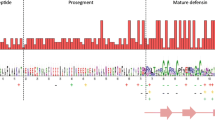
Abstract
Antimicrobial defensins with the cysteine-stabilized α-helical and β-sheet (CSαβ) motif are a large family of ancient, evolutionarily related innate immunity effectors of multicellular organisms. Although the widespread distribution in plants, fungi, and invertebrates suggests their uniqueness to Eukarya, it is unknown whether these eukaryotic defensins originated before or posterior to the emergence of eukaryotes. In this study, we provide evidence in support of the existence of defensin-like peptides (DLPs) in myxobacteria based on structural bioinformatics analysis, which recognized two bacterial peptides with a conserved cysteine-stabilized α-helical motif, a nested structural unit of the CSαβ motif. Similarity in sequence and structure to fungal DLPs together with restricted distribution to the myxobacteria as well as central role of the myxobacteria in the origin of eukaryotes suggest that the bacterial DLPs represent the ancestor of the eukaryotic defensins and could mediate immune defense of early eukaryotes after gene transfer to the proto-eukaryotic genome. Our work thus offers a basis for further investigation of prokaryotic origin of eukaryotic immune effector molecules.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Blandin S, Moita LF, Köcher T, Wilm M, Kafatos F, Levashina EA (2002) Reverse genetics in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae: targeted disruption of the Defensin gene. EMBO Rep 3:852–856
Brogden KA (2005) Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol 3:238–250
Bryson K, McGuffin LJ, Marsden RL, Ward JJ, Sodhi JS, Jones DT (2005) Protein structure prediction servers at University College London. Nucl Acids Res 33:W36–W38
Bulet P, Stocklin R, Menin L (2004) Anti-microbial peptides: from invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol Rev 198:169–184
Castrignanò T, De Meo, PD, Cozzetto, D, Talamo, IG, Tramontano A (2006) The PMDB protein model database. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D306–D309
Cohen-Gonsaud M, Keep NH, Davies AP, Ward J, Henderson B, Labesse G (2004) Resuscitation-promoting factors possess a lysozyme-like domain. Trends Biochem Sci 29:7–10
Cornet B, Bonmatin JM, Hetru C, Hoffmann JA, Ptak M, Vovelle F (1995) Refined three-dimensional solution structure of insect defensin A. Structure 3:435–448
Diep DB, Nes IF (2002) Ribosomally synthesized antibacterial peptides in gram positive bacteria. Curr Drug Targets 3:107–122
Dimarcq JL, Bulet P, Hetru C, Hoffmann J (1998) Cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides in invertebrates. Biopolymers 47:465–477
Duret L, Guex N, Peitsch MC, Bairoch A (1998) New insulin-like proteins with atypical disulfide bond pattern characterized in Caenorhabditis elegans by comparative sequence analysis and homology modeling. Genome Res 8:348–353
Fjell CD, Hancock RE, Cherkasov A (2007) AMPer: a database and an automated discovery tool for antimicrobial peptides. Bioinformatics 23:1148–1155
Froy O (2005) Convergent evolution of invertebrate defensins and nematode antibacterial factors. Trends Microbiol 13:314–319
Froy O, Gurevitz M (2003) Arthropod and mollusk defensins—evolution by exon-shuffling. Trends Genet 19:684–687
Hogg PJ (2003) Disulfide bonds as switches for protein function. Trends Biochem Sci 28:210–214
Lay FT, Anderson MA (2005) Defensins—components of the innate immune system in plants. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:85–101
López-García P, Moreira D (2006) Selective force for the origin of the eukaryotic nucleus. Bioessays 28:525–533
Mitta G, Hubert F, Noel T, Roch P (1999) Myticin, a novel cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptide isolated from haemocytes and plasma of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Eur J Biochem 265:71–78
Moreira D, López-García P (1998) Symbiosis between methanogenic archaea and δ-proteobacteria as the origin of eukaryotes: the syntrophic hypothesis. J Mol Evol 47:517–530
Müller-Esterl W, Fritza H, Kellermannb J, Lottspeichb F, Machleidtc W, Turkd V (1985) Genealogy of mammalian cysteine proteinase inhibitors. Common evolutionary origin of stefins, cystatins and kininogens. FEBS Lett 191:221–226
Mygind PH, Fischer RL, Schnorr KM, Hansen MT, Sönksen CP, Ludvigsen S, Raventós D, Buskov S, Christensen B, De Maria L, Taboureau O, Yaver, D, Elvig-Jørgensen SG, Sørensen MV, Christensen BE, Kjærulff SK, Frimodt-Moller N, Lehrer RI, Zasloff M, Kristensen HH (2005) Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 437:975–980
Nakajima Y, van der Goes van Naters-Yasui A, Taylor D, Yamakawa M (2001) Two isoforms of a member of the arthropod defensin family from the soft tick, Ornithodoros moubata (Acari: Argasidae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:747–751
Peschel A, Sahl HG (2006) The co-evolution of host cationic antimicrobial peptides and microbial resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:529–536
Putsep K, Branden CI, Boman HG, Normark S (1999a) Antibacterial peptide from H. pylori. Nature 398:671–672
Putsep K, Normark S, Boman HG (1999b) The origin of cecropins; implications from synthetic peptides derived from ribosomal protein L1. FEBS Lett 451:249–252
Reichenbach H (1999) The ecology of the myxobacteria. Environ Microbiol 1:15–21
Rodriguez de la Vega RC, Possani LD (2005) On the evolution of invertebrate defensins. Trends Genet 21:330–332
Sharma P, Lönneborg A (1996) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a plant defensin-like protein from roots of Norway spruce. Plant Mol Biol 31:707–712
Tamaoki H, Miura R, Kusunoki M, Kyogoku Y, Kobayashi Y, Moroder L (1998) Folding motifs induced and stabilized by distinct cystine frameworks. Protein Eng 11:649–659
Terras FRG, Eggermont K, Kovaleva V, Raikhel NV, Osborn RW, Kester A, Rees SB, Torrekens S, van Leuven F, Vanderleyden J, Cammue BPA, Broekaert WF (1995) Small cysteine-rich antifungal proteins from radish: their role in host defense. Plant Cell 7:573–588
Wang X, Connor M, Smith R, Maciejewski MW, Howden ME, Nicholson GM, Christie MJ, King GF (2000) Discovery and characterization of a family of insecticidal neurotoxins with a rare vicinal disulfide bridge. Nat Struct Biol 7:505–513
Zhang H, Kato Y (2003) Common structural properties specifically found in the CSαβ -type antimicrobial peptides in nematodes and mollusks: evidence for the same evolutionary origin? Dev Comp Immunol 27:499–503
Zhu S (2008) Discovery of six families of fungal defensin-like peptides provides insights into origin and evolution of the CSalphabeta defensins. Mol Immunol 45:828–838
Zhu S, Gao B (2006) Molecular characterization of a possible progenitor sodium channel toxin from the Old World scorpion Mesobuthus martensii. FEBS Lett 580:5979–5987
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Dr. Purificación López-García for his critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (90608009) and the ‘Bairen Plan’ from the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material. Supplementary data are available at Immunogenetics online.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S. Evidence for myxobacterial origin of eukaryotic defensins. Immunogenetics 59, 949–954 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-007-0259-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-007-0259-x