Abstract
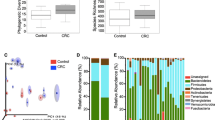
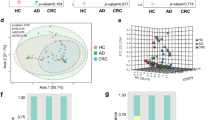
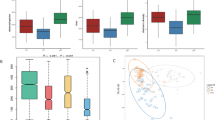
The human gut microbiota is a complex system that is essential to the health of the host. Increasing evidence suggests that the gut microbiota may play an important role in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer (CRC). In this study, we used pyrosequencing of the 16S rRNA gene V3 region to characterize the fecal microbiota of 19 patients with CRC and 20 healthy control subjects. The results revealed striking differences in fecal microbial population patterns between these two groups. Partial least-squares discriminant analysis showed that 17 phylotypes closely related to Bacteroides were enriched in the gut microbiota of CRC patients, whereas nine operational taxonomic units, represented by the butyrate-producing genera Faecalibacterium and Roseburia, were significantly less abundant. A positive correlation was observed between the abundance of Bacteroides species and CRC disease status (R = 0.462, P = 0.046 < 0.5). In addition, 16 genera were significantly more abundant in CRC samples than in controls, including potentially pathogenic Fusobacterium and Campylobacter species at genus level. The dysbiosis of fecal microbiota, characterized by the enrichment of potential pathogens and the decrease in butyrate-producing members, may therefore represent a specific microbial signature of CRC. A greater understanding of the dynamics of the fecal microbiota may assist in the development of novel fecal microbiome-related diagnostic tools for CRC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ley RE, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2006) Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 124(4):837–848. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.02.017
Savage DC (1977) Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol 31:107–133. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000543
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, Pettersson S (2012) Host–gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 336(6086):1262–1267. doi:10.1126/science.1223813
Hooper LV, Littman DR, Macpherson AJ (2012) Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 336(6086):1268–1273. doi:10.1126/science.1223490
Qin J, Li Y, Cai Z, Li S, Zhu J, Zhang F, Liang S, Zhang W, Guan Y, Shen D, Peng Y, Zhang D, Jie Z, Wu W, Qin Y, Xue W, Li J, Han L, Lu D, Wu P, Dai Y, Sun X, Li Z, Tang A, Zhong S, Li X, Chen W, Xu R, Wang M, Feng Q, Gong M, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Hansen T, Sanchez G, Raes J, Falony G, Okuda S, Almeida M, LeChatelier E, Renault P, Pons N, Batto JM, Zhang Z, Chen H, Yang R, Zheng W, Yang H, Wang J, Ehrlich SD, Nielsen R, Pedersen O, Kristiansen K (2012) A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 490(7418):55–60. doi:10.1038/nature11450
Scanlan PD, Shanahan F, Clune Y, Collins JK, O'Sullivan GC, O’Riordan M, Holmes E, Wang Y, Marchesi JR (2008) Culture-independent analysis of the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer and polyposis. Environ Microbiol 10(3):789–798. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01503.x
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444(7122):1027–1031. doi:10.1038/nature05414
De Cruz P, Prideaux L, Wagner J, Ng SC, McSweeney C, Kirkwood C, Morrison M, Kamm MA (2011) Characterization of the gastrointestinal microbiota in health and inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. doi:10.1002/ibd.21751
Tenesa A, Dunlop MG (2009) New insights into the aetiology of colorectal cancer from genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 10(6):353–358. doi:10.1038/nrg2574
Sobhani I, Tap J, Roudot-Thoraval F, Roperch JP, Letulle S, Langella P, Corthier G, Tran Van Nhieu J, Furet JP (2011) Microbial dysbiosis in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. PLoS One 6(1):e16393. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016393
Moore WE, Moore LH (1995) Intestinal floras of populations that have a high risk of colon cancer. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(9):3202–3207
Castellarin M, Warren RL, Freeman JD, Dreolini L, Krzywinski M, Strauss J, Barnes R, Watson P, Allen-Vercoe E, Moore RA, Holt RA (2011) Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res 22(2):299–306. doi:10.1101/gr.126516.111
Kostic AD, Gevers D, Pedamallu CS, Michaud M, Duke F, Earl AM, Ojesina AI, Jung J, Bass AJ, Tabernero J, Baselga J, Liu C, Shivdasani RA, Ogino S, Birren BW, Huttenhower C, Garrett WS, Meyerson M (2011) Genomic analysis identifies association of Fusobacterium with colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res 22(2):292–298. doi:10.1101/gr.126573.111
Petrosino JF, Highlander S, Luna RA, Gibbs RA, Versalovic J (2009) Metagenomic pyrosequencing and microbial identification. Clin Chem 55(5):856–866. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2008.107565
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(16):5261–5267. doi:10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Claesson MJ, O’Sullivan O, Wang Q, Nikkila J, Marchesi JR, Smidt H, de Vos WM, Ross RP, O’Toole PW (2009) Comparative analysis of pyrosequencing and a phylogenetic microarray for exploring microbial community structures in the human distal intestine. PLoS One 4(8):e6669. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006669
Lozupone C, Lladser ME, Knights D, Stombaugh J, Knight R (2011) UniFrac: an effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J 5(2):169–172. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.133
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541. doi:10.1128/AEM.01541-09
Tap J, Mondot S, Levenez F, Pelletier E, Caron C, Furet JP, Ugarte E, Munoz-Tamayo R, Paslier DL, Nalin R, Dore J, Leclerc M (2009) Towards the human intestinal microbiota phylogenetic core. Environ Microbiol 11(10):2574–2584. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01982.x
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5069–5072. doi:10.1128/AEM.03006-05
