Abstract
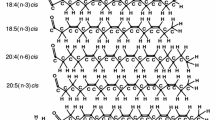
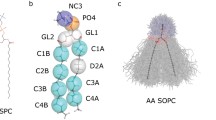
The performance of the GROMOS96 parameter set 45A3 developed for aliphatic alkanes is tested on a bilayer of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) in water in the liquid-crystalline Lα phase. Variants of the force-field parameter set as well as different sets of simulation conditions or simulation parameter sets are evaluated. In the case of the force-field parameters, the van der Waals constants for the non-bonded interaction of the ester carbonyl carbon and the partial charges and charge group definition of the phosphatidylcholine head group are examined. On the methodological side, different cut-off distances for the non-bonded interactions, use of a reaction-field force due to long-range electrostatic interactions, the frequency of removal of the centre of mass motion and the strength of the coupling of the pressure of the system to the pressure bath are tested. The area per lipid, as a measure of structure, the order parameters of the chain carbons, as a measure of membrane fluidity, and the translational diffusion of the lipids in the plane of the bilayer are calculated and compared with experimental values. An optimal set of simulation parameters for which the GROMOS96 parameter set 45A3 yields a head group area, chain order parameters and a lateral diffusion coefficient in accordance with the experimental data is listed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alber F, Folkers G, Carloni P (1999) Dimethyl phosphate: stereoelectronic versus environmental effects. J Phys Chem B 103:6121–6126
Banavali NK, MacKerell AD Jr (2001) Reevaluation of stereoelectronic contributions to the conformational properties of the phosphodiester and N3'-phosphoramidate moieties of nucleic acids. J Am Chem Soc 123:6747–6755
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, Hermans J (1981) Interaction models for water in relation to protein hydration. In: Pullman B (ed) Intermolecular forces. Reidel, Dordrecht, pp 331–342
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690
Berger O, Edholm O, Jahnig F (1997) Molecular dynamics simulations of a fluid bilayer of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine at full hydration, constant pressure, and constant temperature. Biophys J 72:2002–2013
Blume A (1993) Dynamic properties. In: Cevc G (ed) Phospholipids handbook. Dekker, New York, pp 455–511
Chandrasekhar I (1992) Parameter development for molecular dynamics simulation of lipids. In: Gaber BP, Easwaran KRK (eds) Biomembrane structure and function state of the art. Adenine Press, Albany, NY, pp 353–363
Chandrasekhar I, Sasisekharan V (1989) The nomenclature and conformational analysis of lipids and lipid analogues. Mol Cell Biochem 91:173–182
Chandrasekhar I, van Gunsteren W F (2001) Sensitivity of molecular dynamics simulations of lipids to the size of the ester carbon. Curr Sci 81:1325–1327
Chandrasekhar I, van Gunsteren WF (2002) A comparison of the potential energy parameters of aliphatic alkanes: molecular dynamics simulations of triacylglycerols in the alpha phase. Eur Biophys J 31:89–101
Chiu SW, Clark M, Subramaniam S, Scott HL, Jakobsson E (1995) Incorporation of surface tension into molecular dynamics simulation of an interface: a fluid phase lipid bilayer membrane. Biophys J 69:1230–1245
Chiu SW, Clark M, Jakobsson E, Subramaniam S, Scott HL (1999) Optimisation of hydrocarbon chain interaction parameters: application to the simulation of fluid phase bilayers. J Phys Chem B 103:6323–6327
Daura X, Mark AE, van Gunsteren WF (1998) Parametrization of aliphatic CHn united atoms of the GROMOS96 force field. J Comput Chem 19:535–547
Douliez J, Leonard A, Dufour EJ (1995) Restatement of order parameters in biomembranes: calculation of C-C bond order parameters from C-D quadrupolar splittings. Biophys J 68:1727–1739
Egberts E, Berendsen HJC (1988) Molecular dynamics simulation of a smectic liquid crystal with atomic detail. J Chem Phys 89:3718–3732
