Abstract
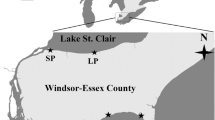
Bacteria play a key role in freshwater biogeochemical cycling as well as water safety, but short-term trends in freshwater bacterial community composition and dynamics are not yet well characterized. We sampled four public beaches in southern Ontario, Canada; in June, July, and August (2016) over a 24-h (diel) cycle at 2-h intervals. Using high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA gene, we found substantial bi-hourly and day/night variation in the bacterial communities with considerable fluctuation in the relative abundance of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria phyla. Moreover, relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae (associated with potential health risk) was significantly high at night in some dial cycles. Diversity was significantly high at night across most of the diel sampling events. qPCR assays showed a substantial bi-hourly variation of Escherichia coli levels with a significant high level of E. coli at night hours in comparison with day hours and the lowest levels at noon and during the afternoon hours. Taken together, these findings highlighted a considerable short-term temporal variation of bacterial communities which helps better understanding of freshwater bacterial dynamics and their ecology. E. coli monitoring showed that multiple samples in different hours will provide more accurate picture of freshwater safety and human health risk.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodds WK, Perkin JS, Gerken JE (2013) Human impact on freshwater ecosystem services: a global perspective. Environ Sci Technol 47:9061–9068
Glasl B, Webster NS, Bourne DG (2017) Microbial indicators as a diagnostic tool for assessing water quality and climate stress in coral reef ecosystems. Mar. Biol. 164:91
Huntscha S, Stravs MA, Bühlmann A, Ahrens CH, Frey JE, Pomati F, Hollender J, Buerge IJ, Balmer ME, Poiger T (2018) Seasonal dynamics of glyphosate and AMPA in Lake Greifensee: rapid microbial degradation in the epilimnion during summer. Environ Sci Technol 52:4641–4649
Berry MA, Davis TW, Cory RM, Duhaime MB, Johengen TH, Kling GW, Marino JA, Den Uyl PA, Gossiaux D, Dick GJ (2017) Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms are a biological disturbance to western Lake Erie bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 19:1149–1162
Butler TM, Wilhelm A-C, Dwyer AC, Webb PN, Baldwin AL, Techtmann SM (2019) Microbial community dynamics during lake ice freezing. Sci. Rep. 9:1–11
Hölker F, Wurzbacher C, Weißenborn C, Monaghan MT, Holzhauer SI, Premke K (2015) Microbial diversity and community respiration in freshwater sediments influenced by artificial light at night. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 370:1–10
Villaescusa JA, Jørgensen SE, Rochera C, Velázquez D, Quesada A, Camacho A (2016) Carbon dynamics modelization and biological community sensitivity to temperature in an oligotrophic freshwater Antarctic lake. Ecol. Model. 319:21–30
Horton DJ, Theis KR, Uzarski DG, Learman DR (2019) Microbial community structure and microbial networks correspond to nutrient gradients within coastal wetlands of the Laurentian Great Lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 95:fiz033
Grubisic LM, Bertilsson S, Eiler A, Heinrich F, Brutemark A, Alonso-Sáez L, Andersson AF, Gantner S, Riemann L, Beier S (2017) Lake bacterioplankton dynamics over diurnal timescales. Freshw. Biol. 62:191–204
Lymer D, Logue JB, Brussaard CP, Baudoux AC, Vrede K, Lindstrom ES (2008) Temporal variation in freshwater viral and bacterial community composition. Freshw. Biol. 53:1163–1175
Pachepsky Y, Shelton D (2011) Escherichia coli and fecal coliforms in freshwater and estuarine sediments. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41:1067–1110
McPhedran K, Seth R, Bejankiwar R (2013) Occurrence and predictive correlations of Escherichia coli and Enterococci at Sandpoint beach (Lake St Clair), Windsor, Ontario and Holiday beach (Lake Erie), Amherstburg, Ontario. Water Qual Res J Canada 48:99–110
