Abstract
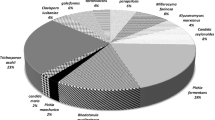
The major objective of the present study was to investigate the occurrence and identity of yeast species in fermented liquid feed (FLF) used for feeding piglets. In total, 40 different Danish farms were included in the analysis. The preparation and composition of FLF was found to be very heterogeneous with high variations in both yeast counts and yeast species composition. The yeast population varied between 6.0 × 103 and 4.2 × 107 cfug−1 with an average yeast count of 8.7 × 106 ± 1.1 × 107 cfug−1. A total of 766 yeasts were isolated and identified by conventional and/or molecular typing techniques. The predominant yeast species in the FLF samples were found to be Candida milleri (58.4%), Kazachstania exigua (17.5%), Candida pararugosa (6.40%) and Kazachstania bulderi (5.09%). No clear separation between isolates of C. milleri and Candida humilis could be obtained based on sequencing of the D1/D2 region of the 26S rRNA gene. The combined use of ITS-RFLP analysis and phenotypic criteria did meanwhile suggest a closer relationship with C. milleri than C. humilis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beal JD, Niven SJ, Campbell A, Brooks PH (2002) The effect of temperature on the growth and persistence of Salmonella in fermented liquid pig feed. Int J Food Microbiol 79:99–104
Beutler HO (2010) Ethanol. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Method of enzymatic analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 598–606
Boesen HT, Jensen TK, Schmidt AS, Jensen BB, Jensen SM, Møller K (2004) The influence of diet on Lawsonia intracellularis colonization in pigs upon experimental challenge. Vet Microbiol 103:35–45
Botes A, Todorov SD, von Mollendorff JW, Botha A, Dicks LMT (2007) Identification of lactic acid bacteria and yeast from boza. Process Biochem 42:267–270
Callon C, Duthoit F, Delbes C, Ferrand M, Le Frileux Y, De Cremoux R, Montel MC (2007) Stability of microbial communities in goat milk during a lactation year: molecular approaches. Syst Appl Microbiol 30:547–560
Canibe N, Hojberg O, Badsberg JH, Jensen BB (2007) Effect of feeding fermented liquid feed and fermented grain on gastrointestinal ecology and growth performance in piglets. J Anim Sci 85:2959–2971
Canibe N, Jensen BB (2003) Fermented and nonfermented liquid feed to growing pigs: effect on aspects of gastrointestinal ecology and growth performance. J Anim Sci 81:2019–2031
Damiani P, Gobbetti M, Cossignani L, Corsetti A, Simonetti MS, Rossi J (1996) The sourdough microflora. Characterization of hetero- and homofermentative lactic acid bacteria, yeasts and their interactions on the basis of the volatile compounds produced. LWT Food Sci Technol 29:63–70
Demeckova V, Kelly D, Coutts AGP, Brooks PH, Campbell A (2002) The effect of fermented liquid feeding on the faecal microbiology and colostrum quality of farrowing sows. Int J Food Microbiol 79:85–97
Fell JW, Boekhout T, Fonseca A, Scorzetti G, Statzell-Tallman A (2000) Biodiversity and systematics of basidiomycetous yeasts as determined by large-subunit rDNA D1/D2 domain sequence analysis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1351–1371
Gullo M, Romano AD, Pulvirenti A, Giudici P (2003) Candida humilis—dominant species in sourdoughs for the production of durum wheat bran flour bread. Int J Food Microbiol 80:55–59
Hammes WP, Brandt MJ, Francis KL, Rosenheim J, Seitter MFH, Vogelmann SA (2005) Microbial ecology of cereal fermentations. Trends Food Sci Technol 16:4–11
Jensen BB, Mikkelsen LL (1998) Feeding liquid diets to pigs. In: Garbsworthy PC, Wiseman J (eds) Recent advances in animal nutrition. Nottingham University Press, Nottingham, pp 107–126
Jespersen L, Nielsen DS, Honholt S, Jakobsen M (2005) Occurrence and diversity of yeasts involved in fermentation of West African cocoa beans. FEMS Yeast Res 5:441–453
Kurtzman CP (2003) Phylogenetic circumscription of Saccharomyces, Kluyveromyces and other members of the Saccharomycetaceae, and the proposal of the new genera Lachancea, Nakaseomyces, Naumovia, Vanderwaltozyma and Zygotorulaspora. FEMS Yeast Res 4:233–245
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (1998) Identification and phylogeny of ascomycetous yeasts from analysis of nuclear large subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA partial sequences. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 73:331–371
Kurtzman CP, Robnett CJ (2003) Phylogenetic relationships among yeasts of the ‘Saccharomyces complex’ determined from multigene sequence analyses. FEMS Yeast Res 3:417–432
