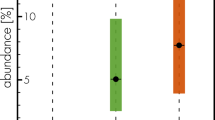
Abstract
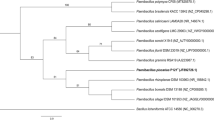
The study of the draft genome of an Antarctic marine ciliate, Euplotes petzi, revealed foreign sequences of bacterial origin belonging to the γ-proteobacterium Francisella that includes pathogenic and environmental species. TEM and FISH analyses confirmed the presence of a Francisella endocytobiont in E. petzi. This endocytobiont was isolated and found to be a new species, named F. adeliensis sp. nov.. F. adeliensis grows well at wide ranges of temperature, salinity, and carbon dioxide concentrations implying that it may colonize new organisms living in deeply diversified habitats. The F. adeliensis genome includes the igl and pdp gene sets (pdpC and pdpE excepted) of the Francisella pathogenicity island needed for intracellular growth. Consistently with an F. adeliensis ancient symbiotic lifestyle, it also contains a single insertion-sequence element. Instead, it lacks genes for the biosynthesis of essential amino acids such as cysteine, lysine, methionine, and tyrosine. In a genome-based phylogenetic tree, F. adeliensis forms a new early branching clade, basal to the evolution of pathogenic species. The correlations of this clade with the other clades raise doubts about a genuine free-living nature of the environmental Francisella species isolated from natural and man-made environments, and suggest to look at F. adeliensis as a pioneer in the Francisella colonization of eukaryotic organisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petroni G, Spring S, Schleifer KH, Verni F, Rosati G (2000) Defensive extrusive ectosymbionts of Euplotidium (Ciliophora) that contain microtubule-like structures are bacteria related to Verrucomicrobia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97:1813–1817
Görtz HD (2006) Symbiotic associations between ciliates and prokaryotes. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 364–402
Fokin SI (2012) Frequency and biodiversity of symbionts in representatives of the main classes of Ciliophora. Eur. J. Protistol. 48:138–148
Dziallas C, Allgaier M, Monaghan MT, Grossart HP (2012) Act together—implications of symbioses in aquatic ciliates. Front. Microbiol. 3:288
Fujishima M, Görtz H-D (1983) Infection of macronuclear anlagen of Paramecium caudatum with the macronucleus-specific symbiont Holospora obtusa. J. Cell Sci. 64:137–146
Fujishima M (2009) Infection and maintenance of Holospora species in Paramecium caudatum. In: Fujishima M (ed) Endosymbionts in Paramecium. Springer, Dordrecht Heidelberg London New York, pp 201–226
Schweikert M, Fujishima M, Görtz HD (2013) Symbiotic associations between ciliates and prokaryotes. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes: prokaryotic biology and symbiotic associations. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 427–463
Vannini C, Ferrantini F, Ristori A, Verni F, Petroni G (2012) Betaproteobacterial symbionts of the ciliate Euplotes: origin and tangled evolutionary path of an obligate microbial association. Environ. Microbiol. 14:2553–2563
Schrallhammer M, Schweikert M, Vallesi A, Verni F, Petroni G (2011) Detection of a novel subspecies of Francisella noatunensis as endosymbiont of the ciliate Euplotes raikovi. Microbial Ecol 61:455–464
Sjödin A, Öhrman C, Bäckman S, Lärkeryd A, Granberg M, Lundmark E et al (2014) Complete genome sequence of Francisella endociliophora strain FSC1006 isolated from a laboratory culture of the marine ciliate Euplotes raikovi. GenomeA 2:e01227–e01214
Sjöstedt A (2005) Family III Francisellaceae fam nov. In: Garrity GM (ed) Bergeys manual of systematic bacteriology. Springer, Baltimore, pp 199–210
Colquhoun DJ, Larsson P, Duodu S, Forsman M (2014) The family Francisellaceae. In: Rosenberg E, EF DL, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 287–314
Dorofe'ev KA (1947) Classification of the causative agent of tularemia. Symposium Research Works Institute Epidemiology and Microbiology Chita 1:170–180
Olsufjev NG, Meshcheryakova IS (1983) Subspecific taxonomy of Francisella tularensis McCoy and Chapin 1912. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 33:872–874
Ottem KF, Nylund A, Karlsbakk E, Friis-Moller A, Kamaishi T (2009) Elevation of Francisella philomiragia subsp noatunensis Mikalsen et al (2007) to Francisella noatunensis comb nov [syn Francisella piscicida Ottem et al (2008) syn nov] and characterization of Francisella noatunensis subsp orientalis subsp nov two important fish pathogens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 106:1231–1243
