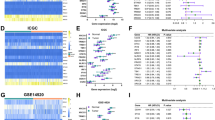
Abstract
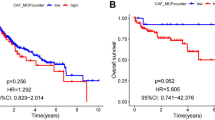
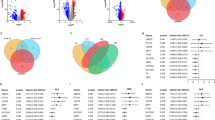
The Notch pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. However, the relationships between Notch pathway-related genes (NPRGs), immunosuppression, and immunotherapy resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unclear. Gene expression data and clinical information were extracted from GSE14520, GSE36376, GSE76427, LIRI-JP, TCGA-LIHC, GSE20140, GSE27150, and IMvigor210 datasets. A consensus clustering analysis based on 10 NPRGs was performed to determine the molecular subtypes, and then a notchScore was constructed based on differentially expressed and prognostic genes between molecular subtypes. Two molecular subgroups with significantly distinct survival and immune cell infiltration were identified. Then, a notchScore was constructed to quantify the Notch index of each patient with HCC. Next, we investigated the correlations between the clinical characteristics and the notchScore using logistic regression. Furthermore, multivariate Cox analysis showed that a high notchScore was an independent predictor of poor overall survival (OS) in the TCGA and LIRI-JP datasets and was associated with higher pathological stages. Additionally, a high notchScore was associated with higher immune cells, higher ESTIMATE score, higher immune score, higher stromal score, higher immune checkpoint, and lower tumor purity, which was consistent with the “immunity tidal model theory.” Importantly, a high notchScore was sensitive to immunotherapy. Additionally, GSEA indicated that several GO and KEGG items associated with apoptosis, immune-related pathways, and cell cycle signal pathways were significantly enriched in the high notchScore phenotype pathway. Our findings propose that a high notchScore is a prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltration and sensitivity to immunotherapy in HCC.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used in the study can be downloaded from the TCGA data repository (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/repository; accessed 26 May 2021), ICGC data (https://icgc.org/; accessed 26 May 2021) and the GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gds/?term = ; accessed 26 May 2021).
Change history
06 October 2022
The Affiliation of the corresponding author "Shitao Xia" has been updated.
References
Ahn S, Hyeon J, Park CK (2013) Notch1 and Notch4 are markers for poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 12(3):286–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1499-3872(13)60046-6
Ansell SM, Vonderheide RH (2013) Cellular composition of the tumor microenvironment. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. https://doi.org/10.1200/EdBook_AM.2013.33.e91
Beverly LJ, Felsher DW, Capobianco AJ (2005) Suppression of p53 by Notch in lymphomagenesis: implications for initiation and regression. Cancer Res 65(16):7159–7168. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-05-1664
Boyiadzis MM, Kirkwood JM, Marshall JL, Pritchard CC, Azad NS, Gulley JL (2018) Significance and implications of FDA approval of pembrolizumab for biomarker-defined disease. J Immunother Cancer 6(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0342-x
Cheng AL, Hsu C, Chan SL, Choo SP, Kudo M (2020) Challenges of combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 72(2):307–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.09.025
David CC, Jacobs DJ (2014) Principal component analysis: a method for determining the essential dynamics of proteins. Methods Mol Biol 1084:193–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-658-0_11
El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C et al (2017) Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 389(10088):2492–2502. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)31046-2
Finn RS, Ryoo BY, Merle P, Kudo M, Bouattour M, Lim HY et al (2020) Pembrolizumab as second-line therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: a randomized, double-blind, phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 38(3):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.19.01307
Finotello F, Trajanoski Z (2018) Quantifying tumor-infiltrating immune cells from transcriptomics data. Cancer Immunol Immunother 67(7):1031–1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-018-2150-z
Galon J, Pagès F, Marincola FM, Angell HK, Thurin M, Lugli A et al (2012) Cancer classification using the IMMUNOSCORE: a worldwide task force. J Transl Med 10:205. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-205
Garcia-Lezana T, Lopez-Canovas JL, Villanueva A (2021) Signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv Cancer Res 149:63–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acr.2020.10.002
Grinchuk OV, Yenamandra SP, Iyer R, Singh M, Lee HK, Lim KH et al (2018) Tumor-adjacent tissue co-expression profile analysis reveals pro-oncogenic ribosomal gene signature for prognosis of resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Oncol 12(1):89–113. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12153
Gu-Trantien C, Loi S, Garaud S, Equeter C, Libin M, de Wind A et al (2013) CD4+ follicular helper T cell infiltration predicts breast cancer survival. J Clin Invest 123(7):2873–2892. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci67428
He G, Yu GY, Temkin V, Ogata H, Kuntzen C, Sakurai T et al (2010) Hepatocyte IKKbeta/NF-kappaB inhibits tumor promotion and progression by preventing oxidative stress-driven STAT3 activation. Cancer Cell 17(3):286–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.048
Hetta HF, Elkady A, Yahia R, Meshall AK, Saad MM, Mekky MA et al (2020) T follicular helper and T follicular regulatory cells in colorectal cancer: a complex interplay. J Immunol Methods 480:112753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2020.112753
Hinshaw DC, Shevde LA (2019) The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res 79(18):4557–4566. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-3962
Hu L, Xue F, Shao M, Deng A, Wei G (2013) Aberrant expression of Notch3 predicts poor survival for hepatocellular carcinomas. Biosci Trends 7(3):152–156
Lim HY, Sohn I, Deng S, Lee J, Jung SH, Mao M et al (2013) Prediction of disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Ann Surg Oncol 20(12):3747–3753. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3070-y
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S et al (2021) Hepatocellular Carcinoma Nat Rev Dis Primers 7(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3