Lacumin L, Cecchini F, Manzano M, Osualdini M, Boscolo D, Orlic S, Comi G (2009) Description of the microflora of sourdoughs by culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Food Microbiol 26:128–135
Lindecrona RH, Jensen TK, Jensen BB, Leser TD, Jiufeng W, Moller K (2003) The influence of diet on the development of swine dysentery upon experimental infection. Anim Sci 76:81–87
Lyberg K, Olstorpe M, Passoth V, Schnurer J, Lindberg JE (2008) Biochemical and microbiological properties of a cereal mix fermented with whey, wet wheat distillers’ grain or water at different temperatures. Anim Feed Sci Technol 144:137–148
Meyer SA, Payne RW, Yarrow D (1998) Candida Berkhout. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts a taxonomic study. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 454–573
Middelhoven WJ, Kurtzman CP, Vaughan-Martini A (2000) Saccharomyces bulderi sp nov., a yeast that ferments gluconolactone. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 77:223–228
Missotten JAM, Goris J, Michiels J, Van Coillie E, Herman L, De Smet S, Dierick NA, Heyndrickx M (2009) Screening of isolated lactic acid bacteria as potential beneficial strains for fermented liquid pig feed production. Anim Feed Sci Technol 150:122–138
Moran CA, Scholten RHJ, Tricarico JM, Brooks PH, Verstegen MWA (2006) Fermentation of wheat: Effects of backslopping different proportions of pre-fermented wheat on the microbial and chemical composition. Arch Anim Nutr 60:158–169
Niven SJ, Beal JD, Brooks PH (2006) The effect of controlled fermentation on the fate of synthetic lysine in liquid diets for pigs. Anim Feed Sci Technol 129:304–315
Olstorpe M, Axelsson L, Schnurer J, Passoth V (2010) Effect of starter culture inoculation on feed hygiene and microbial population development in fermented pig feed composed of a cereal grain mix with wet wheat distillers’ grain. J Appl Microbiol 108:129–138
Olstorpe M, Lyberg K, Lindberg JE, Schnurer J, Passoth V (2008) Population diversity of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria in pig feed fermented with whey, wet wheat distillers’ grains, or water at different temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1696–1703
Pedersen A.Ø. (2010) Fermented liquid feed to piglets. Danish Pig Production No 510.
Pedersen C, Jonsson H, Lindberg JE, Roos S (2004) Microbiological characterization of wet wheat distillers’ grain, with focus on isolation of lactobacilli with potential as probiotics. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1522–1527
Petersen KM, Møller PL, Jespersen L (2001) DNA typing methods for differentiation of Debaryomyces hansenii strains and other yeasts related to surface ripened cheeses. Int J Food Microbiol 69:11–24
Pulvirenti A, Caggia C, Restuccia C, Gullo M, Giudici P (2001) DNA fingerprinting methods used for identification of yeasts isolated from Sicilian sourdoughs. Ann Microbiol 51:107–120
Scholten RHJ, van der Peet-Schwering C, Verstegen MWA, den Hartog LA, Schrama JW, Vesseur PC (1999) Fermented co-products and fermented compound diets for pigs: a review. Anim Feed Sci Technol 82:1–19
Valmorri S, Mortensen HD, Jespersen L, Corsetti A, Gardini F, Suzzi G, Arneborg N (2008) Variations of internal pH in typical Italian sourdough yeasts during co-fermentation with lactobacilli. LWT Food Sci Technol 41:1610–1615
van Winsen RL, Urlings BAP, Lipman LJA, Snijders JMA, Keuzenkamp D, Verheijden JHM, van Knapen F (2001) Effect of fermented feed on the microbial population of the gastrointestinal tracts of pigs. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3071–3076
Vernocchi P, Valmorri S, Gatto V, Torriani S, Gianotti A, Suzzi G, Guerzoni ME, Gardini F (2004) A survey on yeast microbiota associated with an Italian traditional sweet-leavened baked good fermentation. Food Res Int 37:469–476
Yarrow D (1998) Methods for isolation, maintenance and identification of yeasts. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts a taxonomic study. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 77–100
Acknowledgement
This work is supported by The Danish Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Fisheries.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gori, K., Kryger Bjørklund, M., Canibe, N. et al. Occurrence and Identification of Yeast Species in Fermented Liquid Feed for Piglets. Microb Ecol 61, 146–153 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9706-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9706-6