Abstract
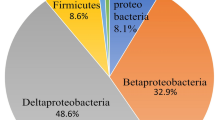
The diversity and function of nitrogen-fixing bacteria colonizing rice roots are not well understood. A field experiment was conducted to determine the diversity of diazotrophic communities associated with roots of modern rice cultivars using culture-independent molecular analyses of nitrogenase gene (nifH) fragments. Experimental treatments included four modern rice cultivars (Oryza sativa, one Indica, one Japonica and two hybrid rice varieties) and three levels (0, 50, and 100 kg N ha−1) of N (urea) fertilizer application. Cloning and sequencing of 103 partial nifH genes showed that a diverse community of diazotrophs was associated with rice roots. However, the nifH gene fragments belonging to betaproteobacteria were dominant, accounting for nearly half of nifH sequences analyzed across the clone libraries. Most of them were similar to nifH fragments retrieved from wild rice and Kallar grass, with Azoarcus spp. being the closest cultured relatives. Alphaproteobacteria were also detected, but their relative abundance in the nifH gene pools was dramatically decreased with N fertilizer application. In addition, a high fraction of nifH gene pools was affiliated with methylotrophs and methane oxidizers. The sequence analysis was consistent with the terminal restriction fragment-length polymorphism (T-RFLP) fingerprinting of the nifH gene fragments, which showed three of four dominant terminal restriction fragments were mainly related to betaproteobacteria based on in silico digestion of nifH sequences. T-RFLP analyses also revealed that the effects of N fertilizer on the nifH gene diversity retrieved from roots varied according to rice cultivars. In summary, the present study revealed the prevalence of betaproteobacterial sequences among the proteobacteria associated with roots of modern rice cultivars. This group of diazotrophs appeared less sensitive to N fertilizer application than diazotrophic alphaproteobacteria. Furthermore, methylotrophs may also play a role in nitrogen fixation on rice roots. However, it must be noted that due to the potential bias of polymerase chain reaction protocol, the significance of non-proteobacterial diazotrophs such as Firmicutes and anaerobic bacteria is possibly underestimated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong W (1969) Rhizosphere oxidation in rice—an analysis of intervarietal differences in oxygen flux from roots. Physiol Plantarum 22:296–303
Auman A, Speake C, Lidstrom M (2001) NifH sequences and nitrogen fixation in type I and type II methanotrophs. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4009–4016
Boddey RM (1995) Biological nitrogen fixation in sugar cane: a key to energetically viable biofuel production. Crit Rev Plant Sci 14:263–279
Bodelier PLE (2003) Interaction between oxygen-releasing roots and microbial processes in flooded soils and sediments. Ecol Studies 168:331–362
Bodelier PLE, Laanbroek HJ (2004) Nitrogen as regulatory factor of methane oxidation in soils and sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:265–277
Bodelier PLE, Roslev P, Henckel T, Frenzel P (2000) Stimulation by ammonium-based fertilizers of methane oxidation in soil around rice roots. Nature 403:421–424
Bosse U, Frenzel P (1998) Methane emissions from rice microcosms: the balance of production, accumulation and oxidation. Biogeochemistry 41:199–214
Boulygina ES, Kuznetsov BB, Marusina AI, Tourova TP, Kravchenko IK, Bykova SA, Kolganova TV, Galchenko VF (2002) A study of nucleotide sequences of nifH genes from the representatives of methanotrophic bacteria. Microbiology 71:425–432
Buckley DH, Huangyutitham V, Hsu SF, Nelson TA (2007) Stable isotope probing with 15N2 reveals novel noncultivated diazotrophs in Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3196–3204
Chin KJ, Lukow T, Conrad R (1999) Effect of temperature on structure and function of the methanogenic archaeal community in an anoxic rice field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2341–2349
Choudhury ATMA, Kennedy IR (2004) Prospects and potentials for systems of biological nitrogen fixation in sustainable rice production. Biol Fertil Soils 39:219–227
Conrad R, Rothfuss F (1991) Methane oxidation in the soil surface layer of a flooded rice field and the effect of ammonium. Biol Fertil Soils 12:28–32
Dean DR, Jacobson MR (1992) Biochemical genetics of nitrogenase. In: Stacy G, Burris RH, Evans HJ (eds) Biological nitrogen fixation. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 763–834
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Engelhard M, Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B (2000) Preferential occurrence of diazotrophic endophytes, Azoarcus spp., in wild rice species and land races of Oryza sativa in comparison with modern races. Environ Microbiol 2:131–141
Galloway JN, Schlesinger WH, Levy HI, Michaels AF, Schnoor JL (1995) Nitrogen fixation: anthropogenic enhancement-environmental response. Global Biogeochem Cycles 9:235–252
Hengstmann U, Chin KJ, Janssen PH, Liesack W (1999) Comparative phylogenetic assignment of environmental sequences of genes encoding 16S rRNA and numerically abundant culturable bacteria from an anoxic rice paddy soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5050–5058
Hurek T, Egener T, Reinhold-Hurek B (1997) Divergence in nitrogenases of Azoarcus spp., Proteobacteria of the β subclass. J Bacteriol 179:4172–4178
Hurek T, Handley LL, Reinhold-Hurek B, Piche Y (2002) Azoarcus grass endophytes contribute fixed nitrogen to the plant in an unculturable state. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:233–242