Egberts E, Marrink S-J, Berendsen HJC (1994) Molecular dynamics simulation of a phospholipid membrane. Eur Biophys J 22:423–436
Feller SE (2000) Molecular dynamics simulations of lipid bilayers. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 5:217–223
Feller SE, MacKerell D Jr (2000) An improved empirical potential energy function for molecular simulations of phospholipids. J Phys Chem B 104:7510–7515
Feller SE, Yin D, Pastor RW, MacKerell D Jr (1997) Molecular dynamics simulation of unsaturated lipid bilayers at low hydration: parametrization and comparison with diffraction studies. Biophys J 73:2269–2279
Florian J, Strajbl M, Warshel A (1998) Conformational flexibility of phosphate, phosphonate, and phosphorothioate methyl esters in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc 120:7959–7966
Forrest LR, Sansom MS (2000) Membrane simulations: bigger and better? Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:174–181
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Zakrrzewski VG, Montgomery JA Jr, Straatmann RE, Burant JC, Dapprich S, Millam JM, Daniels AD, Kudin KN, Strain MC, Farkas O, Tomasi J, Barone V, Cossi M, Cammi R, Mennucci B, Pommeli C, Adamo C, Clifford S, Ochterski J, Petersson GA, Ayala PY, Cui Q, Morokuma K, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Ciolowski J, Oritz JV, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Gomperts R, Martin RL, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Gonzalez C, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Andres JL, Gonzalez C, Head-Gordon M, Replogle ES, Pople JA (1998) Gaussian 98, revision A, 6th edn. Gaussian, Pittsburgh
Gupta G, Rao SN, Sasisekharan V (1982) Conformational flexibility of DNA: an extension of the stereochemical guidelines. FEBS Lett 150:424–428
Hauser H, Pascher I, Pearson RH, Sundell S (1981) Preferred conformation and molecular packing of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta 650:21–51
Hermans J, Berendsen HJC, van Gunsteren WF, Postma JPM (1984) A consistent empirical potential for water-protein interactions. Biopolymers 23:1513–1518
Kusba J, Li L, Gryczynski I, Piszczek G, Johnson M, Lakowicz JR (2002) Lateral diffusion coefficients in membranes measured by resonance energy transfer and a new algorithm for diffusion in two dimensions. Biophys J 82:1358–1372
Leulliot N, Ghomi M, Scalamani G, Bertier G (1999) Ground state properties of the nucleic acid constituents studied by density functional calculations. I. Conformational features of ribose, dimethyl phosphate, uridine, cytidine, 5'-methyl phosphate-uridine, and 3'-methyl phosphate-uridine. J Phys Chem A 103:8716–8724
Lindahl E, Edholm O (2000) Mesoscopic undulations and thickness fluctuations in lipid bilayers from molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 2000:426–433
Lipowsky R, Sackman E (eds) (1995) Structure and dynamics of membranes: from cells to vesicles. Handbook of biological physics, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Nagle JF, Tristram-Nagle S (2000) Structure of lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1469:159–195
Pastor RW, Venable RM (1993) Molecular and stochastic dynamics simulation of lipid membranes. In: van Gunsteren WF, Weiner PK, Wilkinson AJ (eds) Computer simulation of biomolecular systems: theoretical and experimental applications, vol 2. Escom, Leiden, pp 443–463
Pastor RW, Venable RM, Feller SE (2002) Lipid bilayers, NMR relaxation and computer simulations. Acc Chem Res 35:438–446
Petrache HI, Dodd SW, Brown MF (2000) Area per lipid and acyl chain length distributions in fluid phosphatidylcholines determined by 2H NMR spectroscopy. Biophys J 79:3172–3192
Ramachandran GN, Sasisekharan V (1969) Conformation of polypeptides and proteins. Adv Protein Chem 23:283–437
Ryckaert JP, Bellemans A (1975) Molecular dynamics of liquid n-butane near its boiling point. Chem Phys Lett 30:123–126
Ryckaert JP, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJC (1977) Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23:327–341
