Abstract
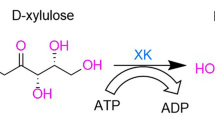
The rare sugar xylitol is a five-carbon polyol (pentitol) that has beneficial health effects. Xylitol has global markets and, therefore, it represents an alternative to current dominant sweeteners. The research on microbial reduction of d-xylose to xylitol has been focused on metabolically engineered Saccharomycess cerevisiae and Candida strains. The Candida strains have an advantage over the metabolically engineered S. cerevisiae in terms of d-xylose uptake and maintenance of the intracellular redox balance. Due to the current industrial scale production of xylitol, it has become an inexpensive starting material for the production of other rare sugar. The first part of this mini-review concentrates on the biochemistry of xylitol biosynthesis and the problems related to intracellular redox balance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruinenberg PM (1986) The NADP(H) redox couple in yeast metabolism. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 52:411–429
Bruinenberg PM, van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1983) An enzymic analysis of NADPH production and consumption in Candida utilis. J Gen Microbiol 129:965–971
van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1986) Redox balances in the metabolism of sugars by yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:199–224
Fiaux J, Petek Çakar Z, Sonderegger M, Wüthrich K, Szyperski T, Sauer U (2003) Metabolic-flux profiling of the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis. Eukaryot Cell 2:170–180
Gancedo JM, Lagunas R (1973) Contribution of the pentose–phosphate pathway to glucose metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a critical analysis on the use labelled glucose. Plant Sci Lett 1:193–200
Gombert AK, dos Santos MM, Christensen B, Nielsen J (2001) Network identification and flux quantification in the central metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under different conditions of glucose repression. J Bacteriol 183:1441–1451
Granström T, Leisola M (2002) Controlled transient changes reveal differences in metabolite production in two Candida yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:511–517
Granström T, Ojamo H, Leisola M (2001) Chemostat study of xylitol production by Candida guilliermondii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:36–42
Hallborn J, Walfridsson M, Airaksinen U, Ojamo H, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Penttila M, Keränen S (1991) Xylitol production by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnology (N Y) 9:1090–1095
Hallborn J, Gorwa M-F, Meinander N, Penttilä M, Keränen S, Hahn-Hägerdahl B (1994) The influence of cosubstrate and aeration on xylitol formation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing XYL1 gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:326–333
Härkönen M, Nuojua P (1979) Eri tekijöiden vaikutus ksyloosin katalyyyttiseen hydraukseen ksylitoliksi. Kemia-Kemi 6:445–447
Johansson B, Hahn-Hagerdal B (2002) The non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway controls the fermentation rate of xylulose but not of xylose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae TMB3001. FEMS Yeast Res 2:277–282
Kuyper M, Harhangi HR, Stave AK, Winkler AA, Jetten MSM, de Laat WTAM, den Ridder JJJ, Op den Camp HJM, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2003) High-level functional expression of a fungal xylose isomerase: the key to efficient ethanolic fermentation of xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 4:69–78
Kuyper M, Toirkens MJ, Diderich JA, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005) Evolutionary engineering of mixed-sugar utilization by a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. FEMS Yeast Res 5:925–934
Ko BS, Kim J, Kim JH (2006) Production of xylitol from d-xylose by a xylitol dehydrogenase gene-disrupted mutant of Candida tropicalis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4207–4213
Kötter P, Ciriacy M (1993) Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Kötter P, Amore R, Hollenberg CP, Ciriacy M (1990) Isolation and characterization of the Pichia stipitis xylitol dehydrogenase gene, XYL2, and construction of a xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformant. Curr Genet 18:493–500
Lang K (1964) Die ernährungsphysiologischen eigenschaften von xylit. Int Z Vitamforsch 34:117–122