Colquhoun DJ, Duodu S (2011) Francisella infections in farmed and wild aquatic organisms. Vet. Res. 8(42):47
Larson MA, Nalbantoglu U, Sayood K, Zentz EB, Cer RZ, Iwen PC, Francesconi SC, Bishop-Lilly KA, Mokashi VP, Sjöstedt A, Hinrichs SH (2016) Reclassification of Wolbachia persica as Francisella persica comb nov and emended description of the family Francisellaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66:1200–1205
Hollis DG, Weaver RE, Steigerwalt AG, Wenger JD, Moss CW, Brenner DJ (1989) Francisella philomiragia comb nov (formerly Yersinia philomiragia) and Francisella tularensis biogroup novicida (formerly Francisella novicida) associated with human disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 27:1601–1608
Mailman TL, Schmidt MH (2005) Francisella philomiragia adenitis and pulmonary nodules in a child with chronic granulomatous disease. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 16:245–248
Sjöstedt A (2007) Tularemia: history epidemiology pathogen physiology and clinical manifestations. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1105:1–29
Di Giuseppe G, Erra F, Frontini F, Dini F, Vallesi A, Luporini P (2014) Improved description of the bipolar ciliate Euplotes petzi and definition of its basal position in the Euplotes phylogenetic tree. Eur. J. Protistol. 50:402–411
Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW, Blackall LL (2002) Design and evaluation of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization. Methods Mol. Biol. 179:29–42
Humrighouse BW, Adcock NJ, Rice EW (2011) Use of acid treatment and a selective medium to enhance the recovery of Francisella tularensis from water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:6729–6732
Petersen JM, Carlson J, Yockey B, Pillai S, Kuske C, Garbalena G et al (2009) Direct isolation of Francisella spp from environmental samples. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 48:663–667
Pavlovich NV, Mishan'kin BN (1987) Transparent nutrient medium for culturing Francisella tularensis. Antibiot Med Biotekhnol 32:133–137
Walker BJ, Abeel T, Shea T, Priest M, Abouelliel A, Sakthikumar S, Cuomo CA, Zeng Q, Wortman J, Young SK, Earl AM (2014) Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS One 9:e112963
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4:406–425
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 70 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33:1870–1874
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glöckne FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64:346–351
Morgulis A, Coulouris G, Raytselis Y, Madden TL, Agarwala R, Schäffer AA (2008) Database indexing for production MegaBLAST searches. Bioinformatics 24:1757–1764
Walsh DA, Zaikova E, Howes CG, Song YC, Wright JJ, Tringe SG, Tortell PD, Hallam SJ (2009) Metagenome of a versatile chemolithoautotroph from expanding oceanic dead zones. Science 326:578–582
Splettstoesser WD, Seibold E, Zeman E, Trebesius K, Podbielski A (2010) Rapid differentiation of Francisella species and subspecies by fluorescent in situ hybridization targeting the 23S rRNA. BMC Microbiol. 10(72):72
Merhej V, Royer-Carenzi M, Pontarotti P, Raoult D (2009) Massive comparative genomic analysis reveals convergent evolution of specialized bacteria. Biol. Direct 4(13):13
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol. Today 33:152–155
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang Y, Wishart DS (2016) PHASTER: a better faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucl Acids Res 44:W16–W21
Siguier P, Pérochon J, Lestrade L, Mahillon J, Chandler M (2006) ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucl Acids Res 34:D32–D36
Gray CG, Cowley SC, Cheung KK, Nano FE (2002) The identification of five genetic loci of Francisella novicida associated with intracellular growth. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 215:53–56
Nano FE, Zhang N, Cowley SC, Klose KE, Cheung KK, Roberts MJ, Ludu JS, Letendre GW, Meierovics AI, Stephens G, Elkins KL (2004) A Francisella tularensis pathogenicity island required for intramacrophage growth. J. Bacteriol. 186:430–6436
Santic M, Abu Kwaik Y (2013) Nutritional virulence of Francisella tularensis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 3:112
