Abstract
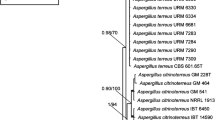
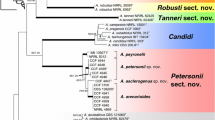
Black koji molds including its albino mutant, the white koji mold, have been widely used for making the distilled spirit shochu in Northeast Asia because they produce citric acid which prevents undesirable contamination from bacteria. Since Inui reported Aspergillus luchuensis from black koji in Okinawa in 1901, many fungal names associated with black koji molds were reported. However, some species are similar and differentiation between species is difficult. Fungal taxonomists tried to arrange a taxonomic system for black koji molds, but the results were not clear. Recently, multi-locus sequence typing has been successfully used to taxonomy of black Aspergillus. According to β-tubulin and calmodulin gene sequences, black koji molds can be subdivided in three species, A. luchuensis, Aspergillus niger, and Aspergillus tubingensis. Aspergillus awamori, Aspergillus kawachii, Aspergillus inuii, Aspergillus nakazawai, and Aspergillus coreanus are synonyms of A. luchuensis, Aspergillus batatae, Aspergillus aureus (or Aspergillus foetidus), Aspergillus miyakoensis, and Aspergillus usamii (including A. usamii mut. shirousamii) are synonyms of A. niger and Aspergillus saitoi and A. saitoi var. kagoshimaensis are synonyms of A. tubingensis. A. luchuensis mut. kawachii was suggested particular names for A. kawachii because of their industrial importance. The history and modern taxonomy of black koji molds is further discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Musallam A (1980) Revision of the black Aspergillus species. Dissertation, Utrecht University
Hong SB, Lee MA, Kim DH, Varga J, Frisvad JC, Perrone G, Gomi K, Yamada O, Machida M, Houbraken J, Samson RA (2013) Aspergillus luchuensis, an industrially important black Aspergillus in East Asia. PLoS ONE e63769
Iizuka H, Yamaguchi T (1954) Studies on the mutation of Aspergillus usamii Sakakuchi et al. Part 2. on Asp. usamii mut. shirousamii. J Agric Chem Soc Jpn 28:972–976 (in Japanese)
Iizuka H, Yamaguchi T (1955) Studies on Aspergillus usamii mut. Shirousamii and its industrial application. J Gen Appl Microbiol 1:194–200 (in Japanese)
Iizuka H, Sugiyama J (1965) Aspergilli isolated from Kuro-koji of Ryuku islands and Kagoshima, Japan. J Jpn Bot 40:230–233
Inui T (1901a) Untersuchungen uber die niederen Organismen welche sich bei der Zubereitung des alkoholischen Getrankes "Awamori" betheiligen. The Journal of the College of Science, Imperial University of Tokyo, Japan 15:465–476 (in German)
Inui T (1901b) Ryukyu awamori hakko kin chyosa houkokusyo. Journal of the Tokyo Chemical Society 22:669–688 (in Japanese)
JCM online catalogue. http://www.jcm.riken.jp/cgi-bin/jcm/jcm_number?JCM=2261. Accessed 15 July 2013
Kitahara K, Kurushima M (1949) Studies on the diastatic enzyme systems of molds. Part 1. Comparison of diastatic enzyme systems of several important molds. J Ferment Technol 27:1–5 (in Japanese)
Kitahara K, Yoshida M (1949) On the so-called Awamori white mold part III. (1) Morphological and several physiological characteristics. J Ferment Technol 27:162–166 (in Japanese)
Kozakiewicz Z (1989) Aspergillus species on stored products. CMI Mycol Pap 161:1–188
Kusters-van Someren MA, Samson RA, Visser J (1991) The use of RFLP analysis in classification of the black Aspergilli: reinterpretation of the A. niger aggregate. Curr Genet 19:21–26
Megnegneau B, Debets F, Hoekstra RF (1993) Genetic variability and relatedness in the complex group of black Aspergilli based on random amplification of polymorphic DNA. Curr Genet 23:323–329
Murakami H (1979a) Classification system of the black Aspergilli. Taxonomic studies on Japanese industrial strains of the Aspergillus (Part 32). J Brew Soc Jpn 74:849–853 (in Japanese)
Murakami H (1979b) Classification system of the black Aspergilli. Taxonomic studies on Japanese industrial strains of the Aspergillus (Part 33). J Brew Soc Jpn 74:854–858 (in Japanese)
Nakazawa R (1911) On awamori-koji fungus (1st report). Government Research Institute, Formosa, Report No. 2:93–97 (in Japanese)
