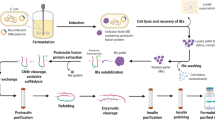
Abstract
Native proinsulin (PI) belongs to the class of the difficult-to-express proteins in Escherichia coli. Problems mainly arise due to its high proteolytic decay and troubles to reproduce the native disulphide pattern. In the present study, human PI was produced in E. coli as a fusion thioredoxin protein (Trx-PI). Such chimeric protein was obtained from the intracellular soluble fraction, and it was purified in one step by affinity chromatography on immobilized phenylarsine oxide. Trx-PI was also recovered from inclusion bodies and purified by anion exchange chromatography. The product identity and integrity were verified by mass analysis (22,173.5 Da) and mapping with Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease. Native PI folding was evaluated by biochemical and also by immunochemical analysis using specific sera from PI antibody-positive diabetic patients that recognise conformational discontinue epitopes. Dose–response curves showed identity between standard PI and Trx-PI. Moreover, surface plasmon resonance technique verified the correct conformation of the recombinant protein. The biochemical and immunochemical assays demonstrated the integrity of the chimera and the epitopes involved in the interaction with antibodies. In conclusion, it was possible to obtain with high-yield purified human PI as a fusion protein in E. coli and useful for analytical purposes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach P, Koczwara K, Knopff A, Naserke H, Ziegler A-G, Bonifacio E (2004) Mature high-affinity immune responses to (pro)insulin anticipate the autoimmune cascade that leads to type 1 diabetes. J Clin Invest 114(4):589–597
Anonymous (1985) Diabetes mellitus. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 727:1–113
Baneyx F (1999) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10(5):411–421
Berzofsky JA, Schechter AN (1981) The concepts of crossreactivity and specificity in immunology. Mol Immunol 18(8):751–763
Chan SJ, Weiss J, Konrad M, White T, Bahl C, Yu SD, Marks D, Steiner DF (1981) Biosynthesis and periplasmic segregation of human proinsulin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78(9):5401–5405
Chopra AK, Brasier AR, Das M, Xu XJ, Peterson JW (1994) Improved synthesis of Salmonella typhimurium enterotoxin using gene fusion expression systems. Gene 144(1):81–85
Economou A (1999) Following the leader: bacterial protein export through the Sec pathway. Trends Microbiol 7(8):315–320
Francetic O, Belin D, Badaut C, Pugsley AP (2000) Expression of the endogenous type II secretion pathway in Escherichia coli leads to chitinase secretion. EMBO J 19(24):6697–6703
Georgiou G, Valax P (1996) Expression of correctly folded proteins in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 7(2):190–197
Hoffman RD, Lane MD (1992) Iodophenylarsine oxide and arsenical affinity chromatography: new probes for dithiol proteins. Application to tubulins and to components of the insulin receptor–glucose transporter signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem 267(20):14005–14011
Kajava AV, Zolov SN, Kalinin AE, Nesmeyanova MA (2000) The net charge of the first 18 residues of the mature sequence affects protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 182(8):2163–2169
Kang Y, Yoon JW (1991) Development of a high-expression vector (Pyk 10–9) of human proinsulin gene. Biotechnol Lett 13:755–760
Kang Y, Yoon JW (1994) Effect of modification of connecting peptide of proinsulin on its export. J Biotechnol 36(1):45–54
Kemmler W, Peterson JD, Steiner DF (1971) Studies on the conversion of proinsulin to insulin. I. Conversion in vitro with trypsin and carboxypeptidase. B J Biol Chem 246(22):6786–6791
Khokhlova OV, Nesmeianova MA (2003) Interaction of SecB and SecA with the N-terminal region of mature alkaline phosphatase on its secretion in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol (Mosk) 37(4):712–718
Kjeldsen T (2000) Yeast secretory expression of insulin precursors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54(3):277–286
Koller DP, Rieb G, Sauber K, Uhlmann E, Wallmeier H (1989) Recombinant Streptomyces lividans secretes a fusion protein of tendamistat and proinsulin. Biotechnology (NY) 7:1055–1059
LaVallie ER, DiBlasio EA, Kovacic S, Grant KL, Schendel PF, McCoy JM (1993) A thioredoxin gene fusion expression system that circumvents inclusion body formation in the E. coli cytoplasm. Biotechnology 11(2):187–193
Mackin RB (1998) Proinsulin: recent observations and controversies. Cell Mol Life Sci 54(7):696–702
