal system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:2653–2659
Zhang SH, Chen H, Xia YF, Liu N, Lu BH, Li W (2014) Current advances of integrated processes combining chemical absorption and biological reduction for NOx removal from flue gas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8497–8512
Zhao B, Wang SX, Xu JY, Fu K, Klimont Z, Hao JM, He KB, Cofala J, Amann M (2013) NOx emissions in China: historical trends and future perspectives. Atoms Chem Phys Discuss 13:16047–16112
Zhou Z, Jing G, Zhou Q (2013) Enhanced NOx removal from flue gas by an integrated process of chemical absorption coupled with two-stage biological reduction using immobilized microorganisms. Process Saf Environ Protect 91:325–332
Acknowledgments
The work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21276233, No. 21306166), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2013 M541783), and the Post doctor Science Preferential Funding of Zhejiang Province, China (No. BSH1301019).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 118 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Chen, H., Xia, Y. et al. Re-acclimation performance and microbial characteristics of a thermophilic biofilter for NOx removal from flue gas. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 6879–6887 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6585-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6585-2