Abstract
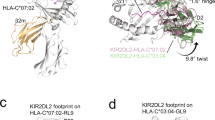
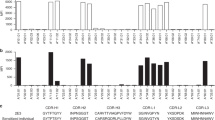
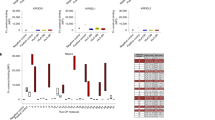
Human killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) recognize A3/11, Bw4, C1, and C2 epitopes carried by mutually exclusive subsets of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A, -B, and -C allotypes. Chimpanzee and orangutan have counterparts to HLA-A, -B, and -C, and KIR that recognize the A3/11, Bw4, C1, and C2 epitopes, either individually or in combination. Because rhesus macaque has counterparts of HLA-A and -B, but not HLA-C, we expected that rhesus KIR would better recognize HLA-A and -B, than HLA-C. Comparison of the interactions of nine rhesus KIR3D with 95 HLA isoforms, showed the KIR have broad specificity for HLA-A, -B, and -C, but vary in avidity. Considering both the strength and breadth of reaction, HLA-C was the major target for rhesus KIR, followed by HLA-B, then HLA-A. Strong reactions with HLA-A were restricted to the minority of allotypes carrying the Bw4 epitope, whereas strong reactions with HLA-B partitioned between allotypes having and lacking Bw4. Contrasting to HLA-A and -B, every HLA-C allotype bound to the nine rhesus KIR. Sequence comparison of high- and low-binding HLA allotypes revealed the importance of polymorphism in the helix of the α1 domain and the peptide-binding pockets. At peptide position 9, nonpolar residues favor binding to rhesus KIR, whereas charged residues do not. Contrary to expectation, rhesus KIR bind more effectively to HLA-C, than to HLA-A and -B. This property is consistent with major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-C having evolved in hominids to be a generally superior ligand for KIR than MHC-A and MHC-B.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-Rached L, Kuhl H, Roos C, ten Hallers B, Zhu B, Carbone L, de Jong PJ, Mootnick AR, Knaust F, Reinhardt R et al (2010a) A small, variable, and irregular killer cell Ig-like receptor locus accompanies the absence of MHC-C and MHC-G in gibbons. J Immunol 184:1379–1391
Abi-Rached L, Moesta AK, Rajalingam R, Guethlein LA, Parham P (2010b) Human-specific evolution and adaptation led to major qualitative differences in the variable receptors of human and chimpanzee natural killer cells. PLoS Genet 6:e1001192
Adams EJ, Parham P (2001) Species-specific evolution of MHC class I genes in the higher primates. Immunol Rev 183:41–64
Barnstable CJ, Bodmer WF, Brown G, Galfre G, Milstein C, Williams AF, Ziegler A (1978). Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell 14:9–20.
Blokhuis JH, van der Wiel MK, Doxiadis GG, Bontrop RE (2010) The mosaic of KIR haplotypes in rhesus macaques. Immunogenetics 62:295–306
Boyington JC, Sun PD (2002) A structural perspective on MHC class I recognition by killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors. Mol Immunol 38:1007–1021
Brodsky FM, Parham P (1982a) Evolution of HLA antigenic determinants: species cross-reactions of monoclonal antibodies. Immunogenetics 15:151–166
Brodsky FM, Parham P (1982b) Monomorphic anti-HLA-A, B, C monoclonal antibodies detecting molecular subunits and combinatorial determinants. J Immunol 128:129–135
Fan QR, Long EO, Wiley DC (2001) Crystal structure of the human natural killer cell inhibitory receptor KIR2DL1-HLA-Cw4 complex. Nat Immunol 2:452–460
Fukami-Kobayashi K, Shiina T, Anzai T, Sano K, Yamazaki M, Inoko H, Tateno Y (2005) Genomic evolution of MHC class I region in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9230–9234
Graef T, Moesta AK, Norman PJ, Abi-Rached L, Vago L, Older Aguilar AM, Gleimer M, Hammond JA, Guethlein LA, Bushnell DA et al (2009) KIR2DS4 is a product of gene conversion with KIR3DL2 that introduced specificity for HLA-A*11 while diminishing avidity for HLA-C. J Exp Med 206:2557–2572
Guethlein LA, Older Aguilar AM, Abi-Rached L, Parham P (2007) Evolution of killer cell Ig-like receptor (KIR) genes: definition of an orangutan KIR haplotype reveals expansion of lineage III KIR associated with the emergence of MHC-C. J Immunol 179:491–504