Schlenkrich M, Brickmann J, MacKerell AD Jr, Karplus M (1996) An empirical potential energy function for phospholipids: criteria for parameter optimization and applications. In: Merz K, Roux B (eds) Biological membranes: a molecular perspective from computation and experiment. Birkhauser, Boston, pp 31–81
Schuler LD (2000) Molecular dynamics simulation of aggregates of lipids: development of force-field parameters and application to membranes and micelles. PhD thesis, ETH-Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland
Schuler LD, van Gunsteren WF (2000) On the choice of dihedral angle potential energy functions for n-alkanes. Mol Simulation 25:301–319
Schuler LD, Daura X, van Gunsteren WF (2001) An improved GROMOS96 force field for aliphatic hydrocarbons in the condensed phase. J Comput Chem 22:1205–1218
Scott WRP, Hünenberger PH, Tironi IG, Mark AE, Billeter SR, Fennen J, Torda AE, Huber T, Krüger P, van Gunsteren WF (1999) The GROMOS biomolecular simulation program package. J Phys Chem A 103:3596–3607
Seelig J, Niederberger W (1974) Deuterium labelled lipids as structural probes in liquid crystalline bilayers. J Am Chem Soc 96:2069–2072
Small DM (1986) The physical chemistry of lipids from alkanes to phospholipids. In: Hanahan D (ed) Handbook of lipid research, vol 4. Plenum, New York
Smondyrev AM, Berkowitz ML (1999) United atom force field for phospholipid membranes: constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation of dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine/water system. J Comput Chem 20:531–545
Stouch TR, Ward KB, Altieri A, Hagler AT (1991) Simulation of lipid crystals: characterisation of potential energy functions and parameters for lecithin molecules. J Comput Chem 12:1033–1046
Tieleman DP, Berendsen HJC (1996) Molecular dynamics of a fully hydrated dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer with different macroscopic boundary conditions and parameters. J Chem Phys 105:4871–4880
Tieleman DP, Marrink SJ, Berendsen HJC (1997) A computer perspective of membranes: molecular dynamics studies of lipid bilayer systems. Biochim Biophys Acta 1331:235–270
Tieleman DP, Hess B, Sansom MSP (2002) Analysis and evaluation of channel models: simulations of alamethicin. Biophys J 83: (in press)
Tironi IG, Sperb R, Smith PE, van Gunsteren WF (1995) A generalised reaction field method for molecular dynamics simulations. J Chem Phys 102:5451–5459
Tobias DJ, Tu K, Klein ML (1997) Atomic scale molecular dynamics simulations of lipid membranes. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 2:115–126
van Gunsteren WF, Berendsen HJC (1987) Groningen molecular simulation (GROMOS) library manual. Biomos, Groningen, The Netherlands
van Gunsteren WF, Berendsen HJC (1990) Computer simulation of molecular dynamics: methodology, applications and perspectives in chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 29:992–1023
van Gunsteren WF, Billeter SR, Eising AA, Hünenberger PH, Krüger P, Mark AE, Scott WRP, Tironi IG (1996) Biomolecular simulation: the GROMOS96 manual and user guide. Hochschulverlag an der ETH Zürich/Biomos, Zürich/ Groningen
van Gunsteren WF, Daura X, Mark AE (1998) The GROMOS force field. In: Schleyer PvR (ed) Encyclopedia of computational chemistry, vol 2. Wiley, Chichester, pp 1211–1216
Wiberg KB, Wong MW (1993) Solvent effects. 4. Effect of solvent on the E/Z energy difference for methyl formate and methyl acetate. J Am Chem Soc 115:1078–1084
Acknowledgements
D.P.T. is a Scholar of the Alberta Heritage Foundation for Medical Research. Financial support by the National Center of Competence in Research (NCCR) Structural Biology of the Swiss National Science Foundation is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandrasekhar, I., Kastenholz, M., Lins, R.D. et al. A consistent potential energy parameter set for lipids: dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine as a benchmark of the GROMOS96 45A3 force field. Eur Biophys J 32, 67–77 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-002-0269-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-002-0269-4