Abstract
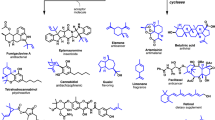
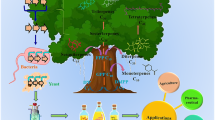
Isoprenoid secondary metabolites are a rich source of commercial products that have not been fully explored. At present, there are isoprenoid products used in cancer therapy, the treatment of infectious diseases, and crop protection. All isoprenoids share universal prenyl diphosphate precursors synthesized via two distinct pathways. From these universal precursors, the biosynthetic pathways to specific isoprenoids diverge resulting in a staggering array of products. Taking advantage of this diversity has been the focus of much effort in metabolic engineering heterologous hosts. In addition, the engineering of the mevalonate pathway has increased levels of the universal precursors available for heterologous production. Finally, we will describe the efforts to produce to commercial terpenoids, paclitaxel and artemisinin.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni A, Giri AP et al (2003) Terpenoid metabolism in wild-type and transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 15:2866–2884
Aubourg S, Lecharny A et al (2002) Genomic analysis of the terpenoid synthase (AtTPS) gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Genet Genomics 267:730–745
Back K, Chappell J (1995) Cloning and bacterial expression of a sesquiterpene cyclase from Hyoscyamus muticus and its molecular comparison to related terpene cyclases. J Biol Chem 270:7375–7381
Back K, Chappell J (1996) Identifying functional domains within terpene cyclases using a domain-swapping strategy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:6841–6845
Back K, Nah J et al (2000) Cloning of a sesquiterpene cyclase and its functional expression by domain swapping strategy. Mol Cell 10:220–225
Barkovich R, Liao JC (2001) Metabolic engineering of isoprenoids. Metab Eng 3:27–39
Bertea CM, Freije JR et al (2005) Identification of intermediates and enzymes involved in the early steps of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Planta Med 71:40–47
Besumbes O, Sauret-Gueto S et al (2004) Metabolic engineering of isoprenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis for the production of taxadiene, the first committed precursor of Taxol. Biotechnol Bioeng 88:168–175
Caruthers JM, Kang I et al (2000) Crystal structure determination of aristolochene synthase from the blue cheese mold, Penicillium roqueforti. J Biol Chem 275:25533–25539
Chen XY, Chen Y et al (1995) Cloning, expression, and characterization of (+)-delta-cadinene synthase: a catalyst for cotton phytoalexin biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 324:255–266
Colby SM, Crock J et al (1998) Germacrene C synthase from Lycopersicon esculentum cv. VFNT Cherry tomato: cDNA isolation, characterization, and bacterial expression of the multiple product sesquiterpene cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2216–2221
Davis EM, Croteau R (2000) Cyclization enzymes in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and diterpenes. Top Curr Chem 209:53–95
Dejong JM, Liu Y et al (2006) Genetic engineering of taxol biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:212–224
Dictionary of natural products (2004) Version 8.1 (HRD), 1st edn. Chapman & Hall, London, UK
Facchini PJ, Chappell J (1992) Gene family for an elicitor-induced sesquiterpene cyclase in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11088–11092
Faldt J, Arimura G et al (2003) Functional identification of AtTPS03 as (E)-beta-ocimene synthase: a monoterpene synthase catalyzing jasmonate-and wound-induced volatile formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 216:745–751
Fleet CM, Yamaguchi S et al (2003) Overexpression of AtCPS and AtKS in Arabidopsis confers increased ent-kaurene production but no increase in bioactive gibberellins. Plant Physiol 132:830–839
Friesen JA, Rodwell VW (2004) The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) reductases. Genome Biol 5:248
Grochowski LL, Xu H et al (2006) Methanocaldococcus jannaschii uses a modified mevalonate pathway for biosynthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate. J Bacteriol 188:3192–3198
Hahn FM, Hurlburt AP et al (1999) Escherichia coli open reading frame 696 is idi, a nonessential gene encoding isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase. J Bacteriol 181:4499–4504
Hamano Y, Kuzuyama T et al (2002) Functional analysis of eubacterial diterpene cyclases responsible for biosynthesis of a diterpene antibiotic, terpentecin. J Biol Chem 277:37098–37104
Hecht S, Eisenreich W et al (2001) Studies on the nonmevalonate pathway to terpenes: the role of the GcpE (IspG) protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14837–14842
Hefner J, Rubenstein SM et al (1996) Cytochrome P450-catalyzed hydroxylation of taxa-4(5),11(12)-diene to taxa-4(20),11(12)-dien-5alpha-ol: the first oxygenation step in taxol biosynthesis. Chem Biol 3:479–489
Hefner J, Ketchum RE et al (1998) Cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase from Taxus canadensis and assessment of the role of this prenyltransferase in cells induced for taxol production. Arch Biochem Biophys 360:62–74
