Abstract
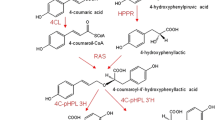
Caffeoylquinic acids are found in artichokes, and they are currently considered important therapeutic or preventive agents for treating Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. We transformed artichoke [the cultivated cardoon or Cynara cardunculus var. altilis DC (Asteraceae)] with the rolC gene, which is a known inducer of secondary metabolism. High-performance liquid chromatography with UV and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HPLC-UV-HRMS) revealed that the predominant metabolites synthesized in the transgenic calli were 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid, and chlorogenic acid. The rolC-transformed calli contained 1.5 % caffeoylquinic acids by dry weight. The overall production of these metabolites was three times higher than that of the corresponding control calli. The enhancing effect of rolC remained stable over long-term cultivation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonhomme V, Laurain Mattar D, Fliniaux MA (2000) Effects of the rolC gene on hairy root: induction development and tropane alkaloid production by Atropa belladonna. J Nat Prod 63:1249–1252
Bulgakov VP (2008) Functions of rol genes in plant secondary metabolism. Biotechnol Adv 26:318–324
Bulgakov VP, Khodakovskaya MV, Labetskaya NV, Chernoded GK, Zhuravlev YN (1998) The impact of plant rolC oncogene on ginsenoside production by ginseng hairy root cultures. Phytochemistry 49:1929–1934
Bulgakov VP, Veselova MV, Tchernoded GK, Kiselev KV, Fedoreyev SA, Zhuravlev YN (2005) Inhibitory effect of the Agrobacterium rhizogenes rolC gene on rabdosiin and rosmarinic acid production in Eritrichium sericeum and Lithospermum erythrorhizon transformed cell cultures. Planta 221:471–478
Bulgakov VP, Shkryl YN, Veremeichick GN (2010) Engineering high yields of secondary metabolites in Rubia cell cultures through transformation with rol genes. Methods Mol Biol 643:229–242
Bulgakov VP, Shkryl YN, Veremeichik GN, Gorpenchenko TY, Vereshchagina YV (2013) Recent advances in the understanding of Agrobacterium rhizogenes-derived genes and their effects on stress resistance and plant metabolism. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 134:1–22
Cao X, Xiao H, Zhang Y, Zou L, Chu Y, Chu X (2010) 1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid-mediated glutathione synthesis through activation of Nrf2 protects against OGD/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in astrocytes. Brain Res 1347:142–148
Chen R, Liu X, Zou J, Yang L, Dai J (2013) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenylpropanoids in cell culture, regenerated plantlets and herbs of Saussurea involucrata. J Pharm Biomed Anal 74:39–46
Clément B, Perot J, Geoffroy P, Legrand M, Zon J, Otten L (2007) Abnormal accumulation of sugars and phenolics in tobacco roots expressing the Agrobacterium T-6b oncogene and the role of these compounds in 6b-induced growth. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:53–62
Clifford MN, Knight S, Kuhnert N (2005) Discriminating between the six isomers of dicaffeoylquinic acid by LC-MS(n). J Agric Food Chem 53:3821–3832
Dong GC, Chuang PH, Chang KC, Jan PS, Hwang PI, Wu HB, Yi M, Zhou HX, Chen HM (2009) Blocking effect of an immuno-suppressive agent, cynarin, on CD28 of T-Cell receptor. Pharm Res 26:375–381
Gális I, Simek P, Van Onckelen HA, Kakiuchi Y, Wabiko H (2002) Resistance of transgenic tobacco seedlings expressing the Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58-6b gene, to growth-inhibitory levels of cytokinin is associated with elevated IAA levels and activation of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell Physiol 43:939–950
Gális I, Kakiuchi Y, Simek P, Wabiko H (2004) Agrobacterium tumefaciens AK-6b gene modulates phenolic compound metabolism in tobacco. Phytochemistry 65:169–179
Georgiev MI, Eibl R, Zhong JJ (2013) Hosting the plant cells in vitro: recent trends in bioreactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:3787–3800
Grishchenko OV, Kiselev KV, Tchernoded GK, Fedoreyev SA, Veselova MV, Bulgakov VP, Zhuravlev YN (2013) The influence of the rolC gene on isoflavonoid production in callus cultures of Maackia amurensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 113:429–435
Heidarian E, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2013) Protective effect of artichoke (Cynara scolymus) leaf extract against lead toxicity in rat. Pharm Biol 51:1104–1109
Helfer A, Pien S, Otten L (2002) Functional diversity and mutational analysis of Agrobacterium 6b oncoproteins. Mol Genet Genomics 267:577–586
Inyushkina YV, Kiselev KV, Bulgakov VP, Zhuravlev YN (2009) Specific genes of cytochrome P450 monooxygenases are implicated in biosynthesis of caffeic acid metabolites in rolC-transgenic culture of Eritrichium sericeum. Biochem Mosc 74:917–924
Kakiuchi Y, Gàlis I, Tamogami S, Wabiko H (2006) Reduction of polar auxin transport in tobacco by the tumorigenic Agrobacterium tumefaciens AK-6b gene. Planta 223:237–247
Koncz C, Schell J (1986) The promoter of TL-DNA gene 5 controls the tissue-specific expression of chimaeric genes carried by a novel type of Agrobacterium binary vector. Mol Gen Genet 204:383–396
