Abstract
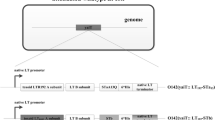
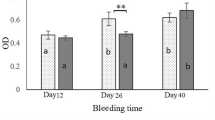
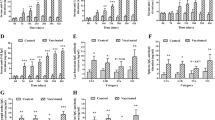
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is an important cause of diarrheal disease and deaths among children in developing countries and the major cause of traveler's diarrhea (TD). Since surface protein colonization factors (CFs) of ETEC are important for pathogenicity and immune protection is mainly mediated by locally produced IgA antibodies in the gut, much effort has focused on the development of an oral CF-based vaccine. The most extensively studied ETEC candidate vaccine is the rCTB-CF ETEC vaccine, containing recombinantly produced cholera B subunit and the most commonly encountered ETEC CFs on the surface of whole inactivated bacteria. Initial clinical trials with this vaccine showed significant immune responses against the key antigens in different age groups in Bangladesh and Egypt and protection against more severe TD in Western travelers. However, when tested in a phase-III trial in Egyptian infants, the protective efficacy of the vaccine was found to be low, indicating the need to improve the immunogenicity of the vaccine, e.g., by increasing the levels of the protective antigens. This review describes different strategies for the construction of recombinant nontoxigenic E. coli and Vibrio cholerae candidate vaccine strains over-expressing higher amounts of ETEC CFs than clinical ETEC isolates selected to produce high levels of the respective CF, e.g., those ETEC strains which have been used in the rCTB-CF ETEC vaccine. Several different expression vectors containing the genes responsible for the expression and assembly of the examined CFs, all downstream of the powerful tac promoter, which could be maintained either with or without antibiotic selection, were constructed. Expression from the tac promoter was under the control of the lacI q repressor present on the plasmids. Following induction with isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside, candidate vaccine strains over-expressing single CFs, unnatural combinations of two CFs, and also hybrid forms of ETEC CFs were produced. Specific monoclonal antibodies against the major subunits of the examined CF were used to quantify the amount of the surface-expressed CF by a dot-blot assay and inhibition ELISA. Oral immunization with formalin- or phenol-inactivated recombinant bacteria over-expressing the CFs was found to induce significantly higher antibody responses compared to immunization with the previously used vaccine strains. We therefore conclude that our constructs may be useful as candidate strains in an oral whole-cell inactivated CF ETEC vaccine.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anantha RP, McVeigh AL, Lee LH, Agnew MK, Cassels FJ, Scott DA, Whittam S, Savarino SJ (2004) Evolutionary and functional relationships of colonization factor antigen i and other class 5 adhesive fimbriae of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 72:7190–7201
Butterton JR, Ryan ET, Acheson DWK, Calderwood SB (1997) Coexpression of the B subunit of Shiga toxin 1 and EaeA from enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in Vibrio cholerae vaccine strains. Infect Immun 65:2127–2135
Caron J, Scott JR (1990) A rns-like regulatory gene for colonization factor antigen I (CFA/I) that controls expression of CFA/I pilin. Infect Immun 58:874–878
Caron J, Coffield LM, Scott JR (1989) A plasmid-encoded regulatory gene, rns, required for expression of the CS1 and CS2 adhesins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:963–967
Cassels FJ, Wolf MK (1995) Colonization factors of diarrheagenic E. coli and their intestinal receptors. J Ind Microbiol 15:214–226
de Haan LA, Willshaw GA, van der Zeijst BA, Gaastra W (1991) The nucleotide sequence of a regulatory gene present on a plasmid in an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain of serotype O167:H5. FEMS Microbiol Lett 67:341–346
Duthy TG, Staendner LH, Manning PA, Heuzenbroeder MW (2002) Identification and characterization of assembly proteins of CS5 pili from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 184:1065–1077
Favre D, Lüdi S, Stoffel M, Frey J, Horn MP, Dietrich G, Spreng S, Viret JF (2006) Expression of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli colonization factors in Vibrio cholerae. Vaccine 24:4354–4368
Frisk A, Lebens M, Johansson C, Ahmed H, Svensson L, Ahlman K, Lagergård T (2001) The role of different protein components from the Haemophilus ducreyi cytolethal distending toxin in the generation of cell toxicity. Microb Pathog 30:313–324
Froehlich BJ, Karakashian A, Sakellaris H, Scott JR (1995) Genes for CS2 pili of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and their interchangeability with those for CS1 pili. Infect Immun 63:48549–48556
Gaastra W, Svennerholm AM (1996) Colonization factors of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Trends Microbiol 4:444–452