Mill A, Schlacher T, Katouli M (2006) Tidal and longitudinal variation of faecal indicator bacteria in an estuarine creek in south-east Queensland, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 52:881–891
VanMensel D, Chaganti SR, Droppo IG, Weisener CG (2019) Exploring bacterial pathogen community dynamics in freshwater beach sediments: a tale of two lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 22:568–583
Jørgensen NO, Tranvik L, Edling H, Granéli W, Lindell M (1998) Effects of sunlight on occurrence and bacterial turnover of specific carbon and nitrogen compounds in lake water. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 25:217–227
Shao K, Gao G, Tang X, Wang Y, Zhang L, Qin B (2013) Low resilience of the particle-attached bacterial community in response to frequent wind-wave disturbance in freshwater mesocosms. Microbes Environ. 28:450–456
Shahraki AH, Chaganti SR, Heath D (2019) Assessing high-throughput environmental DNA extraction methods for meta-barcode characterization of aquatic microbial communities. J. Water Health 17:37–49
He X, Chaganti SR, Heath DD (2017) Population-specific responses to interspecific competition in the gut microbiota of two Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) populations. Microb. Ecol.:1–12
Chern E, Siefring S, Paar J, Doolittle M, Haugland R (2011) Comparison of quantitative PCR assays for Escherichia coli targeting ribosomal RNA and single copy genes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 52:298–306
Shahraki AH, Heath D, Chaganti SR (2019) Recreational water monitoring: nanofluidic qRT-PCR chip for assessing beach water safety. E DNA 1:305–315
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7:335–336
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Logares R, Audic S, Bass D, Bittner L, Boutte C, Christen R, Claverie J-M, Decelle J, Dolan JR, Dunthorn M (2014) Patterns of rare and abundant marine microbial eukaryotes. Curr. Biol. 24:813–821
Hammer Ř, Harper D, Ryan P (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electronica 4:4–9
Wickham H (2011) ggplot2. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews: Computational Statistics 3:180–185
Bryant JA, Aylward FO, Eppley JM, Karl DM, Church MJ, DeLong EF (2016) Wind and sunlight shape microbial diversity in surface waters of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. The ISME J 10:1308–1322
Cloutier DD, Alm EW, McLellan SL (2015) Influence of land use, nutrients, and geography on microbial communities and fecal indicator abundance at Lake Michigan beaches. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81:4904–4913
Gilbert JA, Field D, Swift P, Thomas S, Cummings D, Temperton B, Weynberg K, Huse S, Hughes M, Joint I (2010) The taxonomic and functional diversity of microbes at a temperate coastal site: a multi-omic study of seasonal and diel temporal variation. PLoS One 5:e15545
Mével G, Vernet M, Goutx M, Ghiglione JF (2008) Seasonal to hour variation scales in abundance and production of total and particle-attached bacteria in the open NW Mediterranean Sea (0–1000 m). Biogeosciences 5:1573–1586
Ghiglione J, Mevel G, Pujo-Pay M, Mousseau L, Lebaron P, Goutx M (2007) Diel and seasonal variations in abundance, activity, and community structure of particle-attached and free-living bacteria in NW Mediterranean Sea. Microb. Ecol. 54:217–231
Paver SF, Newton RJ, Coleman ML (2020) Microbial communities of the Laurentian Great Lakes reflect connectivity and local biogeochemistry. Environ. Microbiol. 22:433–446
Guo B, Liu C, Gibson C, Frigon D (2019) Wastewater microbial community structure and functional traits change over short timescales. Sci. Total Environ. 662:779–785
Pearce D, Butler H (2002) Short-term stability of the microbial community structure in a maritime Antarctic lake. Polar Biol. 25:479–487
Cardoso DC, Sandionigi A, Cretoiu MS, Casiraghi M, Stal L, Bolhuis H (2017) Comparison of the active and resident community of a coastal microbial mat. Sci. Rep. 7:1–10