Menin B, Moglia A, Comino C, Lanteri S, Van Herpen TWJM, Beekwilder J (2012) In vitro callogenesis and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of globe artichoke. 7th International Symposium on In Vitro Culture and Horticultural Breeding. Ghent, Belgium. Book Ser Acta Horticult 961:267–271
Miketova P, Schram K, Whitney J, Kearns E, Timmermann B (1999) Mass spectrometry of 3,5- and 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acids and selected derivatives. J Mass Spectrom 34:1240–1252
Moglia A, Lanteri S, Comino C, Acquadro A, de Vos R, Beekwilder J (2008) Stress-induced biosynthesis of dicaffeoylquinic acids in globe artichoke. J Agric Food Chem 56:8641–8649
Negro D, Montesano V, Grieco S, Crupi P, Sarli G, De Lisi A, Sonnante G (2012) Polyphenol compounds in artichoke plant tissues and varieties. J Food Sci 77:244–252
Nilsson O, Olsson O (1997) Getting to the root: the role of the Agrobacterium rhizogenes rol genes in the formation of hairy roots. Physiol Plant 100:463–473
Palazón J, Cusidó RM, Roig C, Piñol MT (1998a) Expression of the rolC gene and nicotine production in transgenic roots and their regenerated plants. Plant Cell Rep 17:384–390
Palazón J, Cusidó RM, Gonzalo J, Bonfill M, Morales S, Piñol MT (1998b) Relation between the amount the rolC gene product and indole alkaloid accumulation in Catharantus roseus transformed root cultures. J Plant Physiol 153:712–718
Petersen M, Abdullah Y, Benner J, Eberle D, Gehlen K, Hücherig S, Janiak V, Kim KH, Sander M, Weitzel C, Wolters S (2009) Evolution of rosmarinic acid biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 70:1663–1679
Rondanelli M, Giacosa A, Opizzi A, Faliva MA, Sala P, Perna S, Riva A, Morazzoni P, Bombardelli E (2013) Beneficial effects of artichoke leaf extract supplementation on increasing HDL-cholesterol in subjects with primary mild hypercholesterolaemia: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Int J Food Sci Nutr 64:7–15
Rondanelli M, Opizzi A, Faliva M, Sala P, Perna S, Riva A, Morazzoni P, Bombardelli E, Giacosa A (2014) Metabolic management in overweight subjects with naive impaired fasting glycaemia by means of a highly standardized extract from Cynara scolymus: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Phytother Res 28:33–41
Schram K, Miketova P, Slanina J, Humpa O, Taborska E (2004) Mass spectrometry of 1,3- and 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acids. J Mass Spectrom 39:384–395
Shen Q, Dai Z, Lu Y (2010) Rapid determination of caffeoylquinic acid derivatives in Cynara scolymus L. by ultrafast liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry based on a fused core C18 column. J Sep Sci 33:3152–3158
Shkryl YN, Veremeichik GN, Bulgakov VP, Tchernoded GK, Mischenko NP, Fedoreyev SA, Zhuravlev YN (2008) Individual and combined effects of the rolA, B and C genes on anthraquinone production in Rubia cordifolia transformed calli. Biotechnol Bioeng 100:118–125
Slanina J, Táborská E, Bochořákova H, Slaninová I, Humpa O, Robinson WE Jr, Schram KH (2001) New and facile method of preparation of the anti-HIV-1 agent, 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid. Tetrahedron Lett 42:3383–3385
Sonnante G, Pignone D, Hammer K (2007) The domestication of artichoke and cardoon: from Roman times to the genomic age. Ann Bot 100:1095–1100
Sonnante G, D’Amore R, Blanco E, Pierri CL, De Palma M, Luo J, Tucci M, Martin C (2010) Novel hydroxycinnamoyl-coenzyme A quinate transferase genes from artichoke are involved in the synthesis of chlorogenic acid. Plant Physiol 153:1224–1238
Spena A, Schmülling T, Koncz C, Schell JS (1987) Independent and synergistic activity of rol A, B and C loci in stimulating abnormal growth in plants. EMBO J 6:3891–3899
Takemura T, Urushisaki T, Fukuoka M, Hosokawa-Muto J, Hata T, Okuda Y, Hori S, Tazawa S, Araki Y, Kuwata K (2012) 3,4-Dicaffeoylquinic acid, a major constituent of Brazilian propolis, increases TRAIL expression and extends the lifetimes of mice infected with the influenza A virus. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012: Article ID 946867, doi: 10.1155/2012/946867
Trajtemberg SP, Apóstolo NM, Fernández G (2006) Calluses of Cynara cardunculus var. cardunculus cardoon (Asteraceae): determination of cynarine and chlorogenic acid by automated high-performance capillary electrophoresis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 42:534–537
Wang M, Soyano T, Machida S, Yang J-Y, Jung C, Chua N-H, Yuan YA (2011) Molecular insights into plant cell proliferation disturbance by Agrobacterium protein 6b. Genes Dev 25:64–76
Xiao HB, Cao X, Wang L, Run XQ, Su Y, Tian C, Sun SG, Liang ZH (2011) 1,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid protects primary neurons from amyloid β1-42-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Chin Med J 124:2628–2635
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research and the “Molecular and Cell Biology” Grant Program of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 53 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vereshchagina, Y.V., Bulgakov, V.P., Grigorchuk, V.P. et al. The rolC gene increases caffeoylquinic acid production in transformed artichoke cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 7773–7780 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5869-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5869-2