Abstract
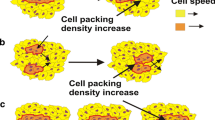
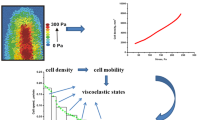
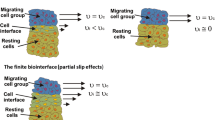
Long-timescale viscoelasticity caused by collective cell migration (CCM) significantly influences cell rearrangement and induces generation of mechanical waves. The phenomenon represents a product of the active turbulence occurring at low Reynolds number. The generation of mechanical waves has been a subject of intensive research primarily in 2D multicellular systems, while 3D systems have not been considered in this context. The aim of this contribution is to discuss the generation of mechanical waves during 3D CCM in two model systems: (1) the fusion of two-cell aggregates and (2) cell aggregate rounding after uni-axial compression, pointing out that mechanical waves represent a characteristic of CCM in general. Such perturbations are also involved in various biological processes, such as embryogenesis, wound healing and cancer invasion. The inter-relation between the viscoelasticity and the appearance of active turbulence remains poorly understood even in 2D. The phenomenon represents a consequence of the competition between the viscoelastic force and the surface tension force which induces successive stiffening and softening of parts of multicellular systems. The viscoelastic force is a product of the residual cell stress accumulation and its inhomogeneous distribution caused by CCM. This modeling consideration represents a powerful tool to address the generation of mechanical waves in CCM towards an understanding of this important but still controversial topic.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alert R, Casademunt J, Joanny J-F (2021) Active turbulence. arXiv:2104.02122v1
Alert R, Trepat X (2020) Physical models of collective cell migration. Annu Rev Condens Matter Phys 11:77–101
Ban E, Wang H, J. Franklin M, Liphardt JT, Janmey PA, Shenoy VB. (2019) Strong triaxial coupling and anomalous Poisson effect in collagen networks. PNAS 116(4):6790-6799
Barriga EH, Mayor R (2019) Adjustable viscoelasticity allows for efficient collective cell migration. Sem Cell Dev Biol 93:55–68
Blanchard GB, Fletcher AG, Schumacher LJ (2019) The devil is in the mesoscale: mechanical and behavioural heterogeneity in collective cell movement. Sem Cell Dev Biol 93:46–54
Casas-Vazquez J, Jou D (2003) Temperature in non-equilibrium states: a review of open problems and current proposals. Rep Prog Phys 66:1937–2023
Dechristé G, Fehrenbach J, Griseti E, Lobjois V, Clair PC (2018) Viscoelastic modeling of the fusion of multicellular tumor spheroids in growth phase. J Theor Biol 454:102–109
Deforet M, Hakim V, Yevick H, Duclos G, Silberzan P (2014) Emergence of collective modes and tri-dimensional structures from epithelial confinement. Nature Comm 5(1):3747. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4747
Gongora C, Candeil L, Vezzio N, Copois V, Denis V, Breil C, Molina F, Fraslon C, Conseiller E et al (2008) Altered expression of cell proliferation-related and interferon-stimulated genes in colon cancer cells resistant to SN38. Cancer Biol & Therapy 7(6):822–832
Groisman A, Steinberg V (1998) Mechanism of elastic instability in Couette flow of polymer solutions: Experiment. Phys Fluids 10(10):2451–2463
Groisman A, Steinberg V (2000) Elastic turbulence in a polymer solution flow. Nature 405:53–55
Grosser S, Lippoldt J, Oswald L, Merkel M , Sussman DM, Renner F, Gottheil P, Morawetz EW , Fuhs T, Xie X, et al. (2021) Cell and Nucleus Shape as an Indicator of Tissue Fluidity in Carcinoma. Phys Rev X 11, 011033.
Guevorkian K, Gonzalez-Rodriguez D, Carlier C, Dufour S, Brochard-Wyart F (2011) Mechanosensitive shivering of model tissues under controlled aspiration. PNAS 108(33):13387–13392
Kosztin I, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Forgacs G (2012) Colloquium: Modeling the dynamics of multicellular systems: Application to tissue engineering. Rev Mod Phys 84(4):1791–1805
Lange JP, Fabry B (2013) Cell and tissue mechanics in cell migration. Exp Cell Res 319:2418–2423
Lee P and Wolgemuth CW. (2011) Crawling Cells Can Close Wounds without Purse Strings or Signaling. PLoS Comput Biol 7(3):e1002007 1–8.
