Abstract
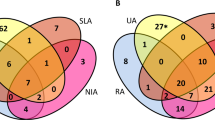
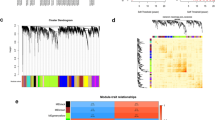
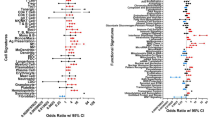
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease whose principal pathological change is aggressive chronic synovial inflammation; however, the specific etiology and pathogenesis have not been fully elucidated. We downloaded the synovial tissue gene expression profiles of four human knees from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, analyzed the differentially expressed genes in the normal and RA groups, and assessed their enrichment in functions and pathways using bioinformatics methods and the STRING online database to establish protein–protein interaction networks. Cytoscape software was used to obtain 10 hub genes; receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated for each hub gene and differential expression analysis of the two groups of hub genes. The CIBERSORT algorithm was used to impute immune infiltration. We identified the signaling pathways that play important roles in RA and 10 hub genes: Ccr1, Ccr2, Ccr5, Ccr7, Cxcl5, Cxcl6, Cxcl13, Ccl13, Adcy2, and Pnoc. The diagnostic value of these 10 hub genes for RA was confirmed using ROC curves and expression analysis. Adcy2, Cxcl13, and Ccr5 are strongly associated with RA development. The study also revealed that the differential infiltration profile of different inflammatory immune cells in the synovial tissue of RA is an extremely critical factor in RA progression. This study may contribute to the understanding of signaling pathways and biological processes associated with RA and the role of inflammatory immune infiltration in the pathogenesis of RA. In addition, this study shows that Adcy2, Cxcl13, and Ccr5 have the potential to be biomarkers for RA treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data are real and guarantee the validity of results.
References
Ajam F, Aghaei M, Mohammadi S et al (2020) PD-1 expression on CD8+CD28− T cells within inflammatory synovium is associated with relapse: a cohort of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Lett 228:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2020.10.005
Andreev D, Liu M, Kachler K et al (2020) Regulatory eosinophils induce the resolution of experimental arthritis and appear in remission state of human rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1–18 https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218902
Arend WP, Firestein GS (2012) Pre-rheumatoid arthritis: predisposition and transition to clinical synovitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8:573–586. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.134
Armas-González E, Domínguez-Luis MJ, Díaz-Martín A et al (2018) Role of CXCL13 and CCL20 in the recruitment of B cells to inflammatory foci in chronic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1611-2
Ballester LY, Luthra R, Kanagal-Shamanna R, Singh RR (2016) Advances in clinical next-generation sequencing: target enrichment and sequencing technologies. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 16:357–372. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737159.2016.1133298
Boissier MC (2011) Cell and cytokine imbalances in rheumatoid synovitis. Jt Bone Spine 78:230–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2010.08.017
Broeren MG, de Vries M, Bennink MB, Arntz OJ, Blom AB, Koenders MI, van Lent PL, van der Kraan PM, van den Berg WB, van de LF (2016) Disease-regulated gene therapy with anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 under control of the CXCL10 promoter for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Gene Ther 27:244–254. https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2015.127
Kanehisa M, Goto S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Han J, Li X, Luo X et al (2020) The mechanisms of hydroxychloroquine in rheumatoid arthritis treatment: inhibition of dendritic cell functions via toll like receptor 9 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 132 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110848
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J (2013) GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinformatics 14 https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-7
Koopmans F, van Nierop P, Andres-Alonso M et al (2019) SynGO: An evidence-based, expert-curated knowledge base for the synapse. Neuron 103:217-234.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.002
Lan YY, Wang YQ, Liu Y (2019) CCR5 silencing reduces inflammatory response, inhibits viability, and promotes apoptosis of synovial cells in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis through the MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 234:18748–18762. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28514
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS et al (2012) The SVA package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 28:882–883. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts034
Lin Y, Huang M, Wang S et al (2021) PAQR11 modulates monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology 163:60–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13303
Liu L, Zhang Y, Zheng X et al (2019) Eosinophils attenuate arthritis by inducing M2 macrophage polarization via inhibiting the IκB/P38 MAPK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:894–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.010
Ma C, Lv Q, Teng S et al (2017) Identifying key genes in rheumatoid arthritis by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Int J Rheum Dis 20:971–979. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13063