Poretsky RS, Hewson I, Sun S, Allen AE, Zehr JP, Moran MA (2009) Comparative day/night metatranscriptomic analysis of microbial communities in the North Pacific subtropical gyre. Environ. Microbiol. 11:1358–1375
Kim Y-M, Nowack S, Olsen MT, Becraft ED, Wood JM, Thiel V, Klapper I, Kühl M, Fredrickson JK, Bryant DA (2015) Diel metabolomics analysis of a hot spring chlorophototrophic microbial mat leads to new hypotheses of community member metabolisms. Front. Microbiol. 6:209
Campbell BJ, Kirchman DL (2013) Bacterial diversity, community structure and potential growth rates along an estuarine salinity gradient. The ISME J 7:210–220
Filippini M, Buesing N, Gessner MO (2008) Temporal dynamics of freshwater bacterio-and virioplankton along a littoral–pelagic gradient. Freshw. Biol. 53:1114–1125
Whitman RL, Nevers MB, Korinek GC, Byappanahalli MN (2004) Solar and temporal effects on Escherichia coli concentration at a Lake Michigan swimming beach. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70:4276–4285
Newton RJ, Jones SE, Eiler A, McMahon KD, Bertilsson S (2011) A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 75:14–49
Berg KA, Lyra C, Sivonen K, Paulin L, Suomalainen S, Tuomi P, Rapala J (2009) High diversity of cultivable heterotrophic bacteria in association with cyanobacterial water blooms. The ISME journal 3:314–325
Bridge JW, Oliver DM, Chadwick D, Godfray HCJ, Heathwaite AL, Kay D, Maheswaran R, McGonigle DF, Nichols G, Pickup R (2010) Engaging with the water sector for public health benefits: waterborne pathogens and diseases in developed countries. Bull. World Health Organ. 88:873–875
Edberg S, Rice E, Karlin R, Allen M (2000) Escherichia coli: the best biological drinking water indicator for public health protection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 88:106S–116S
Ge Z, Whitman RL, Nevers MB, Phanikumar MS (2012) Wave-induced mass transport affects daily Escherichia coli fluctuations in nearshore water. Environ Sci Technol 46:2204–2211
Traister E, Anisfeld SC (2006) Variability of indicator bacteria at different time scales in the upper Hoosic River watershed. Environ Sci Technol 40:4990–4995
Stocker M, Rodriguez-Valentin J, Pachepsky Y, Shelton D (2016) Spatial and temporal variation of fecal indicator organisms in two creeks in Beltsville, Maryland. Water Qual Res J Canada 51:167–179
Maraccini PA, Mattioli MCM, Sassoubre LM, Cao Y, Griffith JF, Ervin JS, Van De Werfhorst LC, Boehm AB (2016) Solar inactivation of Enterococci and Escherichia coli in natural waters: effects of water absorbance and depth. Environ Sci Technol 50:5068–5076
Nelson KL, Boehm AB, Davies-Colley RJ, Dodd MC, Kohn T, Linden KG, Liu Y, Maraccini PA, McNeill K, Mitch WA (2018) Sunlight-mediated inactivation of health-relevant microorganisms in water: a review of mechanisms and modeling approaches. Environ Sci Process Impact 20:1089–1122
Boehm AB (2007) Enterococci concentrations in diverse coastal environments exhibit extreme variability. Environ Sci Technol 41:8227–8232
Acknowledgments
We thank Shelby Mackie (Environmental Genomics Facility, Great Lakes Institute for Environmental Research, Windsor University) for her support and assistance in eDNA extraction and sequencing of the samples. We also thank Keta Patel, Farwa Ziab, Mubarak Zaib, Amber Shaheen, and Zahra Taboun for their assistance in water sample processing and filtration.
Funding
This project was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) post-graduate funding to AHS and NSERC Strategic Partnership Grants for Projects funding to DDH for lab and field costs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 4278 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahraki, A.H., Chaganti, S.R. & Heath, D.D. Diel Dynamics of Freshwater Bacterial Communities at Beaches in Lake Erie and Lake St. Clair, Windsor, Ontario. Microb Ecol 81, 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-020-01539-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-020-01539-0