Abstract
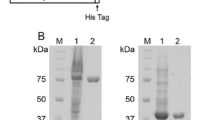
The inherent difficulty of expressing clostridial AT-rich genes in a heterologous host has limited their biotechnological application. We previously reported a plasmid for high-level expression of clostridial genes in Clostridium perfringens (Takamizawa et al., Protein Expr Purif 36:70–75, 2004). In this study, we examined the extracellular proteases of C. perfringens strain 13. Zymographic analysis and caseinase assaying of a culture supernatant showed that it contained a protease activated by dithiothreitol and Ca2+, suggesting that clostripain-like protease (Clp) is the most likely candidate for the major extracellular protease. Disruption of the clp gene by homologous recombination markedly decreased the level of caseinase activity in the culture supernatant. Analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) revealed that the Clp− mutant but not the wild type strain increased the levels of many polypeptides in the culture supernatant after the late exponential growth phase. Such polypeptides included both cytoplasmic and secretory proteins, suggesting proteins secreted or released into the medium were degraded by Clp. To assess the effects of Clp on the productivity and stability of recombinant proteins, 74-kDa NanI sialidase was expressed in the two strains. The mutant strain produced a higher level of NanI activity than the wild type strain. Furthermore, under the conditions where Clp was activated, NanI was degraded easily in the latter culture but not in the former one. These results indicate that the Clp− mutant could serve as a useful strain for efficiently expressing and preparing protease-free clostridial proteins.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babe LM, Schmidt B (1998) Purification and biochemical analysis of WprA, a 52-kDa serine protease secreted by B. subtilis as an active complex with its 23-kDa propeptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1386:211–219
Batard Y, Hehn A, Nedelkina S, Schalk M, Pallett K, Schaller H, Werck-Reichhart D (2000) Increasing expression of P450 and P450-reductase proteins from monocots in heterologous systems. Arch Biochem Biophys 379:161–169
Calderone TL, Stevens RD, Oas TG (1996) High-level misincorporation of lysine for arginine at AGA codons in a fusion protein expressed in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 262:407–412
Capon F, Allen MH, Ameen M, Burden AD, Tillman D, Barker JN, Trembath RC (2004) A synonymous SNP of the corneodesmosin gene leads to increased mRNA stability and demonstrates association with psoriasis across diverse ethnic groups. Hum Mol Genet 13:2361–2368
Coffield JA (2003) Botulinum neurotoxin: the neuromuscular junction revisited. Crit Rev Neurobiol 15:175–196
Duan J, Wainwright MS, Comeron JM, Saitou N, Sanders AR, Gelernter J, Gejman PV (2003) Synonymous mutations in the human dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) affect mRNA stability and synthesis of the receptor. Hum Mol Genet 12:205–216
Gao W, Tyagi S, Kramer FR, Goldman E (1997) Messenger RNA release from ribosomes during 5′-translational blockage by consecutive low-usage arginine but not leucine codons in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 25:707–716
Georgiou G, Segatori L (2005) Preparative expression of secreted proteins in bacteria: status report and future prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:538–545
Jin F, Matsushita O, Katayama S, Jin S, Matsushita C, Minami J, Okabe A (1996) Purification, characterization, and primary structure of Clostridium perfringens lambda-toxin, a thermolysin-like metalloprotease. Infect Immun 64:230–237
Kaji M, Matsushita O, Tamai E, Miyata S, Taniguchi Y, Shimamoto S, Katayama S, Morita S, Okabe A (2003) A novel type of DNA curvature present in a Clostridium perfringens ferredoxin gene: characterization and role in gene expression. Microbiology 149:3083–3091
Katz L, Burge CB (2003) Widespread selection for local RNA secondary structure in coding regions of bacterial genes. Genome Res 13:2042–2051
Kleber-Janke T, Becker WM (2000) Use of modified BL21(DE3) Escherichia coli cells for high-level expression of recombinant peanut allergens affected by poor codon usage. Protein Expr Purif 19:419–424
Kobayashi G, Eto K, Tashiro Y, Okubo K, Sonomoto K, Ishizaki A (2005) Utilization of excess sludge by acetone–butanol–ethanol fermentation employing Clostridium saccharoperbutylacetonicum N1-4 (ATCC 13564). J Biosci Bioeng 99:517–519
Komar AA, Lesnik T, Reiss C (1999) Synonymous codon substitutions affect ribosome traffic and protein folding during in vitro translation. FEBS Lett 462:387–391
Kosugi A, Arai T, Doi RH (2006) Degradation of cellulosome-produced cello-oligosaccharides by an extracellular non-cellulosomal beta-glucan glucohydrolase, BglA, from Clostridium cellulovorans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:20–23
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (Lond.) 227:680–685
Li W, Zhou X, Lu P (2004) Bottlenecks in the expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Res Microbiol 155:605–610
Matsushita O, Okabe A (2001) Clostridial hydrolytic enzymes degrading extracellular components. Toxicon (Oxf.) 39:1769–1780
Matsushita O, Yoshihara K, Katayama S, Minami J, Okabe A (1994) Purification and characterization of Clostridium perfringens 120-kilodalton collagenase and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene. J Bacteriol 176:149–156
Morimoto K, Yoshimoto M, Karita S, Kimura T, Ohmiya K, Sakka K (2007) Characterization of the third chitinase Chi18C of Clostridium paraputrificum M-21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1106–1113
