Abstract
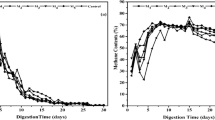
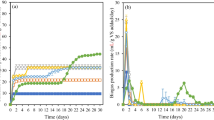
Foaming problem which occurred occasionally during food waste (FW) anaerobic digestion (AD) was investigated with the Malaysian FW by stepwise increase in organic loading (OL) from 0.5 to 7.5 g VS/L. The FW feedstock with carbon to nitrogen (C/N) ratio of 17 was upgraded to C/N ratio of 26 and 30 by mixing with other wastes. The digestion which was carried out at 37 °C in 1-L batch reactors showed that foam formation initiated at OL of 1.5 g VS/L and was further enhanced as OL of feedstock was increased. The digestion foaming reached its maximum at OL of 5.5 g VS/L and did not increase further even when OL was increased to 7.5 g VS/Ld. Increase in the C/N ratio of feedstock significantly enhanced the microbial degradation activity, leading to better removal of foam causing intermediates and reduced foaming in the reactor by up to 60 %.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Franson MAH, American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 21st edn. APHA, Washington
Boe K, Kougias PG, Pacheco F, O-Thong S, Angelidaki I (2012) Effects of substrates and intermediate compounds on foaming in manure digestion systems. Water Sci Technol 66:2146–2154
Bolzonella D, Pavan P, Battistoni P, Cecchi F (2005) Mesophilic anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: Influence of the solid retention time in the waste water treatment process. Process Biochem 40:1453–1460
Dalmau J, Comas J, Rodriguez-Roda I, Pagilla K, Steyer JP (2010) Model development and simulation for predicting risk of foaming in anaerobic digestion systems. Bioresour Technol 101:4306–4314
Deshpande NS, Barigou M (2000) Mechanical suppression of the dynamic foam head in bubble column reactors. Chem Eng Process 39:207–217
Forster-Carneiro T, Perez M, Romero L (2008) Influence of total solid and Inoculum contents on performance of anaerobic reactors treating food waste. Bioresour Technol 99:6994–7002
Frayer M, O’Flaherty E, Gray NF (2011) Evaluating the measurement of activated sludge foam potential. Water 3:424–444
Ganidi N, Sean T, Elise C (2009) Anaerobic digestion foaming causes-a review. Bioresour Technol 100:5546–5554
Ganidi N, Sean T, Elise C (2011) The effect of organic loading rate on foam initiation during mesophilic anaerobic digestion of municipal wastewater sludge. Bioresour Technol 102:6637–6643
Griffin ME, Mcmahon KD, Mackie RI, Raskin L (1998) Methanogenic population dynamics during start-up of anaerobic digesters treating municipal solid waste and biosolids. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:342–355
Griffiths P, Stratton H (2010) Foaming organisms in sewage treatment friend or foe: Victim of bad publicity. 35th Annual Qld Water Industry Operators Workshop, Rockampton, UK
Hansen KH, Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (1998) Anaerobic digestion of swine manure inhibition by ammonia. Water Res 32:5–12
Heard J, Harvey E, Johnson B, Wells J, Angove M (2008) The effect of filamentous bacteria on foam production and stability. Colloids Surf Biointerf 63:21–26
Izumi K, Yu-ki O, Norio N, Chiaki N, Shuichi Y, Tatsuki T (2010) Effects of particle size on anaerobic digestion of food waste. Int Biodegrad 64:601–608
Jiang Y, Heaven S, Banks C (2012) Strategies for stable anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste. Renew Energy 44:206–214
Kougias PG, Boe K, Angelidaki I (2013) Effect of organic loading rate and feedstock composition on foaming in manure-based biogas reactors. Bioresour Technol 144:1–7
Kougias PG, Boe K, Tsapekos P, Angelidaki I (2014) Foam suppression in overloaded manure-based biogas reactors using antifoaming agents. Bioresour Technol 153:198–205
Lahav O, Morgan B (2004) Titration methodologies for monitoring of anaerobic digestion in developing countries-a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:1331–1341
Lee DH, Behera SK, Kim JW, Park HS (2009) Methane production potential of leachate generated from Korean food waste recycling facilities: A lab scale study. Wasman 29:876–882
Liu G, Zhang R, El-Mashad HM, Dong R (2009) Effect of feed to inoculum ratio on biogas yields of food and green wastes. Bioresour Technol 100:5103–5108
Marneri M, Mamais D, Koutsiouki E (2009) Microthrix parvicella and Gordona amarae in mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion systems. Environ Technol 30:5–15
Nitschke M, Pastore GM (2006) Production and properties of a surfactant obtained from Bacillus subtilis grown on cassava wastewater. Bioresour Technol 97:336–341
Pagilla KR, Craney KC, Kido WH (1997) Causes and effects of foaming in anaerobic sludge digesters. Water Sci Technol 36:463–470
Resch C, Worl A, Waltenberger R, Braun R, Kirchmayr R (2011) Enhancement options for the utilization of nitrogen rich animal by-products in anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 102:2503–2510
Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (2002) Bio-surfactants and oil bioremediation, Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:249–252
Seo JY, Heo JS, Kim TH, Joo WH, Crohn DM (2004) Effect of vermiculite addition on compost produced from Korean food waste. Waste Manag 24:891–987
Tanimu MI, Mohd Ghazi TI, Harun MR, Idris A (2014a) Effect of feed loading on biogas methane production in batch mesophilic anaerobic digesters treating food waste. Int J Chem Environ Eng 5:39–41
Tanimu MI, Mohd Ghazi TI, Harun MR, Idris A (2014b) Effect of carbon to nitrogen ratio of food waste on biogas methane production in a batch mesophilic anaerobic digester. Int J Innov Manag Technol 5(2):116-119
Varley J, Brown AK, Boyd JWR, Dodd PW, Gallagher S (2004) Dynamic multipoint measurement of foam behaviour for a continuous fermentation over a range of key process variables. J Biochem Eng 20:61–72
Zeshan O, Karthikeyan CV (2012) Effect of C/N ratio and ammonia-N accumulation in a pilot-scale thermophilic dry anaerobic digester. Bioresour Technol 113:294–302
Zhang Y, Heaven S, Banks CJ (2012a) Strategies for stable anaerobic digestion of Vegetable waste. Renew Energy 44:206–214
Zhang Y, Banks CJ, Heaven S (2012b) Co-digestion of source segregated domestic food waste to improve process stability. Bioresour Technol 114:168–178
Zupancic GD, Uranjek-Zevart N, Ros M (2008) Full-scale anaerobic co-digestion of organic waste and municipal sludge. Biomol Bioeng 32:162–167
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Universiti Putra Malaysia for the financial assistance and facilities through the Research University Grant Scheme (RUGS). We would also like to thank the management of FW treatment plant in Sri Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia, for supplying the sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanimu, M.I., Mohd Ghazi, T.I., Harun, M.R. et al. Effects of feedstock carbon to nitrogen ratio and organic loading on foaming potential in mesophilic food waste anaerobic digestion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 4509–4520 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6486-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6486-4