Majumder S, Crabtree JS, Golde TE, Minter LM, Osborne BA, Miele L (2021) Targeting Notch in oncology: the path forward. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20(2):125–144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-020-00091-3
Mariathasan S, Turley SJ, Nickles D, Castiglioni A, Yuen K, Wang Y et al (2018) TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 554(7693):544–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25501
Meurette O, Mehlen P (2018) Notch signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 34(4):536–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.07.009
Perugorria MJ, Olaizola P, Labiano I, Esparza-Baquer A, Marzioni M, Marin JJG et al (2019) Wnt-β-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(2):121–136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0075-9
Qin S, Ren Z, Meng Z, Chen Z, Chai X, Xiong J et al (2020) Camrelizumab in patients with previously treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, parallel-group, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 21(4):571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(20)30011-5
Qiu H, Zmina PM, Huang AY, Askew D, Bedogni B (2018) Inhibiting Notch1 enhances immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma by preventing Notch1 dependent immune suppressive properties. Cancer Lett 434:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.024
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W et al (2015) limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43(7):e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Lee JS et al (2010) A unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Res 70(24):10202–10212. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-10-2607
Sangro B, Sarobe P, Hervás-Stubbs S, Melero I (2021) Advances in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(8):525–543. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00438-0
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 71(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Song Y, An O, Ren X, Chan THM, Tay DJT, Tang SJ et al (2021) RNA editing mediates the functional switch of COPA in a novel mechanism of hepatocarcinogenesis. J Hepatol 74(1):135–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.021
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(43):15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Topalian SL, Taube JM, Anders RA, Pardoll DM (2016) Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 16(5):275–287. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.36
Villanueva A (2019) Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 380(15):1450–1462. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1713263
Villanueva A, Hoshida Y, Battiston C, Tovar V, Sia D, Alsinet C et al (2011) Combining clinical, pathology, and gene expression data to predict recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 140(5):1501-1512.e1502. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.006
Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2019) Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab 30(1):36–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.001
Wang H, Zhang CZ, Lu SX, Zhang MF, Liu LL, Luo RZ et al (2019) A coiled-coil domain containing 50 splice variant is modulated by serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 3 and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice by the Ras signaling pathway. Hepatology 69(1):179–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30147
Wilkerson MD, Hayes DN (2010) ConsensusClusterPlus: a class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 26(12):1572–1573. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq170
Wu J, Zhu P, Lu T, Du Y, Wang Y, He L et al (2019) The long non-coding RNA LncHDAC2 drives the self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells via activation of Hedgehog signaling. J Hepatol 70(5):918–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.015
Wu T, Dai Y (2017) Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett 387:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.043
Xiong S, Wang R, Chen Q, Luo J, Wang J, Zhao Z et al (2018) Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote stem cell-like properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through IL-6/STAT3/Notch signaling. Am J Cancer Res 8(2):302–316
Yan H, Qu J, Cao W, Liu Y, Zheng G, Zhang E et al (2019) Identification of prognostic genes in the acute myeloid leukemia immune microenvironment based on TCGA data analysis. Cancer Immunol Immunother 68(12):1971–1978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-019-02408-7
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR (2019) A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(10):589–604. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0186-y
Yang SL, Ren QG, Zhang T, Pan X, Wen L, Hu JL et al (2017) Hepatitis B virus X protein and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α stimulate Notch gene expression in liver cancer cells. Oncol Rep 37(1):348–356. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.5211
Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, Cheng AL, Mathurin P, Edeline J et al (2022) Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 459): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 23(1):77–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(21)00604-5
Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S, Ogasawara S, Palmer D et al (2018) Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 19(7):940–952. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(18)30351-6
Zhu Y, Yao S, Chen L (2011) Cell surface signaling molecules in the control of immune responses: a tide model. Immunity 34(4):466–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2011.04.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng Ma and Shitao Xia designed the study, performed statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. Chuanxin Zou helped to draft the manuscript. Shitao Xia conceived the study, participated in its design and coordination, and helped draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, P., Zou, C. & Xia, S. Oncogenic signaling pathway mediated by Notch pathway-related genes induces immunosuppression and immunotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunogenetics 74, 539–557 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-022-01273-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-022-01273-6