Abstract
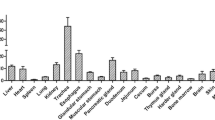
Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), an antiviral innate immunity receptor recognizes double-stranded RNA, preferably of viral origin and induces type I interferon production, which causes maturation of phagocytes and subsequent release of chemical mediators from phagocytes against some viral infections. The present study has characterized TLR3 complementary DNA (cDNA) in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) and nilgai (Boselaphus tragocamelus). TLR3 coding sequences of both buffalo and nilgai were amplified from cultured dendritic cell cDNA and cloned in pGEMT-easy vector for characterization by restriction endonucleases and nucleotide sequencing. Sequence analysis reveals that 2,715-bp-long TLR3 open reading frame encoding 904 amino acids in buffalo as well as nilgai is similar to that of cattle. Buffalo TLR3 has 98.6 and 97.9% identity at nucleotide level with nilgai and cattle, respectively. Likewise, buffalo TLR3 amino acids share 96.7% identity with cattle and 97.8% with nilgai. Non-synonymous substitutions exceeding synonymous substitutions indicate evolution of this receptor through positive selection among these three ruminant species. Buffalo and nilgai appear to have diverged from a common ancestor in phylogenetic analysis. Predicted protein structures of buffalo and nilgai TLR3 from deduced amino acid sequences indicate that the buffalo and nilgai TLR3 ectodomain may be more efficient in ligand binding than that of cattle. Furthermore, TLR3 messenger RNA expression in tissues as quantified by real-time PCR was found higher in nilgai than buffalo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T (2001) Toll-like receptor: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol 2:675–680
Akosy E, Zouain CS, Vanhoutte F, Fontaine J, Pavelka N, Thiebelemont N, Willems F, Ricciardi-Castagonali P, Goldman M, Capron M, Ryeffel B, Trottein F (2005) Double-stranded RNAs from the helminth parasite Schistosoma activate TLR3 in dendritic cells. J Biol Chem 280(1):277–283
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (2001) Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappa B by toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413(6857):732–738
Anderson KV (2000) Toll signaling pathways in innate immune response. Curr Opin Immunol 12:13–19
Baker PE, Knoblock KF (1982) Bovine costimulator II. Generation and maintenance of a costimulator dependent bovine lymphoblastoid cell lines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2:467–469
Baldwin CL, Malu MN, Kinuthia SW, Conrad PA, Groottenhuis JG (1986) Comparative analysis of infection and transformation of lymphocytes from African buffalo and Boran cattle with Theileria parva subsp. Parva and T. parva subsp. Lawrenceit. Infect Immun 53(1):186–191
Bell JK, Askins J, Hall PR, Davies DR, Segal DM (2006) The dsRNA binding site of human toll-like receptor 3. Proc Natl Acad USA 103(23):8792–8797
Bell JK, Botos I, Hall PR, Askins J, Shiloach J, Segal DM, Davies DR (2005) The molecular structure of the toll-like receptor 3 ligand-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(31):10976–10980
Choe J, Kelker MS, Wilson LA (2005) Crystal structure of human toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) ectodomain. Science 309(5734):585
Ezenwa VO (2004) Interaction among host diet, nutritional status and gastrointestinal parasite infection in wild bovis. Int J Parasitol 34:535–542
Farina C, Krumbholz M, Giese T, Hartmann G, Aloisi F, Meinl E (2005) Preferential expression and function of Toll-like receptor 3 in human astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol 159(1–2):12–19
Funami K, Matsumoto M, Oshiumi H, Akazawa T, Yamamoto A, Seya T (2004) The cytoplasmic “linker region” in toll-like receptor 3 controls receptor localization and spicing. Int Immunol 16(8):1143–1154
Gaydos JK, Davidson WR, Elvinger F, Mead DG, Howerth EW, Stallknecht DE (2002) Innate resistance to epizootic hemorrhagic disease in white-tailed deer. J Wildl Dis 38:713–719
Guillot L, Le Geffic R, Bloch S, Escriou N, Akira S, Chignard M, Si-Tahar M (2005) Involvement of toll-like receptor 3 in the immune response of lung epithelial cells to double-stranded RNA and influenza A virus. J Biol Chem 280(7):5571–5580