Myers GS, Rasko DA, Cheung JK, Ravel J, Seshadri R, DeBoy RT, Ren Q, Varga J, Awad MM, Brinkac LM, Daugherty SC, Haft DH, Dodson RJ, Madupu R, Nelson WC, Rosovitz MJ, Sullivan SA, Khouri H, Dimitrov GI, Watkins KL, Mulligan S, Benton J, Radune D, Fisher DJ, Atkins HS, Hiscox T, Jost BH, Billington SJ, Songer JG, McClane BA, Titball RW, Rood JI, Melville SB, Paulsen IT (2006) Skewed genomic variability in strains of the toxigenic bacterial pathogen, Clostridium perfringens. Genome Res 16:1031–1040
Ninomiya M, Matsushita O, Minami J, Sakamoto H, Nakano M, Okabe A (1994) Role of alpha-toxin in Clostridium perfringens infection determined by using recombinants of C. perfringens and Bacillus subtilis. Infect Immun 62:5032–5039
Park CH, Lee SJ, Lee SG, Lee WS, Byun SM (2004) Hetero- and autoprocessing of the extracellular metalloprotease (Mpr) in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 186:6457–6464
Philippe VA, Mendez MB, Huang IH, Orsaria LM, Sarker MR, Grau RR (2006) Inorganic phosphate induces spore morphogenesis and enterotoxin production in the intestinal pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Infect Immun 74:3651–3656
Press WH, Robins H (2006) Isochores exhibit evidence of genes interacting with the large-scale genomic environment. Genetics 174:1029–1040
Qureshi N, Li XL, Hughes S, Saha BC, Cotta MA (2006) Butanol production from corn fiber xylan using Clostridium acetobutylicum. Biotechnol Prog 22:673–680
Shabalina SA, Ogurtsov AY, Spiridonov NA (2006) A periodic pattern of mRNA secondary structure created by the genetic code. Nucleic Acids Res 34:2428–2437
Sharp PM, Bailes E, Grocock RJ, Peden JF, Sockett RE (2005) Variation in the strength of selected codon usage bias among bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 33:1141–1153
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M (1996) Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem 68:850–858
Shimizu T, Ohtani K, Hirakawa H, Ohshima K, Yamashita A, Shiba T, Ogasawara N, Hattori M, Kuhara S, Hayashi H (2002a) Complete genome sequence of Clostridium perfringens, an anaerobic flesh-eater. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:996–1001
Shimizu T, Shima K, Yoshino K, Yonezawa K, Shimizu T, Hayashi H (2002b) Proteome and transcriptome analysis of the virulence genes regulated by the VirR/VirS system in Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol 184:2587–2594
Schubert K, Bichlmaier AM, Mager E, Wolff K, Ruhland G, Fiedler F (2000) P45, an extracellular 45 kDa protein of Listeria monocytogenes with similarity to protein p60 and exhibiting peptidoglycan lytic activity. Arch Microbiol 173:21–28
Shukla HD, Sharma SK (2005) Clostridium botulinum: a bug with beauty and weapon. Crit Rev Microbiol 31:11–18
Spanjaard RA, Chen K, Walker JR, van Duin J (1990) Frameshift suppression at tandem AGA and AGG codons by cloned tRNA genes: assigning a codon to argU tRNA and T4 tRNA(Arg). Nucleic Acids Res 18:5031–5036
Takamizawa A, Miyata S, Matsushita O, Kaji, M, Taniguchi Y, Tamai E, Shimamoto S, Okabe A (2004) High-level expression of clostridial sialidase using a ferredoxin gene promoter-based plasmid. Protein Expr Purif 36:70–75
Tokumitsu H, Hatano N, Inuzuka H, Sueyoshi Y, Yokokura S, Ichimura T, Nozaki N, Kobayashi R (2005) Phosphorylation of Numb family proteins. Possible involvement of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem 280:35108–35118
Ullmann D, Bordusa F (2004) Clostripain. In: Barrett AJ, Rawlings ND, Woessner JF (eds) Handbook of proteolytic enzymes, 2nd edn. Elsevier, London, pp 1317–1319
Vitikainen M, Hyyryläinen HL, Kivimäki A, Kontinen VP, Sarvas M (2005) Secretion of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis can be improved by engineering cell components affecting post-translocational protein folding and degradation. J Appl Microbiol 99:363–375
Wu J, Haussler D (2006) Coding exon detection using comparative sequences. J Comput Biol 13:1148–1164
Wu X, Jornvall H, Berndt KD, Oppermann U (2004) Codon optimization reveals critical factors for high level expression of two rare codon genes in Escherichia coli: RNA stability and secondary structure but not tRNA abundance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313:89–96
Yin J, Li G, Ren X, Herrler G (2007) Select what you need: a comparative evaluation of the advantages and limitations of frequently used expression systems for foreign genes. J Biotechnol 127:335–347
Zhang H, Bruns MA, Logan BE (2006) Biological hydrogen production by Clostridium acetobutylicum in an unsaturated flow reactor. Water Res 40:728–734
Zverlov VV, Berezina O, Velikodvorskaya GA, Schwarz WH (2006) Bacterial acetone and butanol production by industrial fermentation in the Soviet Union: use of hydrolyzed agricultural waste for biorefinery. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:587–597
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant-in-aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (grant for Scientific Research C 18590428). We wish to thank Prof. Osamu Matsushita (Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Kitasato University) for the invaluable advice and helpful discussion, and Mr. N. J. Halewood for the assistance in preparing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, H., Tamai, E., Miyata, S. et al. Construction and characterization of a clostripain-like protease-deficient mutant of Clostridium perfringens as a strain for clostridial gene expression. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77, 1063–1071 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1245-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1245-9