Lee JK, Koo BS, Kim SY (2003) Cloning and characterization of the xyl1 gene, encoding an NADH-preferring xylose reductase from Candida parapsilosis, and its functional expression in Candida tropicalis. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6179–6188
Lohman RL (1957) The polyols. In: Pigman W (ed) The carbohydrates: chemistry, biochemistry and physiology. Academic, New York, pp 245–246
Lunzer R, Mamnun Y, Haltrich D, Kulbe KD, Nidetzky B (1998) Structural and functional properties of a yeast xylitol dehydrogenase, a Zn2+-containing metalloenzyme similar to medium-chain sorbitol dehydrogenases. Biochem J 336:91–99
Melaja A, Hämäläinen L, Heikkilä HO (1981) Menetelmä ksylitolin suhteen rikastuneen polyolin vesiliuoksen valmistamiseksi. FI 589388 (Finnish patent)
Mellinghoff CH (1961) Uber die verwendbarkeit des xylit als ersatzzukker bei diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr 39:447
Minard KI, Jennings GT, Loftus TM, Xuan D, McAlister-Henn L (1998) Sources of NADPH and expression of mammalian NADP+-specific isocitrate dehydrogenases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 273:31486–31493
Mäkinen KK (1992) Dietary prevention of dental caries by xylitol-clinical effectiveness and safety. J Appl Nutr 44:16–28
Mäkinen KK (2000) The rocky road of xylitol to its clinical application. J Dent Res 79:1352–1355
Nidetzky B, Helmer H, Klimacek M, Lunzer R, Mayer G (2003) Characterization of recombinant xylitol dehydrogenase from Galactocandida mastotermitis expressed in Escherichia coli. Chem Biol Interact 143–144:533–542
Onishi H, Suzuki T (1966) The production of xylitol, l-arabinitol and ribitol by yeasts. Agric Biol Chem 30:1139–1144
Onishi H, Suzuki T (1969) Microbial production of xylitol from glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 18:1031–1035
Oura E (1997) Reaction products of yeast fermentation. Process Biochem 12:19–21
Ojamo H (1994) Yeast xylose metabolism and xylitol production. PhD thesis, Helsinki University of Technology, Finland
Rizzi M, Harwart K, Bui Thanh NA, Dellweg H (1989) A kinetic study of the NAD+-xylitol-dehydrogenase from the yeast Pichia stipitis. J Ferment Bioeng 67:25–30
dos Santos MM, Raghevendran V, Kötter P, Olsson L, Nielsen J (2004) Manipulation of malic enzyme in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for increasing NADPH production capacity aerobically in different cellular compartments. Metab Eng 6:352–363
Sonderegger M, Sauer U (2003) Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for anaerobic growth on xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1990–1998
Sonderegger M, Jeppsson M, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Sauer U (2004) Molecular basis for anaerobic growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on xylose, investigated by global gene expression and metabolic flux analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2307–2317
Traff-Bjerre KL, Jeppsson M, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2004) Endogenous NADPH-dependent aldose reductase activity influences product formation during xylose consumption in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 21:141–150
Uhari M, Kontiokari T, Koskela M, Niemelä M (1996) Xylitol chewing gum in prevention of acute otitis media: double blind randomised trial. Br Med J 313:1180–1184
Verho R, Londesborough J, Penttila M, Richard P (2003) Engineering redox cofactor regeneration for improved pentose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5892–5897
Wahlbom CF, van Zyl WH, Jonsson LJ, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Otero RR (2003) Generation of the improved recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae TMB 3400 by random mutagenesis and physiological comparison with Pichia stipitis CBS 6054. FEMS Yeast Res 3:319–326
Yahashi Y, Horitsu H, Kawai K, Suzuki T, Takamizawa K (1996) Production of xylitol from d-xylose by Candida tropicalis: the effect of d-glucose feeding. J Ferment Bioeng 81:148–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granström, T.B., Izumori, K. & Leisola, M. A rare sugar xylitol. Part I: the biochemistry and biosynthesis of xylitol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 277–281 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0761-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0761-3