Jorgenson RL, Young SL, Lesmeister MJ, Lyddon TD, Misfeldt ML (2005) Human endometrial epithelial cells cyclically express toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and exhibit TLR3-dependent responses to dsRNA. Hum Immunol 66(5):469–482
Kariko K, Ni H, Capodici J, Lamphier M, Weissmann D (2004a) mRNA is an endogenous ligand for Toll-like receptor 3. J Biol Chem 279(13):12542–12550
Kariko K, Bhuyan P, Capodici J, Weissman D (2004b) Small interfering RNAs mediate sequence-independent gene suppression and induce immune activation by signaling through toll-like receptor 3. J Immunol 172:6545–6549
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Letunic I, Copley RR, Schmidt S, Ciccarelli FD, Doerks T, Scultz J, Ponting CP, Bork P (2004) SMART 4.0: towards genomic data integration. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D142–D144
Meas S, Seto J, Sugimoto C, Bikhsh M, Riaz M, Sato T, Naeem K, Ohashi K, Onuma M (2000) Infection of bovine immunodeficiency virus and bovine leukemia viurs in water buffalo and cattle population in Pakistan. J Vet Med Sci 62(3):329–331
Menzies M, Ingham A (2006) Identification and expression of Toll-like receptors 1–10 in selected bovine and ovine tissues. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 109(1–2):23–30
Muzio M, Bosisio D, Polentarutti N, D’amico G, Stoppacciaro A, Mancinelli R, van’t Veer C, Penton-Rol G, Ruco LP, Allavena P, Mantovani A (2000) Differential expression and regulation of toll-like receptors (TLR) in human leukocytes: selective expression of TLR3 in dendritic cells. J Immunol 164(11):5998–6004
Rehli M (2002) Of mice and men: species variation of toll-like receptor expression. Trends Immunol 23(8):375–378
Rock FL, Hardiman G, Timans JC, Kastelein RA, Bazan JF (1998) A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:588
Rodroguez MF, Wiens GD, Purcell MK, Palti Y (2005) Characterization of toll-like receptor 3 gene in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunogenetics 57(7):510–519
Sarkar SN, Smith HL, Rowe TM, Sen GC (2003) Double-stranded RNA signaling by Toll-like receptor 3 requires specific tyrosine residue in its cytoplasmic domain. J Biol Chem 278(7):4393–4396
Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP (1998) SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5857–5864
Sen GC, Sarkar SN (2005) Transcriptional signaling by double-stranded RNA: role of TLR3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16(1):1–14
Sun J, Duffy KE, Ranjith-Kumar CT, Xiong J, Lamb RJ, Santos J, Masarapu H, Cunningham M, Holzenburg A, Sarisky RT, Mbow ML, Kao C (2006) Structural and functional analyses of the human toll-like receptor 3: role of glycosylation. J Biol Chem 281(16):11144–11151
Takeda K, Akira S (2005) Toll-like receptor in innate immunity. Int Immunol 17(1):1–14
Wesch D, Beetz S, Oberg H, Marget M, Krengel K, Kabelitz, D (2006) Direct costimulatory effect of TLR3 ligand poly (I:C) on human γδ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 176(3):1348–1354
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to the Director of the Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Izatnagar for providing necessary facilities to carry out the work. A. D. is thankful to ICAR for providing the Junior Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Photographs
(A, B) Buffalo Dendritic cells; C Immature Dendritic cell; D Mature Dendritic cell (E, F) Nilgai Dendritic cells. Dendritic cells are marked by arrow (DOC 10718 kb)
Table 1
Changes in the nucleotide positions in the TLR3 coding sequences (DOC 184 kb)
Table 2
Changes in the amino acid positions in different domain of TLR3 protein sequences (DOC 114 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhara, A., Saini, M., Das, D.K. et al. Molecular characterization of coding sequences and analysis of Toll-like receptor 3 mRNA expression in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) and nilgai (Boselaphus tragocamelus). Immunogenetics 59, 69–76 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-006-0174-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-006-0174-6