Hezari M, Lewis NG et al (1995) Purification and characterization of taxa-4(5),11(12)-diene synthase from pacific yew (Taxus brevifolia) that catalyzes the first committed step of taxol biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 322:437–444
Hilker M, Kobs C et al (2002) Insect egg deposition induces Pinus sylvestris to attract egg parasitoids. J Exp Biol 205:455–461
Hohn TM, Ohlrogge JB (1991) Expression of a fungal sesquiterpene cyclase gene in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol 97:460–462
Horiguchi T, Rithner CD et al (2002) Studies on taxol biosynthesis. Preparation of taxa-4(20),11(12)-dien-5 alpha-acetoxy-10 beta-ol by deoxygenation of a taxadiene tetraacetate obtained from Japanese yew. J Org Chem 67:4901–4903
Huang Q, Roessner CA et al (2001) Engineering Escherichia coli for the synthesis of taxadiene, a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of taxol. Bioorg Med Chem 9:2237–2242
Jennewein S, Rithner CD et al (2003) Taxoid metabolism: taxoid 14beta-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 413:262–270
Jennewein S, Long RM et al (2004) Cytochrome p450 taxadiene 5alpha-hydroxylase, a mechanistically unusual monooxygenase catalyzing the first oxygenation step of taxol biosynthesis. Chem Biol 11:379–387
Kappers IF, Aharoni A et al (2005) Genetic engineering of terpenoid metabolism attracts bodyguards to Arabidopsis. Science 309:2070–2072
Kuzma J, Nemecek-Marshall M et al (1995) Bacteria produce the volatile hydrocarbon isoprene. Curr Microbiol 30:97–103
Lange BM, Croteau R (1999a) Genetic engineering of essential oil production in mint. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:139–144
Lange BM, Croteau R (1999b) Isoprenoid biosynthesis via a mevalonate-independent pathway in plants: cloning and heterologous expression of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase from peppermint. Arch Biochem Biophys 365:170–174
Lange BM, Wildung MR et al (2000) Probing essential oil biosynthesis and secretion by functional evaluation of expressed sequence tags from mint glandular trichomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2934–2939
Lesburg CA, Zhai G et al (1997) Crystal structure of pentalenene synthase: mechanistic insights on terpenoid cyclization reactions in biology. Science 277:1820–1824
Lesburg CA, Caruthers JM et al (1998) Managing and manipulating carbocations in biology: terpenoid cyclase structure and mechanism. Curr Opin Struct Biol 8:695–703
Little DB, Croteau RB (2002) Alteration of product formation by directed mutagenesis and truncation of the multiple-product sesquiterpene synthases delta-selinene synthase and gamma-humulene synthase. Arch Biochem Biophys 402:120–235
Lucker J, Schwab W et al (2004) Metabolic engineering of monoterpene biosynthesis: two-step production of (+)-trans-isopiperitenol by tobacco. Plant J 39:135–145
Luttgen H, Rohdich F et al (2000) Biosynthesis of terpenoids: YchB protein of Escherichia coli phosphorylates the 2-hydroxy group of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2C-methyl-D-erythritol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1062–1067
Mahmoud SS, Croteau RB (2001) Metabolic engineering of essential oil yield and composition in mint by altering expression of deoxyxylulose phosphate reductoisomerase and menthofuran synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:8915–8920
Mahmoud SS, Croteau RB (2003) Menthofuran regulates essential oil biosynthesis in peppermint by controlling a downstream monoterpene reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14481–14486
Martin VJ, Yoshikuni Y et al (2001) The in vivo synthesis of plant sesquiterpenes by Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 75:497–503
Martin VJ, Pitera DJ et al (2003) Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids. Nat Biotechnol 21:796–802
Mercke P, Crock J et al (1999) Cloning, expression, and characterization of epi-cedrol synthase, a sesquiterpene cyclase from Artemisia annua L. Arch Biochem Biophys 369:213–222
Mercke P, Bengtsson M et al (2000) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of amorpha-4,11-diene synthase, a key enzyme of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Arch Biochem Biophys 381:173–180
Nakano C, Okamura T et al (2005) Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv3377c encodes the diterpene cyclase for producing the halimane skeleton. Chem Commun (Camb) 8:1016–1018
Ohnuma SI, Nakazawa T et al (1996a) Conversion from farnesyl diphosphate synthase to geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase by random chemical mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 271:10087–10095
Ohnuma SI, Narita K et al (1996b) A role of the amino acid residue located on the fifth position before the first aspartate-rich motif of farnesyl diphosphate synthase on determination of the final product. J Biol Chem 271:30748–30754
Rasmann S, Kollner TG et al (2005) Recruitment of entomopathogenic nematodes by insect-damaged maize roots. Nature 434:732–737
Reiling KK, Yoshikuni Y et al (2004) Mono and diterpene production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 87:200–212
