Abstract
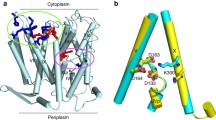
Understanding the flow of ions through E. coli porin outer membrane protein F (OmpF) requires knowledge of the charge state of all titratable residues located along the permeation pathway. Earlier theoretical studies proved successful in the calculation of the pK values of most residues. The (apparent) pK of Asp37 (D37), on the other hand, appeared rather sensitive to the (unknown) protein dielectric used. We addressed the protonation state of D37 experimentally by replacing D37 with a (neutral) valine. This D37V mutant expressed reduced cation selectivity, in agreement with the view that D37 in wild-type (WT) OmpF is fully ionized, i.e., deprotonated. The introduction of a (positively charged) arginine at position 37 evoked current fluctuations. Similar behavior was observed in the D37K mutant and the cysteine mutants D37C-MTSEA and D37C-MTSET. Nontitratable [2-(trimethylammonium)ethyl]-methanethiosulfonate (MTSET) carries a permanent and pH-independent charge of 1e, implying that the fluctuations of the D37C-MTSET mutant do not represent (de)protonation reactions of MTSET. We therefore conclude that these fluctuations reflect transitions between conformational substates evoked by structural instabilities due to the positive charge at that particular position in the pore lumen. Based on the similarities between D37C-MTSET fluctuations and those seen in the other mutants, notably D37K, the underlying mechanism of these fluctuations may be (essentially) the same in all four mutants studied.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilella-Arzo M, Garćia-Celma JJ, Cervera J, Alcaraz A, Aguililla VM (2007) Electrostatic properties and macroscopic electrodiffusion in OmpF porin and mutants. Bioelectrochemistry 70:320–327
Alcaraz A, Nestorovich EM, Aguilella-Arzo M, Aguililla VM, Bezrukov SM (2004) Salting out the ionic selectivity of a wide channel: the asymmetry of OmpF. Biophys J 87:943–957
Alcaraz A, Ramírez P, Garćia-Giménez E, López ML, Andrio A, Aguilella VM (2006) A pH-tunable nanofluidic diode: electrochemical rectification in a reconstituted single ion channel. J Phys Chem B 110:21205–21209
Asandei A, Mereuta L, Luchian T (2008) Influence of membrane potentials upon reversible protonation of acidic residues from the OmpF eyelet. Biophys Chem 135:32–40
Benz R, Janko K, Boos KW, Läuger P (1978) Formation of large, ion-permeable membrane channels by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 511:305–319
Benz R, Janko K, Läuger P (1979) Ionic selectivity of pores formed by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 551:238–247
Bredin J, Saint N, Malléa M, Dé E, Molle G, Pagès J-M, Simonet V (2002) Alteration of pore properties of Escherichia coli OmpF induced by mutation of key residues in anti-loop 3 region. Biochem J 363:521–528
Cowan SW, Schirmer T, Rummel G, Steiert M, Ghosh R, Pauptit RA, Jansonius JN, Rosenbusch JP (1992) Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. Coli porins. Nature 358:727–733
Danelon C, Grandl J, Hovius R, Vogel H (2007) Modulation of proton-induced current fluctuations in the human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:76–98
Delcour AH (2003) Solute uptake through general porins. Front Biosci 8:1055–1071
Garćia-Giménez E, Alcaraz A, Aguilella VM, Ramírez P (2009) Directional ion selectivity in a biological nanopore with bipolar structure. J Membrane Sci 331:137–142
Im W, Roux B (2002a) Ions and counterions in a biological channel: a molecular dynamics simulation of OmpF porin from Escherichia coli in an explicit membrane with 1 M KCl aqueous salt solution. J Mol Biol 319:1177–1197
Im W, Roux B (2002b) Ion permeation and selectivity of OmpF porin: a theoretical study based on molecular dynamics, Brownian dynamics, and continuum electrodiffusion theory. J Mol Biol 322:851–869
Karshikoff A, Spassov V, Cowan SW, Ladenstein R, Schirmer T (1994) Electrostatic properties of two porin channels from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 240:372–384
Kasianowicz JJ, Bezrukov SM (1995) Proton dynamics of the α-toxin ion channel from spectral analysis of pH-dependent current fluctuations. Biophys J 69:94–105
Liu N, Delcour AH (1998) The spontaneous gating activity of OmpC porin is affected by mutations of a putative hydrogen bond network or of a salt bridge between the L3 loop and the barrel. Protein Eng 11:797–802