Hansasuta P, Dong T, Thananchai H, Weekes M, Willberg C, Aldemir H, Rowland-Jones S, Braud VM (2004) Recognition of HLA-A3 and HLA-A11 by KIR3DL2 is peptide-specific. Eur J Immunol 34:1673–1679
Hershberger KL, Kurian J, Korber BT, Letvin NL (2005) Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) of the African-origin sabaeus monkey: evidence for recombination events in the evolution of KIR. Eur J Immunol 35:922–935
Kruse PH, Rosner C, Walter L (2010) Characterization of rhesus macaque KIR genotypes and haplotypes. Immunogenetics 62:281–293
LaBonte ML, Hershberger KL, Korber B, Letvin NL (2001) The KIR and CD94/NKG2 families of molecules in the rhesus monkey. Immunol Rev 183:25–40
Mandelboim O, Reyburn HT, Sheu EG, Vales-Gomez M, Davis DM, Pazmany L, Strominger JL (1997) The binding site of NK receptors on HLA-C molecules. Immunity 6:341–350
Moesta AK, Norman PJ, Yawata M, Yawata N, Gleimer M, Parham P (2008) Synergistic polymorphism at two positions distal to the ligand-binding site makes KIR2DL2 a stronger receptor for HLA-C than KIR2DL3. J Immunol 180:3969–3979
Moesta AK, Abi-Rached L, Norman PJ, Parham P (2009) Chimpanzees use more varied receptors and ligands than humans for inhibitory killer cell Ig-like receptor recognition of the MHC-C1 and MHC-C2 epitopes. J Immunol 182:3628–3637
Older Aguilar AM, Guethlein LA, Adams EJ, Abi-Rached L, Moesta AK, Parham P (2010) Coevolution of killer cell Ig-like receptors with HLA-C to become the major variable regulators of human NK cells. J Immunol 185:4238–4251
Palacios C, Cuervo LC, Cadavid LF (2011). Evolutionary patterns of killer cell Ig-like receptor genes in Old World monkeys. Gene 474:39–51.
Parham P, Abi-Rached L, Matevosyan L, Moesta AK, Norman PJ, Older Aguilar AM, Guethlein LA (2010) Primate-specific regulation of natural killer cells. J Med Primatol 39:194–212
Purdy AK, Campbell KS (2009) Natural killer cells and cancer: regulation by the killer cell Ig-like receptors (KIR). Cancer Biol Ther 8:2211–2220
Rajalingam R, Parham P, Abi-Rached L (2004) Domain shuffling has been the main mechanism forming new hominoid killer cell Ig-like receptors. J Immunol 172:356–369
Rammensee H, Bachmann J, Emmerich NP, Bachor OA, Stevanovic S (1999) SYFPEITHI: database for MHC ligands and peptide motifs. Immunogenetics 50:213–219
Robinson J, Mistry K, McWilliam H, Lopez R, Parham P, Marsh SG (2011) The IMGT/HLA database. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D1171–D1176
Rosner C, Kruse PH, Hermes M, Otto N, Walter L (2011) Rhesus macaque inhibitory and activating KIR3D interact with Mamu-A-encoded ligands. J Immunol 186:2156–2163
Sambrook JG, Bashirova A, Palmer S, Sims S, Trowsdale J, Abi-Rached L, Parham P, Carrington M, Beck S (2005) Single haplotype analysis demonstrates rapid evolution of the killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) loci in primates. Genome Res 15:25–35
Sanjanwala B, Draghi M, Norman PJ, Guethlein LA, Parham P (2008) Polymorphic sites away from the Bw4 epitope that affect interaction of Bw4+ HLA-B with KIR3DL1. J Immunol 181:6293–6300
Sharma D, Bastard K, Guethlein LA, Norman PJ, Yawata N, Yawata M, Pando M, Thananchai H, Dong T, Rowland-Jones S et al (2009) Dimorphic motifs in D0 and D1 + D2 domains of killer cell Ig-like receptor 3DL1 combine to form receptors with high, moderate, and no avidity for the complex of a peptide derived from HIV and HLA-A*2402. J Immunol 183:4569–4582
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants AI31168 and AI24258 to P.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Older Aguilar, A.M., Guethlein, L.A., Hermes, M. et al. Rhesus macaque KIR bind human MHC class I with broad specificity and recognize HLA-C more effectively than HLA-A and HLA-B. Immunogenetics 63, 577–585 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-011-0535-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-011-0535-7