Hall ER, Wierzba TF, Åhrén C, Rao MR, Bassily S, Francis W, Girgis FY, Safwat M, Lee YJ, Svennerholm A-M, Clemens JD, Savarino SJ (2001) Induction of systemic antifimbria and antitoxin antibody responses in Egyptian children and adults by an oral, killed enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli plus cholera toxin B subunit vaccine. Infect Immun 69:2853–2857
Isidean SD, Riddle MS, Savarino SJ, Porter CK (2011) A systematic review of ETEC epidemiology focusing on colonization factor and toxin expression. Vaccine 29:6167–6178
Jansson L, Tobias J, Lebens M, Svennerholm AM, Teneberg S (2006) Glycosphingolipid binding specificity of colonization factor antigen I from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 74:3488–3497
Jansson L, Tobias J, Jarefjäll C, Lebens M, Svennerholm AM, Teneberg S (2009) Sulfatide recognition by colonization factor antigen CS6 from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. PlosOne 4:e.4487
Jordi BJ, van der Zeijst BA, Gaastra W (1994) Regions of the CFA/I promoter involved in the activation by the transcriptional activator CfaD and repression by the histone-like protein H-NS. Biochimie 76:1052–1054
Levine MM, Nalin DR, Hoover DL, Bergquist EJ, Hornick BB, Young CR (1979) Immunity to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 23:729–736
Li YF, Poole S, Rasulova F, McVeigh AL, Savarino SJ, Xia D (2007) A receptor-binding site as revealed by the crystal structure of CfaE, the colonization factor antigen I fimbrial adhesin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 282:23970–23980
Li YF, Poole S, Nishio K, Jang K, Rasulova F, McVeigh A, Savarino SJ, Xia D, Bullitt E (2009) Structure of CFA/I fimbriae from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10793–10798
López-Vidal Y, Klemm P, Svennerholm AM (1988) Monoclonal antibodies against different epitopes on colonization factor antigen I of enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol 26:1967–1972
López-Vidal Y, Calva JJ, Trujillo A, Ponce de León A, Ramos A, Svennerholm AM, Ruiz-Palacios GM (1990) Enterotoxins and adhesins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: are they risk factors for acute diarrhea in the community? J Infect Dis 162:442–447
Lundgren A, Leach S, Jertborn M, Kaim J, Wiklund G, Adamsson J, Eklund L, Bourgeois L, Walker R, Tobias J, Holmgren J, Svennerholm AM (2011) Clinical trial of an inactivated whole cell ETEC prototype vaccine. The 6th international conference on vaccines for enteric diseases. Cannes, France
McConnell MM, Thomas LV, Willshaw GA, Smith HR, Rowe B (1988) Genetic control and properties of coli surface antigens of colonization factor antigen IV (PCF8775) of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 56:1974–1980
Owen RL, Pierce NF, Apple RT, Cray WC Jr (1986) M cell transport of Vibrio cholerae from the intestinal lumen into Peyer's patches: a mechanism for antigen sampling and for microbial transepithelial migration. J Infect Dis 153:1108–1118
Perez-Casal J, Swartley JS, Scott JR (1990) Gene encoding the major subunit of CS1 pili of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 58:3594–3600
Poole ST, McVeigh AL, Anantha RP, Lee LH, Akay YM, Pontzer EA, Scott DA, Bullitt E, Savarino SJ (2007) Donor strand complementation governs intersubunit interaction of fimbriae of the alternate chaperone pathway. Mol Microbiol 63:1372–1384
Qadri F, Svennerholm AM, Faruque ASG, Sack RB (2005) Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC): epidemiology, microbiology, and clinical features in developing countries. Clin Microbiol Rev 18:465–483
Qadri F, Ahmed T, Ahmed F, Begum YA, Sack DA, Svennerholm AM (2006) Reduced doses of oral killed enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli plus cholera toxin B subunit vaccine is safe and immunogenic in Bangladeshi infants 6–17 months of age: dosing studies in different age groups. Vaccine 24:1726–1733
Qadri F, Saha A, Ahmed T, Al Tarique A, Begum YA, Svennerholm AM (2007) Disease burden due to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in the first 2 years of life in an urban community in Bangladesh. Infect Immun 75:3961–3968
Ranallo RT, Fonseka CP, Cassels F, Srinivasan J, Venkatesan MM (2005) Construction and characterization of bivalent Shigella flexneri 2a vaccine strains SC608(pCFAI) and SC608(pCFAI/LTB) that express antigens from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 73:258–267
Rudin A, Olbe L, Svennerholm AM (1996) Monoclonal antibodies against fimbrial subunits of colonization factor antigen I (CFA/I) inhibit binding to human enterocytes and protect against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli expressing heterologous colonization factors. Microb Pathog 21:35–45
Sack DA, Shimko J, Torres O, Bourgeois AL, Francia DS, Gustafsson B, Kärnell A, Nyquist I, Svennerholm AM (2007) Randomised, double-blind, safety and efficacy of a killed oral vaccine for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea of travellers to Guatemala and Mexico. Vaccine 25:4392–4400