James EK, Olivares FL (1998) Infection and colonization of sugar cane and other graminaceous plants by endophytic diazotrophs. Crit Rev Plant Sci 17:77–119
Karl D, Bergman B, Capone D, Carpenter E, Letelier R, Lipschultz F, Paerl H, Sigman D, Stal L (2002) Dinitrogen fixation in the world’s oceans. Biogeochem 57/58:47–98
Knauth S, Hurek T, Brar D, Reinhold-Hurek B (2005) Influence of different Oryza cultivars on expression of nifH gene pools in roots of rice. Environ Microbiol 7:1725–1733
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Briefings Bioinform 5:150–163
Ladha JK, Reddy PM (1995) Extension of nitrogen fixation to rice necessity and possibilities. GeoJournal 35:363–372
Larimer FW, Harwood CS (2004) Complete genome sequence of the metabolically versatile photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Nat Biotechnol 22:55–61
Lima E, Boddey RM, Döbereiner J (1987) Quantification of biological nitrogen fixation associated with sugar cane using a 15N-aided nitrogen balance. Soil Bio Biochem 19:165–170
Lovell CR, Piceno YM, Quattro JM, Bagwell CE (2000) Molecular analysis of diazotroph diversity in the rhizosphere of smooth cordgrass, Spartina alterniflora. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3814–3822
Lu YH, Rosencrantz D, Liesack W, Conrad R (2006) Structure and activity of bacterial community inhabiting rice roots and the rhizosphere. Environ Microbiol 8:1351–1360
Lüdemann H, Arth I, Liesack W (2000) Spatial changes in the bacterial community structure along a vertical oxygen gradient in flooded paddy soil cores. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:754–762
Methe BA, Nelson KE, Eisen JA, Paulsen IT, Nelson W, Heidelberg JF, Wu D, Wu M, Ward N, Beanan MJ, Dodson RJ, Madupu R, Brinkac LM, Daugherty SC, DeBoy RT, Durkin AS, Gwinn M, Kolonay JF, Sullivan SA, Haft DH, Selengut J, Davidsen TM, Zafar N, White O, Tran B, Romero C, Forberger HA, Weidman J, Khouri H, Feldblyum TV, Utterback TR, Van Aken SE, Lovley DR, Fraser CM (2003) Genome of Geobacter sulfurreducens: metal reduction in subsurface environments. Science 302:1967–1969
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2-chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. ASA, SSSA, Madison, WI, USA
Piceno YM, Lovell CR (2000) Stability in natural bacterial communities. I. Nutrient addition effects on rhizosphere diazotroph assemblage composition. Microb Ecol 39:32–40
Poly F, Monrozier LJ, Bally R (2001) Improvement in the RFLP procedure for studying the diversity of nifH genes in communities of nitrogen fixers in soil. Res Microbiol 152:95–103
Reinhold-Hurek B, Hurek T (1998) Life in grasses: diazotrophic endophytes. Trends Microbiol 6:139–144
Revsbech NP, Pedersen O, Reichardt W, Briones A (1999) Microsensor analysis of oxygen and pH in the rice rhizosphere under field and laboratory conditions. Biol Fert Soils 29:379–385
Saleena LM, Rangarajan S, Nair S (2002) Diversity of Azospirillum strains isolated from rice plants grown in saline and nonsaline sites of coastal agricultural ecosystem. Microb Ecol 44:271–277
Stoltzfus JR, So R, Malarvithi PP, Ladha JK, de Bruijn FJ (1997) Isolation of endophytic bacteria from rice and assessment of their potential for supplying rice with biologically fixed nitrogen. Plant Soil 194:25–36
Tan Z, Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B (2003) Effect of N-fertilizer, plant genotype and environmental conditions on nifH gene pools in roots of rice. Environ Microbiol 5:1009–1015
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
TraÃn Van V, NgoÃkeà S, Berge O, Faure D, Bally R, Hebbar P, Heulin T (1997) Isolation of Azospirillum lipoferum from the rhizosphere of rice by a new, simple method. Can J Microbiol 43:486–490
Ueda T, Suga Y, Yahiro N, Matsuguchi T (1995) Remarkable N2-fixing bacterial diversity detected in rice roots by molecular evolutionary analysis of nifH gene sequences. J Bacteriol 177:1414–1417
Weber S, Stubner S, Conrad R (2001) Bacterial populations colonizing and degrading rice straw in anoxic paddy soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1318–1327
Yanni YG, Rizk RY, Corich V, Squartini A, Ninke K, Hollingsworth SP, Orgambide G, de Bruijn F, Stoltzfus J, Buckley D, Schmidt TM, Mateos PF, Ladha JK, Dazzo FB (1997) Natural endophytic association between Rhizobium leguminosarum bv trifolii and rice roots and assessment of its potential to promote rice growth. Plant Soil 194:99–114
Zani S, Mellon MT, Collier JL, Zehr JP (2000) Expression of nifH genes in natural microbial assemblages in Lake George, New York, detected by reverse transcriptase PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3119–3124
Zehr JP, Jenkins BD, Short SM, Steward GF (2003) Nitrogenase gene diversity and microbial community structure: a cross-system comparison. Environ Microbiol 5:539–554
Zhang L, Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B (2006) Position of the fluorescent label is a crucial factor determining signal intensity in microarray hybridizations. Nucleic Acids Res 34:395–396
Acknowledgements
We thank Shiwen Huang and Ling Wang at the China National Rice Research Institute for the assistance in field preparation and general management. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions on the revision of this manuscript. This study was partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 40625003) and the Chang Jiang Scholars Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Ma, K. & Lu, Y. Prevalence of Betaproteobacterial Sequences in nifH Gene Pools Associated with Roots of Modern Rice Cultivars. Microb Ecol 57, 58–68 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-008-9403-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-008-9403-x