Ro DK, Paradise EM et al (2006) Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast. Nature 440:940–943
Rodriguez-Concepcion M (2004) The MEP pathway: a new target for the development of herbicides, antibiotics and antimalarial drugs. Curr Pharm Des 10:2391–2400
Rohdich F, Wungsintaweekul J et al (1999) Cytidine 5′-triphosphate-dependent biosynthesis of isoprenoids: YgbP protein of Escherichia coli catalyzes the formation of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11758–11763
Rohdich F, Hecht S et al (2002) Studies on the nonmevalonate terpene biosynthetic pathway: metabolic role of IspH (LytB) protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1158–1163
Rohmer M, Knani M et al (1993) Isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria: a novel pathway for the early steps leading to isopentenyl diphosphate. Biochem J 295(Pt 2):517–524
Roth RJ, Acton N (1989) A simple conversion of artemisinic acid into artemisinin. J Nat Prod 52:1183–1185
Rynkiewicz MJ, Cane DE et al (2001) Structure of trichodiene synthase from Fusarium sporotrichioides provides mechanistic inferences on the terpene cyclization cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13543–13548
Rynkiewicz MJ, Cane DE et al (2002) X-ray crystal structures of D100E trichodiene synthase and its pyrophosphate complex reveal the basis for terpene product diversity. Biochemistry 41:1732–1741
Smit A, Mushegian A (2000) Biosynthesis of isoprenoids via mevalonate in Archaea: the lost pathway. Genome Res 10:1468–1484
Starks CM, Back K et al (1997) Structural basis for cyclic terpene biosynthesis by tobacco 5-epi-aristolochene synthase. Science 277:1815–1820
Steele CL, Crock J et al (1998a) Sesquiterpene synthases from grand fir (Abies grandis). Comparison of constitutive and wound-induced activities, and cDNA isolation, characterization, and bacterial expression of delta-selinene synthase and gamma-humulene synthase. J Biol Chem 273:2078–2089
Steele CL, Katoh S et al (1998b) Regulation of oleoresinosis in grand fir (Abies grandis): differential transcriptional control of monoterpene, sesquiterpene, and diterpene synthase genes in responses to wounding. Plant Physiol 116:1497–1504
Szkopinska A, Swiezewska E et al (2000) The regulation of activity of main mevalonic acid pathway enzymes: farnesyl diphosphate synthase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase, and squalene synthase in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267:473–477
Takahashi S, Kuzuyama T et al (1998) A 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9879–9884
Tarshis LC, Yan M et al (1994) Crystal structure of recombinant farnesyl diphosphate synthase at 2.6-A resolution. Biochemistry 33:10871–10877
Tholl D, Chen F et al (2005) Two sesquiterpene synthases are responsible for the complex mixture of sesquiterpenes emitted from Arabidopsis flowers. Plant J 42:757–771
Umeno D, Tobias AV et al (2005) Diversifying carotenoid biosynthetic pathways by directed evolution. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 69:51–78
Veen M, Lang C (2004) Production of lipid compounds in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:635–646
Vogel BS, Wildung MR et al (1996) Abietadiene synthase from grand fir (Abies grandis): cDNA isolation, characterization, and bacterial expression of a bifunctional diterpene cyclase involved in resin acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 271:23262–23268
Walker K, Ketchum REB et al (1999) Partial purification and characterization of acetyl coenzyme A: taxa-4(20),11(12)-dien-5alpha-ol O-acetyl transferase that catalyzes the first acylation step of taxol biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 364:273–279
Wallaart TE, Bouwmeester HJ et al (2001) Amorpha-4,11-diene synthase: cloning and functional expression of a key enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of the novel antimalarial drug artemisinin. Planta 212:460–465
Wildung MR, Croteau R (1996) A cDNA clone for taxadiene synthase, the diterpene cyclase that catalyzes the committed step of taxol biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 271:9201–9204
Williams DC, Carroll BJ et al (2000) Intramolecular proton transfer in the cyclization of geranylgeranyl diphosphate to the taxadiene precursor of taxol catalyzed by recombinant taxadiene synthase. Chem Biol 7:969–977
Yang D, Shipman LW et al (2002) Structure of the Methanococcus jannaschii mevalonate kinase, a member of the GHMP kinase superfamily. J Biol Chem 277:9462–9467
Yoshikuni Y, Ferrin TE et al (2006) Designed divergent evolution of enzyme function. Nature 440:1078–1082
Yoshioka H, Yamada N et al (1999) cDNA cloning of sesquiterpene cyclase and squalene synthase, and expression of the genes in potato tuber infected with Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell Physiol 40:993–998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Withers, S.T., Keasling, J.D. Biosynthesis and engineering of isoprenoid small molecules. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73, 980–990 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0593-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0593-1