Mathur R, Rotroff D, Ma J et al (2018) gsea Gene set analysis methods: a systematic comparison. BioData Min 11:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13040-018-0166-8
McInnes IB, Schett G (2017) Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 389:2328–2337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31472-1
Moadab F, Khorramdelazad H, Abbasifard M (2021) Role of CCL2/CCR2 axis in the immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: latest evidence and therapeutic approaches. Life Sci 269:119034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119034
Moschovakis GL, Bubke A, Friedrichsen M et al (2017) T cell specific Cxcr5 deficiency prevents rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08935-6
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR et al (2015) Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods 12:453–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3337
Okamura Y, Mishima S, Kashiwakura J ichi et al (2017) The dual regulation of substance P-mediated inflammation via human synovial mast cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Allergol Int 66:S9–S20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2017.03.002
Quinn SN, Graves SH, Dains-McGahee C et al (2017) Adenylyl cyclase 3/adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 (CAP1) complex mediates the anti-migratory effect of forskolin in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Carcinog 56:1344–1360. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22598
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D et al (2015) Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv007
Rivellese F, Nerviani A, Rossi FW et al (2017) Mast cells in rheumatoid arthritis: friends or foes? Autoimmun Rev 16:557–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.04.001
Rivellese F, Suurmond J, Habets K et al (2015) Ability of interleukin-33- and immune complex-triggered activation of human mast cells to down-regulate monocyte-mediated immune responses. Arthritis Rheumatol 67:2343–2353. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39192
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A et al (2011) pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-77
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Suurmond J, Rivellese F, Dorjée AL et al (2015) Toll-like receptor triggering augments activation of human mast cells by anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1915–1923. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205562
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D et al (2019) STRING v11: protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D607–D613. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1131
Thakur R, Laye JP, Lauss M et al (2019) Transcriptomic analysis reveals prognostic molecular signatures of stage I melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 25:7424–7435. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3659
Ungethuem U, Haeupl T, Witt H et al (2010) Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics 42 A:267–282. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00004.2010
Van Raemdonck K, Umar S, Shahrara S (2020) The pathogenic importance of CCL21 and CCR7 in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 55:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.05.007
Walter W, Sánchez-Cabo F, Ricote M (2015) GOplot: an R package for visually combining expression data with functional analysis. Bioinformatics 31:2912–2914. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv300
Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ (2021) The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol 22:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-00816-x
Woetzel D, Huber R, Kupfer P et al (2014) Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther 16 https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4526
Yamaguchi A, Nozawa K, Fujishiro M et al (2013) CC motif chemokine ligand 13 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis. Mod Rheumatol 23:856–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-012-0752-4
Zhang Y, Evan Johnson W, Parmigiani G (2020a) Robustifying genomic classifiers to batch effects via ensemble learning. bioRxiv 27:btaa986. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa986
Zhang Y, Luan D, Liu Y et al (2020b) Helicid reverses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and promotes GDNF levels in C6 glioma cells through modulation of prepronociceptin. Chem Biodivers 17. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202000063
Zhoujie W, dan Wang D, Tao J et al (2020) Deficiency of β-arrestin2 exacerbates inflammatory arthritis by facilitating plasma cell formation Acta Pharmacol Sin 1–12 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00507-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sheng Fang conceived the original idea and designed the outline of the study. Xin Xu helped collected and organized the data. Lin Zhong and An-Quan Wang helped check the data. Wei-Lu Gao, Ming Lu, and Zong-Sheng Yin aided in revising the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, S., Xu, X., Zhong, L. et al. Bioinformatics-based study to identify immune infiltration and inflammatory-related hub genes as biomarkers for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunogenetics 73, 435–448 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-021-01224-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-021-01224-7