Lou K-L, Saint N, Prilipov A, Rummel G, Benson SA, Rosenbusch JP, Schirmer T (1996) Structural and functional characterization of OmpF porin mutants selected for larger pore size. J Biol Chem 271:20669–20675
Miedema H, Meter-Arkema A, Wierenga J, Tang J, Eisenberg B, Nonner W, Hektor H, Gillespie D, Meijberg W (2004) Permation properties of an engineered bacterial OmpF porin containing the EEEE-locus of Ca2+ channels. Biophys J 87:3137–3147
Miedema H, Vrouenraets M, Wierenga J, Eisenberg B, Gillespie D, Meijberg W, Nonner W (2006a) Ca2+ selectivity of a chemically modified OmpF with reduced pore volume. Biophys J 91:4392–4400
Miedema H, Vrouenraets M, Wierenga J, Eisenberg B, Schirmer T, Baslé A, Meijberg W (2006b) Conductance and selectivity fluctuations in D127 mutants of the bacterial porin OmpF. Eur Biophys J 36:13–22
Miedema H, Vrouenraets M, Wierenga J, Meijberg W, Robillard G, Eisenberg B (2007) A biological porin engineered into a molecular, nanofluidic diode. Nano Lett 7:2886–2891
Nestorovich EM, Rostovtseva TK, Bezrukov SM (2003) Residue ionization and ion transport through OmpF channels. Biophys J 85:3718–3729
Ng JA, Vora T, Krishnamurthy V, Chung S-H (2008) Estimating the dielectric constant of the channel protein and pore. Eur Biophys J 37:213–222
Parker DR, Norvell WA, Chaney RL (1995) GEOCHEM-PC: a chemical speciation program for IBM and compatible personal computers. In: Loeppert RH, Schwab AP, Goldberg S (eds) Chemical equilibrium and reaction models. SSSA, Special publication number 42, Soil Science Society of America/American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WC, pp 253–269
Pezeshki S, Chimerel C, Bessonov AN, Winterhalter M, Kleinekathöfer U (2009) Understanding ion conductance on a molecular level: an all-atom modeling of the bacterial porin OmpF. Biophys J 97:1898–1906
Phale PS, Philippsen A, Kiefhaber T, Koebnik R, Phale VP, Schirmer T, Rosenbusch JP (1998) Stability of trimeric OmpF porin: the contributions of the latching loop L2. Biochemistry 37:15663–15670
Phale PS, Philippsen A, Widmer C, Pahe VP, Rosenbusch JP, Schirmer T (2001) Role of charged residues at the OmpF porin channel constriction probed by mutagenesis and simulation. Biochemistry 40:6319–6325
Prod’hom B, Pietrobon D, Hess P (1987) Direct measurement of proton transfer rates to a Group controlling the dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel. Nature 329:243–246
Root MJ, MacKinnon R (1994) Two identical noninteracting sites in an ion channel revealed by proton transfer. Science 265:1852–1856
Saint N, Lou K-L, Widmer C, Luckey M, Schirmer T, Rosenbusch JP (1996) Structural and functional characterization of OmpF porin mutants selected for larger pore size. J Biol Chem 271:20676–20680
Saxena K, Drosou V, Maier E, Benz R, Ludwig B (1999) Ion selectivity reversal and induction of voltage-gating by site-directed mutations in the Paracoccus denitrificans porin. Biochemistry 38:2206–2212
Schirmer T (1998) General and specific porins from bacterial outer membranes. J Struct Biol 121:101–109
Schirmer T, Phale PS (1999) Brownian dynamics simulation of ion flow through porin channels. J Mol Biol 294:1159–1167
Steidl JV, Yool AJ (2001) Distinct mechanisms of Block of Kv1.5 channels by tertiary and quaternary amine clofilium compounds. Biophys J 81:2606–2613
Varma S, Jakobsson E (2004) Ionization states of residues in OmpF and mutants: Effects of dielectric constant and interactions between residues. Biophys J 86:690–704
Varma S, Jakobsson E (2006) The influence of amino acid protonation states on molecular dynamics simulations of the bacterial porin OmpF. Biophys J 90:112–123
Vrouenraets M, Wierenga J, Meijberg W, Miedema H (2006) Chemical modification of the bacterial porin OmpF: gain of selectivity by volume reduction. Biophys J 90:1202–1211
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by NanoNed, a nanotechnology program from the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vrouenraets, M., Miedema, H. The ionization state of D37 in E. coli porin OmpF and the nature of conductance fluctuations in D37 mutants. Eur Biophys J 39, 1563–1571 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-010-0613-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-010-0613-z