Abstract.
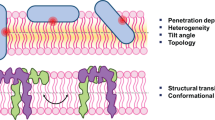
The environment of both the hydrophilic and hydrophobic sides of α-helical δ-toxin are probed by tryptophanyl (Trp) fluorescence, when self-association occurs in solution and on binding to membranes. The fluorescence parameters of staphylococcal δ-toxin (Trp15 on the polar side of the amphipathic helix) and synthetic analogues with single Trp at position 5 or 16 (on the apolar side) were studied. The time-resolved fluorescence decays of the peptides in solution show that the local environment of their single Trp is always heterogeneous. Although the self-association degree increases with concentration, as shown by fluorescence anisotropy decays, the lifetimes (and their statistical weight) of Trp16 do not change, contrary to what is observed for Trp15. The first step of self-association is then driven by hydrophobic interactions between apolar sides of α-helices, whilst further oligomerization involves their polar side (Trp15) via electrostatic interactions. This is supported by dissociation induced by salt. For all self-associated peptides, the polarity of the Trp microenvironment was not significantly modified upon binding to phospholipid vesicles, as indicated by the small shifts of the fluorescence emission spectra and lifetime values. However, the relative populations of the lifetime classes vary with bound-peptide density similar to the rates of their global motions in bilayers or smaller particles. Quenching experiments by water or lipid-soluble compounds show changes of the orientation of membrane-inserted peptides, from probably dimers lying flat at the interface at low peptide density, to oligomers spanning the membrane and inducing membrane fragmentation at high peptide density.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Revised version: 25 August 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talbot, JC., Thiaudière, E., Vincent, M. et al. Dynamics and orientation of amphipathic peptides in solution and bound to membranes: a steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence study of staphylococcal δ-toxin and its synthetic analogues. Eur Biophys J 30, 147–161 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490000118
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490000118