Malik A, Jenzsch M, Lübbert A, Rudolph R, Söhling B (2007) Periplasmic production of native human proinsulin as a fusion to E. coli ecotin. Protein Expr Purif 55(1):100–111
Mergulhão FJ, Taipa MA, Cabral JM, Monteiro GA (2004) Evaluation of bottlenecks in proinsulin secretion by Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 109(1–2):31–43
Novikov AA, Borukhov SI, Strongin AY (1990) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase signal sequence fused in frame with human proinsulin is properly processed by Bacillus subtilis cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 169(1):297–301
Olmos-Soto J, Contreras-Flores R (2003) Genetic system constructed to overproduce and secrete proinsulin in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62(4):369–373
Papouchado ML, Valdez SN, Ghiringhelli D, Poskus E, Ermacora MR (1997) Expression of properly folded human glutamate decarboxylase 65 as a fusion protein in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 246(2):350–359
Pines O, Inouye M (1999) Expression and secretion of proteins in E. coli. Mol Biotechnol 12(1):25–34
Pugsley AP, Francetic O, Driessen AJ, de Lorenzo V (2004) Getting out: protein traffic in prokaryotes. Mol Microbiol 52(1):3–11
Real Farmacopea Española (1997) Análisis Estadístico, Segunda edn. Ministerio de Sanidad y Consumo, Madrid
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour
Samuelsson E, Moks T, Nilsson B, Uhlen M (1994) Enhanced in vitro refolding of insulin-like growth factor I using a solubilizing fusion partner. Biochemistry 33(14):4207–4211
Shägger H, von Jagow G (1987) Tricine–sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem 166:368–379
Shen SH (1984) Multiple joined genes prevent product degradation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 81(15):4627–4631
Sung WL, Yao FL, Zahab DM, Narang SA (1986) Short synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide leader sequences enhance accumulation of human proinsulin synthesized in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83(3):561–565
Talmadge K, Brosius J, Gilbert W (1981) An ‘internal’ signal sequence directs secretion and processing or proinsulin in bacteria. Nature 294(5837):176–178
Talmadge K, Gilbert W (1982) Cellular location affects protein stability in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79(6):1830–1833
Tang JG, Hu MH (1993) Production of human proinsulin in Escherichia coli in a non-fusion form. Biotechnol Lett 15:661–666
Thim L, Hansen MT, Norris K, Hoegh I, Boel E, Forstrom J, Ammerer G, Fiil NP (1986) Secretion and processing of insulin precursors in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83(18):6766–6770
Tikhonov RV, Pechenov SE, Belacheu IA, Yakimov SA, Klyushnichenko VE, Boldireva EF, Korobko VG, Tunes H, Thiemann JE, Vilela L, Wulfson AN (2001) Recombinant human insulin. VIII. Isolation of fusion protein--S-sulfonate, biotechnological precursor of human insulin, from the biomass of transformed Escherichia coli cells. Protein Expr Purif 21(1):176–182
Valdez SN, Iacono RF, Villalba A, Cardoso_Landaburu A, Ermacora MR, Poskus E (2003) A radioligand-binding assay for detecting antibodies specific for proinsulin and insulin using 35S-proinsulin. J Immunol Methods 279(1–2):173–181
Wilkinson DL, Ma NT, Haught C, Harrison RG (1995) Purification by immobilized metal affinity chromatography of human atrial natriuretic peptide expressed in a novel thioredoxin fusion protein. Biotechnol Prog 11(3):265–269
Winter J, Neubauer P, Glockshuber R, Rudolph R (2000) Increased production of human proinsulin in the periplasmic space of Escherichia coli by fusion to DsbA. J Biotechnol 84(2):175–185
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Mazza and A.G. Krochik at the J. P. Garrahan National Pediatrics Hospital and the Hemotherapy Division at the José de San Martín Clinical Hospital (Buenos Aires, Argentina) for collecting and providing the sera of diabetic patients and control individuals. We are grateful to Graeme Bell, University of Chicago, USA, for the gift of pBR328–preproinsulin vector. We also thank Eli Lilly for the generous supply of standard proinsulin. This work was supported in part by grants from FONCYT Programme of the Agency for Science and Technology Promotion (ANPCyT), National Research Council (CONICET) and the University of Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trabucchi, A., Guerra, L.L., Faccinetti, N.I. et al. Expression and characterization of human proinsulin fused to thioredoxin in Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94, 1565–1576 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3721-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3721-5