Sadeghi H, Bregenholt S, Wegmann D, Petersen JS, Holmgren J, Lebens M (2002) Genetic fusion of human insulin B-chain to the B-subunit of cholera toxin enhances in vitro antigen presentation and induction of bystander suppression in vivo. Immunology 106:237–245
Sakellaris H, Penumalli VR, Scott JR (1999) The level of expression of the minor pilin subunit, CooD, determines the number of CS1 pili assembled on the cell surface of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 181:1694–1697
Sánchez J, Holmgren J (2005) Virulence factors, pathogenesis and vaccine protection in cholera and ETEC diarrhea. Curr Opin Immunol 17:388–398
Savarino SJ, Hall ER, Bassily S, Wierzba TF, Youssef FG, Peruski LF Jr, Abu-Elyazeed R, Rao M, Francis WM, El Mohamady H, Safwat M, Naficy AB, Svennerholm AM, Jertborn M, Lee YJ, Clemens JD, Pride Study Group (2002) Introductory evaluation of an oral, killed whole cell enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli plus cholera toxin B subunit vaccine in Egyptian infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 21:322–330
Svennerholm AM (2011) From cholera to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine development. Indian J Med Res 133:188–196
Svennerholm A-M, Glenn G (2010) Vaccines against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. (ETEC). In: Levine MM et al (eds) New generation vaccines, 4th edn. Informa Healthcare, USA, pp 714–722
Svennerholm AM, Tobias J (2008) Vaccines against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Expert Rev Vaccines 7:795–804
Tobias J, Lebens M, Källgård S, Nicklasso M, Svennerholm AM (2008a) Role of different genes in the CS6 operon for surface expression of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli colonization factor CS6. Vaccine 26:5373–5380
Tobias J, Lebens M, Bölin I, Wiklund G, Svennerholm AM (2008b) Construction of non-toxic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae strains expressing high and immunogenic levels of enterotoxigenic E. coli colonization factor I fimbriae. Vaccine 26:743–752
Tobias J, Holmgren J, Hellman M, Nygren E, Lebens M, Svennerholm AM (2010a) Over-expression of major colonization factors of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, alone or together, on non-toxigenic E. coli bacteria. Vaccine 28:6977–6984
Tobias J, Holmgren J, Svennerholm AM, Lebens M (2010b) Construction and expression of immunogenic hybrid enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli CFA/I and CS2 colonization fimbriae for use in vaccines. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1355–1365
Tobias J, Svennerholm AM, Carlin NIA, Lebens M, Holmgren J (2011) Construction of a non-toxigenic Escherichia coli oral vaccine strain expressing large amounts of CS6 and inducing strong intestinal and serum anti-CS6 antibody responses in mice. Vaccine 29:8863–8869
Vesikari T (1999) Rotavirus vaccine studies in Europe. Acta Paediat Suppl 88:9–13
Viboud GI, Binsztein N, Svennerholm AM (1993) A new fimbrial putative colonization factor, PCFO20, in human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 61:5190–5197
Walker RI, Steel D, Aguado T (2007) Analysis of strategies to successfully vaccinate infants in developing countries against enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) disease. Vaccine 25:2545–2566
Wennerås C, Erling V (2004) Prevalence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-associated diarrhoea and carrier state in the developing world. J Health Popul Nutr 22:370–382
Wolf MK (1997) Occurrence, distribution, and associations of O and H serogroups, colonization factor antigens, and toxins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev 10:569–584
Wolf MK, de Haan LA, Cassels FJ, Willshaw GA, Warren R, Boedeker EC, Gasstra W (1997) The CS6 colonization factor of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli contains two heterologous major subunits. FEMS Microbiol Lett 148:35–42
Yakhchali B, Maning PA (1997) Epitope analysis of the CS3 fimbrial subunit of human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and the construction of novel CS3::ST and CS3::LT-B immunogens. Behring Inst Mitt 98:124–134
Ziethlow V, Favre D, Viret JF, Frey J, Stoffel MH (2008) Assessment by electron-microscopy of recombinant Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella vaccine strains expressing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-specific surface antigens. Clin Microbiol Infect 14:282–286
Acknowledgments
The work described in this review was supported by grants from the Marianne and Marcus Wallenberg Foundation, the Swedish Research Council (VR), the Sahlgrenska University Hospital (ALF), and the Swedish Agency for Research and Economic Cooperation (Sida-Sarec).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tobias, J., Svennerholm, AM. Strategies to overexpress enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) colonization factors for the construction of oral whole-cell inactivated ETEC vaccine candidates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 2291–2300 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3930-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-3930-6