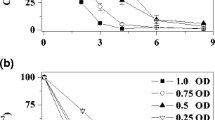
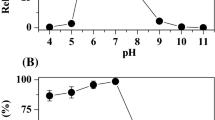
Abstract
Electron transfer pathways for azoreduction by S. decolorationis S12 were studied using a mutant S12-22 which had a transposon insertion in ccmA. The results imply that there are two different pathways for electron transport to azo bonds. The colony of S12-22 was whitish and incapable of producing mature c-type cytochromes whose α-peak was at 553 nm in the wild type S12. The mutant S12-22 could not use formate as the sole electron donor for azoreduction either in vivo or in vitro, but intact cells of S12-22 were able to reduce azo dyes of low polarity, such as methyl red, when NADH was served as the sole electron donor. Although the highly polar-sulfonated amaranth could not be reduced by intact cells of S12-22, it could be efficiently reduced by cell extracts of the mutant when NADH was provided as the sole electron donor. These results suggest that the mature c-type cytochromes are essential electron mediators for the extracellular azoreduction of intact cells, while the other pathway without the involvement of mature c-type cytochromes, NADH-dependent oxidoreductase-mediated electron transfer pathway can reduce lowly polar sulfonated azo dyes inside the whole cells or highly polar sulfonated azo dyes in the cell extracts without bacterial membrane barriers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexeyev MF, Shokolenko IN (1995) Mini-Tn10 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis and gene delivery into the chromosome of Gram-negative bacteria. Gene 160:59–62
Arnold RG, Dichristina TJ, Hoffmann MR (1986) Inhibitor studies of dissimilative Fe (III) reduction by Pseudomonas sp. strain 200 (“Pseudomonas ferrireductans”). Appl Environ Microbiol 52:281–289
Bouhenni R, Gehrke A, Saffarini D (2005) Identification of genes involved in cytochrome c biogenesis in Shewanella oneidensis, using a modified mariner transposon. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4935–4937
Brigé A, Motte B, Borloo J, Buysschaert G, Devreese B, Van Beeumen JJ (2008) Bacterial decolorization of textile dyes is an extracellular process requiring a multicomponent electron transfer pathway. Microb Biotechnol 1:40–52
Fredrich E, Van Heek P, Leif H, Ohnishi T, Forche E, Kunze B, Jansen R, Trowitzsch-Kienast W, Hofle G, Reichenbach H, Weiss H (1994) Two binding sites of inhibitors in NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I). Eur J Biochem 219:691–698
Ghosh DK, Mandal A, Chaudhuri J (1992) Purification and partial characterization of two azoreductases from Shigella dysenteriae type 1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 77:229–233
Ghosh DK, Ghosh S, Sadhukhan P, Mandal A, Chaudhuri J (1993) Purification of two azoreductases from Escherichia coli K12. Indian J Exp Biol 31:951–954
Goldmann BS, Gabbert KK, Kranz RG (1996) Use of heme reporters for studies of cytochrome biosynthesis and heme transport. J Bacteriol 178:6338–6347
Groh JL, Luo Q, Ballard JD, Krumholz LR (2005) A method adapting microarray technology for signature-tagged mutagenesis of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20 and Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in anaerobic sediment survival experiments. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7064–7074
Gutman M, Singer TP, Beinert H, Casida JE (1970) Reaction sites of rotenone, piericidin A, and amytal in relation to the nonheme iron components of NADH dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 65:763–770
Heidelberg J, Paulsen I, Nealson K, Gaidos E, Nelson W, Read T et al (2002) Genome sequence of the dissimilatory metal ion-reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis. Nat Biotechnol 20:1118–1123
Hong Y, Guo J, Xu Z, Xu M, Sun G (2007a) Humic substances act as electron acceptor and redox mediator for microbial dissimilatory azoreduction by Shewanella decolorationis S12. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:428–437
Hong Y, Xu M, Guo J, Xu Z, Chen X, Sun G (2007b) Respiration and growth of Shewanella decolorationis S12 with azo compound as sole electron acceptor. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:64–72
Horitsu H, Takada M, Idaka E, Tomoyeda M, Ogawa T (1977) Degradation of p-aminoazobenzene by Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Appl Microbiol 4:217–224
Ito K, Nakanishi M, Lee WC, Zhi Y, Sasaki H, Zenno S, Saigo K, Kitade Y, Tanokura M (2008) Expansion of substrate specificity and catalytic mechanism of azoreductase by X-ray crystallography and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 283:13889–13896
Keck A, Klein J, Kudlich M, Stolz A, Knackmuss HJ, Mattes R (1997) Reduction of azo dyes by redox mediators originating in the naphthalenesulfonic acid degradation of Sphingom onas sp. strain BN6. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3684–3690
