Abstract
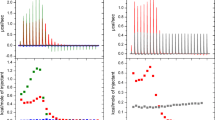
Triclosan is a hydrophobic antibacterial agent used in dermatological preparations and oral hygiene products. Although the molecular mechanism of action of this molecule has been attributed to inhibition of fatty acid biosynthesis, earlier work in our laboratories strongly suggested that the antibacterial action of Triclosan is mediated at least partly through its membranotropic effects. In order to assess its location in phospholipid membranes, high-resolution magic-angle spinning natural abundance 13C NMR of Triclosan embedded within egg yolk lecithin model membranes has been used to obtain 13C spin–lattice relaxation times for both Triclosan and lecithin carbon atoms in the presence of Gd3+ ions. The results indicate that Triclosan is localized in the upper region of the phospholipid membrane, its hydroxyl group residing in the vicinity of the C=O/C2 carbon atoms of the acyl chain of the phospholipid, and the rest of the Triclosan molecule is probably aligned in a nearly perpendicular orientation with respect to the phospholipid molecule. Intercalation of Triclosan into bacterial cell membranes likely compromises the functional integrity of those membranes, thereby accounting for at least some of this compound’s antibacterial effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COLOC:
-
correlation by long-range coupling
- EYL:
-
egg yolk lecithin
- HETCOR:
-
heteronuclear chemical-shift correlation
- MAS:
-
magic-angle spinning
- MLV:
-
multilamellar vesicles
References
Auger M (2000) Biological membrane structure by solid-state NMR. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2:119–124
Bechinger B (2000) Biophysical investigations of membrane perturbations by polypeptides using solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Mol Membr Biol 17:135–142
Bernabeu A, Shapiro S, Villalaín J (2002) A MAS-NMR study of the location of (+)-totarol, a diterpenoid bioactive molecule, in phospholipid model membranes. Chem Phys Lipids 119:33–39
Bhargava HN, Leonard PA (1996) Triclosan: applications and safety. Am J Infect Control 24:209–218
Heath RJ, Rubin JR, Holland DR, Zhang E, Snow ME, Rock CO (1999) Mechanism of triclosan inhibition of bacterial fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem 274:11110–11114
Heath RJ, Su N, Murphy CK, Rock CO (2000) The enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductases FabI and FabL from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 275:40128–40133
Ipsen JH, Mouritsen OG, Bloom M (1990) Relationships between lipid membrane area, hydrophobic thickness, and acyl-chain orientational order. The effects of cholesterol. Biophys J 57:405–412
Jones RD, Jampani HB, Newman JL, Lee AS (2000) Triclosan: a review of effectiveness and safety in health care settings. Am J Infect Control 28:184–196
Levy CW, Roujeinikova A, Sedelnikova S, Baker PJ, Stuitje AR, Slabas AR, Rice DW, Rafferty JB (1999) Molecular basis of triclosan activity. Nature 398:383–384
McMurry LM, Oethinger M, Levy SB (1998) Triclosan targets lipid synthesis. Nature 394:531–532
Modéer T, Bengtsson A, Rölla G (1996) Triclosan reduces prostaglandin biosynthesis in human gingival fibroblasts challenged with interleukin-1 in vitro. J Clin Periodontol 23:927–933
Mustafa M, Bakhiet M, Wondimu B, Modéer T (2000) Effect of triclosan on interferon-gamma production and major histocompatibility complex class II expression in human gingival fibroblasts. J Clin Periodontol 27:733–737
Nagle JF (1993) Area/lipid of bilayers from NMR. Biophys J 64:1476–1481
Nezil FA, Bloom M (1992) Combined influence of cholesterol and synthetic amphiphilic peptides upon bilayer thickness in model membranes. Biophys J 61:1176–1183
Oldfield E, Bowers JL, Forbes J (1987) High-resolution proton and carbon-13 NMR of membranes: why sonicate? Biochemistry 26:6919–6923
Parikh SL, Xiao G, Tonge PJ (2000) Inhibition of InhA, the enoyl reductase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, by triclosan and isoniazid. Biochemistry 39:7645–7650
Qiu X, Janson CA, Court RI, Smyth MG, Payne DJ, Abdel-Meguid SS (1999) Molecular basis for triclosan activity involves a flipping loop in the active site. Protein Sci 8:2529–2532
Regös J, Hitz HR (1974) Investigations on the mode of action of Triclosan, a broad spectrum antimicrobial agent. Zentralbl Bakteriol Abt Orig A 226:390–401
Regös J, Zak O, Solf R, Vischer WA, Weirich EG (1979) Antimicrobial spectrum of triclosan, a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent for topical application. II. Comparison with some other antimicrobial agents. Dermatologica 158:72–79
Roujeinikova A, Levy CW, Rowsell S, Sedelnikova S, Baker PJ, Minshull CA, Mistry A, Colls JG, Camble R, Stuitje AR, Slabas AR, Rafferty JB, Pauptit RA, Viner R, Rice DW (1999) Crystallographic analysis of triclosan bound to enoyl reductase. J Mol Biol 294:527–535
Salgado J, Villalaín J, Gómez-Fernández JC (1993) Magic angle spinning 13C-NMR spin-lattice relaxation study of the location and effects of α-tocopherol, ubiquinol-10 and ubiquinone-10 in unsonicated model membranes. Eur J Biophys 22:151–155
Sankaram MB, Thompson TE (1992) Deuterium magnetic resonance study of phase equilibria and membrane thickness in binary phospholipid mixed bilayers. Biochemistry 31:8258–8268
Schweizer HP (2001) Triclosan: a widely used biocide and its link to antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol Lett 202:1–7
Shapiro S, Guggenheim B (1995) The action of thymol on oral bacteria. Oral Microbiol Immunol 10:241–246
Skaare AB, Kjaerheim V, Barkvoll P, Rölla G (1997) Does the nature of the solvent affect the anti-inflammatory capacity of triclosan? An experimental study. J Clin Periodontol 24:124–128
Stewart MJ, Parikh S, Xiao G, Tonge PJ, Kisker C (1999) Structural basis and mechanism of enoyl reductase inhibition by triclosan. J Mol Biol 290:859–865
Villalaín J (1996) Location of cholesterol in model membranes by magic-angle-sample-spinning NMR. Eur J Biochem 241:586–593
Villalaín J (1997) Location of the toxic molecule abietic acid in model membranes by MAS-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta 1328:281–289
Villalaín J, Mateo CR, Aranda FJ, Shapiro S, Micol V (2001) Membranotropic effects of the antibacterial agent Triclosan. Arch Biochem Biophys 390:128–136
Zuckerbraun HL, Babich H, May RJ, Sinensky MC (1998) Triclosan: cytotoxicity, mode of action, and induction of apoptosis in human gingival cells in vitro. Eur J Oral Sci 106:628–636
Acknowledgements
This work was supported partly by grants PM98-0100 and BMC2002-00158 from MCYT, Madrid (to J.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guillén, J., Bernabeu, A., Shapiro, S. et al. Location and orientation of Triclosan in phospholipid model membranes. Eur Biophys J 33, 448–453 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-003-0378-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-003-0378-8