Abstract
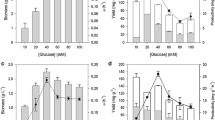
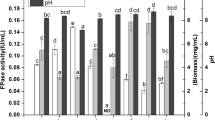
Fermentation media with different initial concentrations of ammonium and phosphate salts were used to study the inhibitory effects of those ions on growth and production of epothilone in Sorangium cellulosum and Myxococcus xanthus. The native epothilone producer, S. cellulosum was more sensitive to ammonium and phosphate than the heterologous producer, M. xanthus. An ammonium concentration of 12 mM reduced epothilone titers by 90% in S. cellulosum but by only 40% in M. xanthus. When 5 mM phosphate was added to the medium, production in both strains was 60% lower. Higher phosphate concentrations had little additional effect on M. xanthus titers, but epothilone production with 17 mM extra-cellular phosphate in S. cellulosum was 95% lower than in the control condition. The effect of iron supplementation to the fermentation medium was also investigated. Both strains showed best production with 20 μM iron added to the medium.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boeck LD, Favret ME, Wetzel RW (1992) Biosynthesis of thiopeptide antibiotic A10255 in stirred reactors using a chemically defined medium supplemented with continuous nutrient feeds. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 45:1278–1285
Carreras C, Frykman S, Ou S, Cadapan L, Zavala S, Woo E, Leaf T, Carney J, Burlingame M, Patel S, Ashley G, Licari P (2002) Saccharopolyspora erthraea-catalyzed bioconversion of 6-deoxyerythronolide B analogs for production of novel erythromycins. J Biotechnol 92:217–228
Desai RP, Leaf T, Woo E, Licari P (2002) Enhanced production of heterologous macrolide aglycones by fed-batch cultivation of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:297–301
Dworkin M (1962) Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol 84:250–257
Gerth K, Bedorf N, Höfle G, Irschik H, Reichenbach H (1996) Epothilons A and B: antifungal and cytotoxic compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (myxobacteria)—production, physio-chemical, and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 49:560–563
Gerth K, Steinmetz H, Höfle G, Reichenbach H (2001) Studies on the biosynthesis of epothilones: the PKS and epothilone C/D monooxygenase. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 54:144–148
Hajjah H, Niederberger P, Duboc P (2001) Lovastatin biosynthesis by Aspergillus terreus in a chemically defined medium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:2596–2602
Hecht V, Bischoff L, Gerth K (1990) Hollow fiber supported gas membrane for in situ removal of ammonium during an antibiotic fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:1042–1050
Jacobsen JR, Hutchinson CR, Cane DE, Khosla C (1997) Precursor-directed biosynthesis of erythromycin analogs by an engineered polyketide synthase. Science 277:367–369
Jain D, Nielsen JBK, Buckland BC (1992) Kinetics of efrotomycin synthesis in a synthetic fermentation medium. Bioprocess Eng 7:257–263
Jaoua S, Neff S, Schupp T (1992) Transfer of mobilized plasmids to Sorangium cellulosum and evidence for their integration into the chromosome. Plasmid 28:157–165
Julien B, Shah S (2002) Heterologous expression of Epothilone biosynthetic genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:2772–2778
Junker B, Mann Z, Gailliot K, Wilson BJ (1998) Use of soybean oil and ammonium sulfate additions to optimize secondary metabolite production. Biotechnol Bioeng 60:580–588
Kao CM, Katz L, Khosla C (1994) Engineered biosynthesis of a complete macrolactone in a heterologous host. Science 265:509–512
Kealey JT, Liu L, Santi DV, Betlach MC, Barr PJ (1998) Production of a polyketide natural product in nonpolyketide-producing prokaryotic and eukaryotic hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:505–509
Lau J, Frykman S, Regentin R, Ou S, Tsuruta H, Licari P (2002) Optimizing the heterologous production of epothilone D in Myxococcus xanthus. Biotechnol Bioeng 78:280–288
Martin J (1989) Molecular mechanisms for the control by phosphate of the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites. In: Shapiro S (ed) Regulation of secondary metabolism in Actinomycetes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla., pp 213–238
Omura S, Tanaka Y, Kitao C, Tanaka H, Iwai Y (1980) Stimulation of Leucomycin production by magnesium phosphate and its relevance to nitrogen catabolite regulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 18:691–695
Pfeifer BA, Admiraal SJ, Gramajo H, Cane DE, Khosla C (2001) Biosynthesis of complex polyketides in a metabolically engineered strain of E. coli. Science 291:1790–1792
Reichenbach H (1999) Myxobacteria. In: Flickinger MC, Drew SW (eds) The encyclopedia of bioprocess technology: fermentation, biocatalysis, and bioseparation. Wiley, New York, pp 1822–1832
Schimana J, Walker M, Zeeck A, Fielder HP (2001) Simocyclinones: diversity of metabolites is dependent on fermentation conditions. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 27:144–148
Shapiro S (1989) Nitrogen assimilation in Actinomycetes and the influence of nitrogen nutrition on Actinomycete secondary metabolism. In: Shapiro S (ed) Regulation of secondary metabolism in Actinomycetes. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla., pp 135–212
Tolchinsky S, Fuchs N, Varon M, Rosenberg E (1992) Use of Tn5lac to study expression of genes required for production of the antibiotic TA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36:2322–2327
Yalpani N, Altier DJ, Barbour E, Cigan AL, Scelonge CJ (2001) Production of 6-methylsalicylic acid by expression of a fungal polyketide synthase activates disease resistance in tobacco. Plant Cell 13:1401–1409
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Regentin, R., Frykman, S., Lau, J. et al. Nutrient regulation of epothilone biosynthesis in heterologous and native production strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61, 451–455 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1263-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1263-1