Abstract.
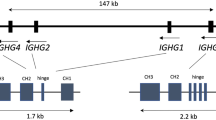
Here we describe a hitherto unknown proline/threonine polymorphism at residue 72 of the human IgG2 CH1 domain (EU numbering 189) and show that it is linked to the known valine/methionine polymorphism at residue 52 of CH2 (EU numbering 282) defining the G2m(n+)/G2m(n–) allotypes. We sequenced the entire constant region of the heavy-chain gene for secreted IgG2 in five IGHG2*02 homozygous individuals covering CH1, hinge, CH2, and CH3 regions (≈2 kb). Proline 72 in CH1 of G2m(n–) is changed to threonine in the G2m(n+) [G2m(23)] allotype. Based on the crystal structure of human IgG1, this amino acid position is expected to be surface exposed in IgG2. Besides this structural difference, we identified two silent nucleotide polymorphisms in the CH1 region and seven in the introns. Finally, we developed a sequence-specific PCR typing system detecting the polymorphisms in the CH1 and CH2 regions. We typed 64 Danish Caucasians and found that the CH1 and CH2 region polymorphisms are in complete linkage disequilibrium in this population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hougs, L., Svejgaard, A. & Barington, T. The first constant-domain (CH1) exon of human IGHG2 is polymorphic and in strong linkage disequilibrium with the CH2 exon polymorphism encoding the G2m(n+) allotype in Caucasians. Immunogenetics 52, 242–248 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510000278
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510000278