Marmottant P, Mgharbel A, Kafer J, Audren B, Rieu JP, Vial JC, van der Sanden B, Maree AFM, Graner F, Delanoe-Ayari H (2009) The role of fluctuations and stress on the effective viscosity of cell aggregates. PNAS 106(41):17271–17275
Mc Cann C, Kriebel PW, Parent CA, Losert W (2010) Cell speed, persistence and information transmission during signal relay and collective migration. J Cell Sci 123(10):1724–1731
Mombach JCM, Robert D, Graner F, Gillet G, Thomas GL, Idiart M, Rieu JP (2005) Rounding of aggregates of biological cells: experiments and simulations. Phys A 352:525–534
Mondal S, Phukan M, Ghatak A (2015) Estimation of solid–liquid interfacial tension using curved surface of a soft solid. PNAS 112(41):12563–12568
Nnetu KD, Knorr M, Kaes J, Zink M (2012) The impact of jamming on boundaries of collectively moving weak-interacting cells. New J Phys 14:115012
Notbohm J, Banerjee S, Utuje KJC, Gweon B, Jang H, Park Y, Shin J, Butler JP, Fredberg JJ, Marchetti MC (2016) Cellular contraction and polarization drive collective cellular motion. Biophys J 110(12):2729–2738
Ongenae S, Cuvelier M, Vangheel J, Ramon H, Smeets B (2021) Activity-induced fluidization and arrested coalescence in fusion of cellular aggregates. Front Phys. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2021.649821
Oriola D, Marin-Riera M, Anlas K, Gritti N, Matsumiya M, Aalderink G, Ebisuya M, Sharpe J, Trivedi V (2020) Arrested coalescence of multicellular aggregates. https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.01455
Oswald L, Grosser S, Smith DM, Kaes JA (2017) Jamming transition in cancer. J Phys d: Appl Phys 50(483001):1–17
Pajic-Lijakovic I. (2021) Basic concept of viscoelasticity, in Viscoelasticity and collective cell migration, eds. I. Pajic-Lijakovic and E. Barriga, Chapter 2, Elsevier, ISBN: 9780128203118.
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2017a) Successive relaxation cycles during long-time cell aggregate rounding after uni-axial compression. J Biol Phys 43(2):197–209
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2017b) Viscoelasticity of multicellular surfaces. J Biomech 60:1–8
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2019a) Long-time viscoelasticity of multicellular surfaces caused by collective cell migration—multi-scale modeling considerations. Sem Cell Dev Biol 93:87–96
Pajic-Lijakovic I. and Milivojevic M. (2019b) Functional epithelium remodeling in response to applied stress under in vitro conditions. Appl Bionics Biomech. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/48927
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2019c) Jamming state transition and collective cell migration. J Biol Eng 13:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13036-019-0201-4
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2020a) Collective cell migration and residual stress accumulation: rheological consideration. J Biomech 108:109898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2020.109898
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2020b) Mechanical oscillations in 2D collective cell migration: the elastic turbulence. Front Phys. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphy.2020.585681
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2021a) Multiscale nature of cell rearrangement caused by collective cell migration. Europ Biophys J 50:1–14
Pajic-Lijakovic I, Milivojevic M (2021b) Viscoelasticity and cell jamming state transition. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.19.436195
Pérez-González C, Alert R, Blanch-Mercader C, Gómez-González M, Kolodziej T, Bazellieres E, Casademunt J, Trepat X (2019) Active wetting of epithelial tissues. Nature Phys 15(1):79–88
Petrolli V, Boudou T, Balland M, Cappello G. (2021) Oscillations in collective cell migration, in Viscoelasticity and collective cell migration, eds. I. Pajic-Lijakovic and E. Barriga, Chapter 8, Elsevier, ISBN: 9780128203118.
Rieu JP, Upadhyaya A, Glazier JA, Ouchi NB, Sawada Y (2000) Diffusion and Deformations of Single Hydra Cells in Cellular Aggregates. Biophys J 79:1903–1914
Serra-Picamal X, Conte V, Vincent R, Anon E, Tambe DT, Bazellieres E, Butler JP, Fredberg JJ, Trepat X (2012) Mechanical waves during tissue expansion. Nature Phys 8(8):628–634
Shafiee A, McCune M, Forgacs G, Kosztin I (2015) Post-deposition bioink self-assembly: a quantitative study. Biofabric 7:045005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/7/4/045005
Tambe DT, Croutelle U, Trepat X, Park CY, Kim JH, Millet E, Butler JP, Fredberg JJ. (2013) Monolayer Stress Microscopy: Limitations, Artifacts, and Accuracy of Recovered Intercellular Stresses. PLoS ONE 8(2):e55172 1–13.
Tlili S, Gauquelin E, Li B, Cardoso O, Ladoux B, Delanoë-Ayari H, F Graner F. (2018) Collective cell migration without proliferation: density determines cell velocity and wave velocity. R Soc Open Sci 5:172421, https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.172421
Tlili S, Durande M, Gay C, Ladoux B, Graner F, Delanoë-Ayari H. (2020) Migrating Epithelial Monolayer Flows Like a Maxwell Viscoelastic Liquid. Phys Rev Lett 125:088102.
Trepat X, Wasserman MR, Angelini TE, Millet E, Weitz DA, Butler JP, Fredberg JJ (2009) Physical forces during collective cell migration. Nature Phys 5:426–430
Tschoegl NW, Knauss WG, Emri I (2002) Poisson’s ratio in linear viscoelasticity—a critical review. Mech Time-Depend Mat 6:3–51
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Contract No. 451-03-9/2021-14/200135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pajic-Lijakovic, I., Milivojevic, M. Mechanical waves caused by collective cell migration: generation. Eur Biophys J 51, 1–13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-021-01581-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-021-01581-x