Kudlich M, Keck A, Klein J, Stolz A (1997) Localization of the enzyme system involved in anaerobic reduction of azo dyes by Sphingomonas sp. strain BN6 and effect of artificial redox mediators on the rate of azo dye reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3691–3694
Maier J, Kandelbauer A, Erlacher A, Cavaco-Paulo A, Gubitz G (2004) A new alkali-thermostable azoreductase from Bacillus sp. strain SF. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:837–844
Meyer T, Tsapin A, Vandenberghe I, de Smet L, Frishman D, Nealson K, Cusanovich M, van Beeumen J (2004) Identification of 42 possible cytochrome c genes in the Shewanella oneidensis genome and characterization of six soluble cytochromes. OMICS 8:57–77
Moser D, Nealson K (1996) Growth of the facultative anaerobe Shewanella putrefaciens by elemental sulfur reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2100–2105
Moutaouakkil A, Zeroual Y, Zohra-Dzayri F, Talbi M, Lee K, Blaghen M (2003) Purification and partial characterization of azoreductase from Enterobacter agglomerans. Arch Biochem Biophys 413:139–146
Myers CR, Carstens BP, Antholine WE, Myers JM (2000) Chromium (VI) reductase activity is associated with the cytoplasmic membrane of anaerobically grown Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Appl Microbiol 88:98–106
Nakanishi M, Yatome C, Ishida N, Kitade Y (2001) Putative ACP phosphodiesterase gene (acpD) encodes an azoreductase. J Biol Chem 276:46394–46399
Nealson K, Saffarini D (1994) Iron and manganese in anaerobic respiration: environmental significance, physiology, and regulation. Annu Rev Microbiol 48:311–343
Rafii F, Cerniglia CE (1993) Comparison of the azoreductase and nitroreductase from Clostridium perfringens. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1731–1734
Ramalho PA, Paiva S, Cavaco-Paulo A, Casal M, Cardoso MH, Ramalho MT (2005) Azo reductase activity of intact Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells is dependent on the Fre1p component of plasma membrane ferric reductase. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3882–3888
Rau J, Stolz A (2003) Oxygen-insensitive nitroreductases NfsA and NfsB of Escherichia coli function under anaerobic conditions as lawsone-dependent azo reductases. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3448–3455
Russ R, Rau J, Stolz A (2000) The function of cytoplasmatic flavin reductases in the bacterial reduction of azo dyes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1429–1434
Saltikov CW, Cifuentes A, Venkateswaran K, Newman DK (2003) The ars detoxification system is advantageous but not required for As (V) respiration by the genetically tractable Shewanella species strain ANA-3. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2800–2809
Stolz A (2001) Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:69–80
Suzuki Y, Yoda T, Ruhul A, Sugiura W (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of the gene coding for azoreductase from Bacillus sp. OY1–2 isolated from soil. J Biol Chem 276:9059–9065
Thöny-Meyer L, Ritz D, Hennecke H (1994) Cytochrome c biogenesis in bacteria: a possible pathway begins to emerge. Mol Microbiol 12:1–9
Thöny-Meyer L, Fischer F, Kunzler P, Ritz D, Hennecke H (1995) Escherichia coli genes required for cytochrome c maturation. J Bacteriol 177:4321–4326
Throne-Holst M, Thöny-Meyer L, Hederstedt L (1997) Escherichia coli ccm in-frame deletion mutants can produce periplasmic cytochrome b but not cytochrome c. FEBS Lett 410:351–355
Van der Zee FP, Bouwman RHM, Strik DPBTB, Lettinga G, Field JA (2001) Application of redox mediators to accelerate the transformation of reactive azo dyes in anaerobic bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 75:691–701
Wade R, DiChristina T (2000) Isolation of U (VI) reduction-deficient mutants of Shewanella putrefaciens. FEMS Microbiol Lett 184:143–146
Zimmermann T, Kulla HG, Leisinger T (1982) Properties of purified orange II azoreductase, the enzyme initiating azo dye degradation by Pseudomonas KF46. Eur J Biochem 129:197–203
Zimmermann T, Gasser F, Kulla HG, Leisinger T (1984) Comparison of two bacterial azoreductases acquired during adaptation to growth on azo dyes. Arch Microbiol 138:37–43
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (30500009 and 30670020), Chinese National Programs for High Technology Research and Development (2006AA06Z322), and Natural Science Foundation Guangdong province (9351007002000001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Xu, M., Wei, J. et al. Two different electron transfer pathways may involve in azoreduction in Shewanella decolorationis S12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 743–751 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2376-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2376-y