Abstract
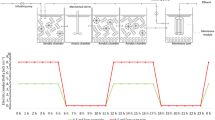
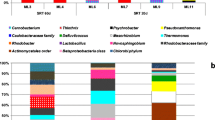
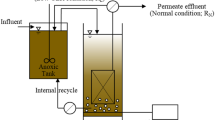
This study isolated strains in suspended liquor, the surface fouling layer, and biofilm inside hollow-fiber membranes of a membrane bioreactor (MBR); analyzed their distributions, sizes, surface charges, and growth behaviors; and determined the quantities of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) secreted by these strains under different organic loadings. Three strains, which may penetrate the microfiltration membranes, were close relatives of the Ralstonia mannitolilytica strain SDV (GenBank Accession No. GU451066), Arthrobacter sp. BJQ-2 (GenBank Accession No. GU451067), and Actinobacterium DS3 (GenBank Accession No. GU451068). Among these three strains, only Arthrobacter sp. developed an internal biofilm. The relatively short length of Arthrobacter sp. minimizes resistance to cells moving through the membrane matrix, thereby enhancing its ability to build a biofilm in the interior surface of membranes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adav SS, Lee DJ (2008) Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances from aerobic granule with compact interior structure. J Haz Mater 154:1120–1126
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2007) Effects of aeration intensity on formation of phenol-fed aerobic granules and extracellular polymeric substances. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:175–182
Adav SS, Lee DJ, Show KY, Tay JH (2008) Aerobic granular sludge: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 26:411–423
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Baker JS, Dudley LY (1998) Biofouling in membrane systems—a review. Desalination 118:81–90
Brindle K, Stephenson T (1996) The application of membrane biological reactors for the treatment of wastewaters. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:601–610
Charcosset C (2006) Membrane processes in biotechnology: an overview. Biotechnol Adv 24:482–492
Frolund B, Keiding K, Nielsen PH (1995) Enzymatic activity in the activated sludge flocs matrix. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:755–761
Gaudy AF (1962) Colorimetric determination of protein and carbohydrate. Ind Water Wastes 7:17–22
Juang YC, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2008) Fouling layer on hollow-fibre membrane in aerobic granule membrane bioreactor. J Chin Inst Chem Engrs 39:657–661
Juang YC, Su A, Fang LH, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2010a) Fouling with aerobic granule membrane bioreactor (AGMBR). Water Science and Technology, accepted
Juang YC, Adav SS, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2010b) Influence of internal biofilm growth on residual permeability loss in aerobic granular membrane bioreactor. Environ Sci Technol 44:1267–1273
Juang YC, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2010c) Visualizing fouling layer in membrane bioreactor. Separation Science and Technology doi:10.1080/01496391003666882
Judd S (2004) A review of fouling of membrane bioreactors in sewage treatment. Water Sci Technol 49:229–235
Judd S (2005) Fouling control in submerged membrane bioreactors. Water Sci Technol 51:27–34
Jun Z, Yang FL, Meng FG, Peng A, Di W (2007) Comparison of membrane fouling during short-term filtration of aerobic granular sludge and activated sludge. J Environ Sci China 19:1281–1286
Liao BQ, Bagley DM, Kraemer HE, Leppard GG, Liss SN (2004) A review of biofouling and its control in membrane separation bioreactors. Water Environ Res 76:425–436
Lü F, Zhang H, Chang CH, Lee DJ, He PJ, Shao LM, Su A (2008) Dissolved organic matter and estrogenic potential of landfill leachate. Chemosphere 72:1381–1386
Marrot B, Barrios-Martinez A, Moulin P, Roche N (2004) Industrial wastewater treatment in a membrane bioreactor: a review. Environ Progr 23:59–68
Ramesh A, Lee DJ, Wang ML, Hsu JP, Juang RS, Hwang KJ, Liu JC, Tseng ST (2006) Biofouling in membrane bioreactor. Sep Sci Technol 41:1345–1370
Tay JH, Yang P, Zhuang WQ, Tay STL, Pan ZH (2008) Reactor performance and membrane filtration in aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 304:24–32
Visvanathan C, Ben Aim R, Parameshwaran K (2000) Membrane separation bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 30:1–48
Wang JF, Wang X, Zhao ZG, Li JW (2008) Organics and nitrogen removal and sludge stability in aerobic granular sludge membrane bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:679–685
Acknowledgement
This project is partly supported by the State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment (SKLUWRE), Harbin Institute of Technology and by Project 50821002 (National Creative Research Groups) supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juang, YC., Adav, S.S. & Lee, DJ. Strains of internal biofilm in aerobic granular membrane bioreactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 1987–1993 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2527-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2527-1