Xu Y, Labedan B, Glansdorff N (2007) Surprising arginine biosynthesis: a reappraisal of the enzymology and evolution of the pathway in microorganisms. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 71:36–47
Velasco AM, Leguina JI, Lazcano A (2002) Molecular evolution of the lysine biosynthetic pathways. J. Mol. Evol. 55:445–449
Ferla MP, Patrick WM (2014) Bacterial methionine biosynthesis. Microbiology 160:1571–1584
Ahmad S, Jensen RA (1988) The phylogenetic origin of the bifunctional tyrosine-pathway protein in the enteric lineage of bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 16:295–310
Challacombe JF, Petersen JM, Hodge D, Pillai S, Kuske CR (2017) Whole-genome relationships among Francisella bacteria of diverse origins define new species and provide specific regions for detection. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 83:e02589–e02516
Sjödin A, Svensson K, Öhrman C, Ahlinder J, Lindgren P, Duodu S, Johansson A, Colquhoun DJ, Larsson P, Forsman M (2012) Genome characterisation of the genus Francisella reveals insight into similar evolutionary paths in pathogens of mammals and fish. BMC Genomics 13:268
Qu PH, Chen SY, Scholz HC, Busse HJ, Gu Q, Kämpfer P et al (2013) Francisella guangzhouensis sp nov isolated from air conditioning systems. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63:3628–3635
Qu PH, Li Y, Salam N, Chen SY, Liu L, Gu Q et al (2016) Allofrancisella inopinata gen nov sp nov and Allofrancisella frigidaquae sp nov isolated from water-cooling systems and transfer of Francisella guangzhouensis Qu et al 2013 to the new genus as Allofrancisella guangzhouensis comb nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66:4832–4838
Jiang J, Zhang Q, Warren A, Al-Rasheid KA, Song W (2010) Morphology and SSU rRNA gene-based phylogeny of two marine Euplotes species E orientalis spec nov and E raikovi (Ciliophora Euplotida). Eur. J. Protistol. 46:121–132
Pucciarelli S, Devaraj RR, Mancini A, Ballarini P, Castelli M, Schrallhammer M, Petroni G, Miceli C (2015) Microbial consortium associated with the Antarctic marine ciliate Euplotes focardii: an investigation from genomic sequences. Microbial Ecol 70:484–497
Valbonesi A, Luporini P (1993) Biology of Euplotes focardii an Antarctic ciliate. Polar Biol. 13:489–493
Di Giuseppe G, Dini F, Vallesi A, Luporini P (2015) Genetic relationships in bipolar species of the protist ciliate Euplotes. Hydrobiologia 761:71–83
Ahlinder J, Ohrman C, Svensson K, Lindgren P, Johansson A, Forsman M et al (2012) Increased knowledge of Francisella genus diversity highlights the benefits of optimised DNA-based assays. BMC Microbiol. 12:220
Moran NA, Plague GR (2004) Genomic changes following host restriction in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 14:627–633
Dutta C, Paul S (2012) Microbial lifestyle and genome signatures. Curr Genomics 13:153–162
Brodmann M, Dreier RF, Broz P, Basler M (2017) Francisella requires dynamic type VI secretion system and ClpB to deliver effectors for phagosomal escape. Nat. Commun. 8:15853
Checroun C, Wehrly TD, Fischer ER, Hayes SF, Celli J (2006) Autophagy-mediated reentry of Francisella tularensis into the endocytic compartment after cytoplasmic replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103:14578–14583
Acknowledgments
E.V. was supported by the Universidad de Sevilla (Movilidad Docente ERASMUS). We acknowledge the National Genomics Infrastructure (NGI)/Uppsala Genome Center and UPPMAX for providing assistance in massive parallel sequencing and computational infrastructure..
Funding
This work was financially supported by the PNRA (Programma Nazionale di Ricerca in Antartide) from the Italian Ministry of Research (MIUR), FAR (Fondo Ateneo Ricerca) from the University of Camerino, by the Swedish Ministry of Defence (A4040), and the Swedish Civil Contingencies Agency (B4010). The work performed at NGI/Uppsala Genome Center was funded by RFI/VR and Science for Life Laboratory, Sweden.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallesi, A., Sjödin, A., Petrelli, D. et al. A New Species of the γ-Proteobacterium Francisella, F. adeliensis Sp. Nov., Endocytobiont in an Antarctic Marine Ciliate and Potential Evolutionary Forerunner of Pathogenic Species. Microb Ecol 77, 587–596 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1256-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-018-1256-3