Boutaga K, van Winkelhoff AJ, Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM, Savelkoul PH (2005) Periodontal pathogens: a quantitative comparison of anaerobic culture and real-time PCR. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 45(2):191–199. doi:10.1016/j.femsim.2005.03.011
Kumar PS, Brooker MR, Dowd SE, Camerlengo T (2011) Target region selection is a critical determinant of community fingerprints generated by 16S pyrosequencing. PLoS One 6(6):e20956. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020956
Zhang H, DiBaise JK, Zuccolo A, Kudrna D, Braidotti M, Yu Y, Parameswaran P, Crowell MD, Wing R, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2009) Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(7):2365–2370. doi:10.1073/pnas.0812600106
Huse SM, Dethlefsen L, Huber JA, Mark Welch D, Relman DA, Sogin ML (2008) Exploring microbial diversity and taxonomy using SSU rRNA hypervariable tag sequencing. PLoS Genet 4(11):e1000255. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000255
Dethlefsen L, Huse S, Sogin ML, Relman DA (2008) The pervasive effects of an antibiotic on the human gut microbiota, as revealed by deep 16S rRNA sequencing. PLoS Biol 6(11):e280. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060280
Toprak NU, Yagci A, Gulluoglu BM, Akin ML, Demirkalem P, Celenk T, Soyletir G (2006) A possible role of Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin in the aetiology of colorectal cancer. Clin Microbiol Infect 12(8):782–786. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01494.x
Kim JM, Oh YK, Kim YJ, Oh HB, Cho YJ (2001) Polarized secretion of CXC chemokines by human intestinal epithelial cells in response to Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin: NF-kappa B plays a major role in the regulation of IL-8 expression. Clin Exp Immunol 123(3):421–427. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01462.x
Sanfilippo L, Li CK, Seth R, Balwin TJ, Menozzi MG, Mahida YR (2000) Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces the expression of IL-8 and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) by human colonic epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol 119(3):456–463. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01155.x
Wu S, Morin PJ, Maouyo D, Sears CL (2003) Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces c-Myc expression and cellular proliferation. Gastroenterology 124(2):392–400. doi:10.1053/gast.2003.50047
Wu S, Rhee KJ, Albesiano E, Rabizadeh S, Wu X, Yen HR, Huso DL, Brancati FL, Wick E, McAllister F, Housseau F, Pardoll DM, Sears CL (2009) A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat Med 15(9):1016–1022. doi:10.1038/nm.2015
Ivanov II, Frutos Rde L, Manel N, Yoshinaga K, Rifkin DB, Sartor RB, Finlay BB, Littman DR (2008) Specific microbiota direct the differentiation of IL-17-producing T-helper cells in the mucosa of the small intestine. Cell Host Microbe 4(4):337–349. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2008.09.009
Le Gouvello S, Bastuji-Garin S, Aloulou N, Mansour H, Chaumette MT, Berrehar F, Seikour A, Charachon A, Karoui M, Leroy K, Farcet JP, Sobhani I (2008) High prevalence of Foxp3 and IL17 in MMR-proficient colorectal carcinomas. Gut 57(6):772–779. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.123794
Allen-Vercoe E, Strauss J, Chadee K (2011) Fusobacterium nucleatum: an emerging gut pathogen? Gut Microbes 2(5):294–298. doi:10.1128/IAI.05118-11
Mondot S, Kang S, Furet JP, Aguirre de Carcer D, McSweeney C, Morrison M, Marteau P, Dore J, Leclerc M (2011) Highlighting new phylogenetic specificities of Crohn’s disease microbiota. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17(1):185–192. doi:10.1002/ibd.21436
Balamurugan R, Rajendiran E, George S, Samuel GV, Ramakrishna BS (2008) Real-time polymerase chain reaction quantification of specific butyrate-producing bacteria, Desulfovibrio and Enterococcus faecalis in the feces of patients with colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(8 Pt 1):1298–1303. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05490.x
Wang T, Cai G, Qiu Y, Fei N, Zhang M, Pang X, Jia W, Cai S, Zhao L (2011) Structural segregation of gut microbiota between colorectal cancer patients and healthy volunteers. ISME J. doi:10.1038/ismej.2011.109
Peppoloni S, Posteraro B, Colombari B, Manca L, Hartke A, Giard JC, Sanguinetti M, Fadda G, Blasi E (2011) Role of the (Mn) superoxide dismutase of Enterococcus faecalis in the in vitro interaction with microglia. Microbiology 157(Pt 6):1816–1822. doi:10.1099/mic.0.047381-0
Wang X, Huycke MM (2007) Extracellular superoxide production by Enterococcus faecalis promotes chromosomal instability in mammalian cells. Gastroenterology 132(2):551–561. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.040
Man SM (2011) The clinical importance of emerging Campylobacter species. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8(12):669–685. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2011.191
Zheng J, Meng J, Zhao S, Singh R, Song W (2008) Campylobacter-induced interleukin-8 secretion in polarized human intestinal epithelial cells requires Campylobacter-secreted cytolethal distending toxin- and Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Infect Immun 76(10):4498–4508. doi:10.1128/IAI.01317-07
Scheppach W, Weiler F (2004) The butyrate story: old wine in new bottles? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 7(5):563–567
Sokol H, Seksik P, Furet JP, Firmesse O, Nion-Larmurier I, Beaugerie L, Cosnes J, Corthier G, Marteau P, Dore J (2009) Low counts of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in colitis microbiota. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15(8):1183–1189. doi:10.1002/ibd.20903
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program: 2009CB522605), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, grant no. 81021003), and The Capital Health Research and Development of Special (grant no. 2011-4022-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 159 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, N., Yang, X., Zhang, R. et al. Dysbiosis Signature of Fecal Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Microb Ecol 66, 462–470 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0245-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0245-9