Nakazawa R (1915) On awamori-koji fungus (2nd report). Government Research Institute, Formosa, Report No. 4:215–222 (in Japanese)
Nakazawa R, Kobayashi T (1915) Test making of Awamori. Government Research Institute, Formosa, Report No. 4:223–229 (in Japanese)
Nakazawa R, Simo M, Watanabe H (1936) Study on microorganisms in awamori fermentation (I): Aspergillus. J Agric Chem Soc Jpn 12:931–974 (in Japanese)
Nehira T (1945) Classification of black Aspergilli (2). J Ferment Technol 23:18–21 (in Japanese)
Parenicova L, Benen JAE, Samson RA, Visser J (1997) Evaluation of RFLP analysis of the classification of selected black Aspergilli. Mycol Res 101:810–814
Parenicova L, Skouboe P, Frisvad JC, Samson RA, Rossen L, Ten Hoor-Suykerbuyk M, Visser J (2001) Combined molecular and biochemical approach identifies Aspergillus japonicus and Aspergillus aculeatus as two species. Appl Environ Microb 67:521–527
Perrone G, Stea G, Epifani F, Varga J, Frisvad JC, Samson RA (2011) Aspergillus niger contains the cryptic phylogenetic species A. awamori. Fungal Biol 115:1138–1150
Peterson ST (2000) Phylogenetic relationships in Aspergillus based on rDNA sequence analysis. In: Samson RA, Pitt JI (eds) Integration of modern taxonomic methods for Penicillium and Aspergillus classification. Harwood Academic, Amsterdam, pp 323–355
Peterson SW (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of Aspergillus species using DNA sequences from four loci. Mycologia 100:205–226
Raper KB, Fennell DI (1965) Aspergillus niger group. In: The genus Aspergillus. The Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore, pp 293–356
Saito (1907) Mikrobiologische studien uber die zubereitung des bataten branntweines auf der insel Hachijo (Japan). Centr Bakteriol Parasitenk Abt II 18:30–37
Sakaguchi K, Iizuka H, Yamazaki S (1950) A study on black Aspergilli. J Agric Chem Soc Jpn 24:138–142 (in Japanese)
Samson RA, Houbraken J, Kuijpers AFA, Frank JM, Frisvad JC (2004) New ochratoxin A or sclerotium producing species in Aspergillus section Nigri. Stud Mycol 50:45–61
Samson RA, Noonim P, Meijer M, Houbraken J, Frisvad JC, Varga J (2007) Diagnostic tools to identify black Aspergilli. Stud Mycol 59:129–145
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thom C, Raper KB (1945) A manual of the Aspergilli. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Varga J, Kevei F, Fekete C, Coenen A, Kozakiewicz Z, Croft JH (1993) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in the mitochondrial DNAs of the Aspergillus niger aggregate. Mycol Res 97:1207–1212
Varga J, Rigó K, Tóth B, Téren J, Kozakiewicz Z (2003) Evolutionary relationships among Aspergillus species producing economically important mycotoxins. Food Technol Biotechnol 41:29–36
Varga J, Frisvad JC, Kocsubé S, Brankovics B, Tóth B, Szigeti G, Samson RA (2011) New and revisited species in Aspergillus section Nigri. Stud Mycol 69:1–17
Yamada O, Takara R, Hamada R, Hayashi R, Tsukahara M, Mikami S (2011) Molecular biological researches of Kuro-koji molds, their classification and safety. J Biosci Bioeng 112:233–237
Yokoyama K, Wang L, Miyaji M, Nishimura K (2001) Identification, classification and phylogeny of the Aspergillus section Nigri inferred from mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. FEMS Microbiol lett 200:241–246
Yu TS, Yeo SH, Kim HS (2004) A new species of hyphomycetes, Aspergillus coreanus sp. nov., isolated from traditional Korean nuruk. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:182–187
Acknowledgments
We thank Masayuki Machida for sharing his view on the taxonomy of black koji mold species. This work was partly supported by the National Academy of Agricultural Science (NAAS), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea (project no. PJ00866601).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, SB., Yamada, O. & Samson, R.A. Taxonomic re-evaluation of black koji molds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 555–561 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5332-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5332-9