Abstract
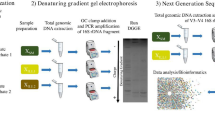
Differential emergence and diversity of bacterial communities from activated sludge in response to varied cultural conditions using 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) were investigated by coupling molecular analyses based on 16S rDNA with functional genes. We employed three different cultural conditions: (1) a culture sequentially fed a high concentration (300 mg/L) of 2,4-D (HS); (2) a culture continuously fed a low concentration (10 mg/L) of 2,4-D (LC); and (3) a serial batch culture in which 1% (v/v) of culture was transferred to a fresh medium containing a high concentration (300 mg/L) of 2,4-D (HB). The HS and LC bioreactors were operated for 3 months and HB was repeatedly transferred for 1 month. The 2,4-D was stably degraded under all the cultural conditions tested. PCR amplification and cloning-based analysis of functional genes using community DNAs from the cultures revealed five different oxygenase genes that may be involved in the initial step of 2,4-D degradation. All five gene-types were present in HS, while one of the five genes, type V (tftA) was not detected in LC. Quantitative PCR analysis showed that in HS, Ralstonia eutropha JMP 134 type-tfdA4 (type I) was the most abundant in copy number (2.0 ± 0.1 × 107 copies/μg DNA) followed by RASC type-tfdA (type II) (1.8 ± 1.0 × 106 copies/μg DNA), putative cadA-like gene (type IV) (2.6 ± 0.8 × 105 copies/μg DNA), cadA gene (type III) (1.3 ± 1.0 × 104 copies/μg DNA), and tftA gene (type V) (3.5 ± 1.1 × 103 copies/μg DNA). Similar results were obtained in LC. In contrast, HB contained only type I and type III genes, and the type I gene was five orders of magnitude greater in copy number than the type III gene. Denaturing gel gradient electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis of PCR, amplified 16S rDNA fragments of bacterial communities in the three different cultures showed low similarity coefficient values (≤0.35) when compared to the original activated sludge, suggesting that 2,4-D amendment caused a drastic change in the bacterial community. Particularly, HB showed only six bands (16–18 bands in the other cultures) and very low similarity coefficient values when compared to the other communities (0.10 to HS, 0.17 to LC, and 0.0 to original sludge). These results indicated that serial batch culturing (HB) resulted in a phylogenetically limited number of 2,4-D degrading bacteria carrying limited catabolic genes whereas more diverse 2,4-D degraders and catabolic genes were present in HS and LC. Therefore, the approach used for monitoring should be taken into account when one evaluates the population dynamics of contaminant-degrading bacteria at bioremediation sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
SF Altschul W Gish W Miller EW Myers DJ Lipman (1990) ArticleTitleBasic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215 403–410 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmbi.1990.9999 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXitVGmsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle2231712
MA Bhat M Tsuda K Horiike M Nozaki CS Vaidyanathan T Nakazawa (1994) ArticleTitleIdentification and characterization of a new plasmid carrying genes for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate from Pseudomonas cepacia CSV90. Appl Environ Microbiol 60 307–312 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXitV2ltbk%3D Occurrence Handle7509586
GR Chaudry GH Huang (1988) ArticleTitleIsolation and characterization of a new plasmid from a Flavobacterium sp. which carries the genes from the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. J Bacteriol 170 3897–3902 Occurrence Handle2842290
AO Crockett CT Wittwer (2001) ArticleTitleFluorescein-labeled oligonucleotides for real-time PCR: using the inherent quenching of deoxyguanosine nucleotides. Anal Biochem 290 89–97 Occurrence Handle10.1006/abio.2000.4957 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXht1artLc%3D Occurrence Handle11180941
CE Danganan RW Ye DL Daubaras L Xun AM Chakarabarty (1994) ArticleTitleNucleotide sequence and functional analysis of the genes encoding 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid oxygenase in Pseudomonas cepacia AC1100. Appl Environ Microbiol 60 4100–4106 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXhvFGmtbs%3D Occurrence Handle7527626
CE Danganan S Shankar RW Ye AM Chakrabarty (1995) ArticleTitleSubstrate diversity and expression of the 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid oxygenase from Burkholderia cepacia AC1100. Appl Environ Microbiol 61 4500–4504 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXpslCmtbw%3D Occurrence Handle8534119
LR Dice (1945) ArticleTitleMeasures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26 297–302
RH Don JM Pemberton (1981) ArticleTitleProperties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 145 681–686 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXhtFOlurs%3D Occurrence Handle6257648
RH Don JM Pemberton (1985) ArticleTitleGenetic and physical map of the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degradative plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol 161 466–468 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhtVOitbk%3D Occurrence Handle3968031
RH Don AJ Weightman HJ Knackmuss KN Timmis (1985) ArticleTitleTransposon mutagenesis and cloning analysis of the pathways for degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 3-chlorobenzoate in Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134 (pJP4). J Bacteriol 161 85–90 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhs1Wntrg%3D Occurrence Handle2981813
RH Don PT Cox BJ Wainwright K Barker JS Mattick (1991) ArticleTitle“touchdown” PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 19 4008 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmtVShu70%3D Occurrence Handle1861999
WC Evance BSW Smith HN Fernley JI Davies (1971) ArticleTitleBacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J 122 543–551 Occurrence Handle5123888
F Fukumori RP Hausinger (1993) ArticleTitleAlcaligenes eutrophus IMP 134 “2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid monooxygenase” is an α-ketoglutarate-dependant dioxygenase. J Bacteriol 175 2083–2086 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXitVyitbY%3D Occurrence Handle8458850
RR Fulthorpe C McGowan OV Maltseva WE Holben JM Tiedje (1995) ArticleTitle2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading bacteria contain mosaics of catabolic genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61 3274–3281 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnvVyisLk%3D Occurrence Handle7574638
RA Haugland DJ Schlemn RP Lyons III PR Sferra AM Chakrabarty (1990) ArticleTitleDegradation of the chlorinated phenoxyacetate herbicides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid by pure and mixed bacterial cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 56 1357–1362 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXkslCmsrw%3D Occurrence Handle2339889
DA Hogan DH Buckley CH Nakatsu TM Schmidt RP Hausinger (1997) ArticleTitleDistribution of the tfdA gene in soil bacteria that do not degrade 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D). Microb Ecol 34 90–96 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002489900038 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXltVWksbc%3D Occurrence Handle9230096
WE Holbon BM Schroeter VG Matheson RH Olsen JK Kukor VO Biederbeck AE Smith JM Tiedje (1992) ArticleTitleGene probe analysis of soil microbial populations selected by amendment with 2,4-dechlorophenoxyacetic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 58 3941–3948 Occurrence Handle1476437
K Itoh R Kanda Y Sumita H Kim Y Kamagata K Suyama H Yamamoto RP Hausinger JM Tiedje (2002) ArticleTitletfdA-like genes in 2,4-D degrading bacteria that belong to Bradyrhizobium–Agromonas–Nitrobacter–Afipia cluster in α-Proteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 68 3449–3454 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.7.3449-3454.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xlt1SntLg%3D Occurrence Handle12089027
JO Ka WE Holben JM Tiedje (1994) ArticleTitleGenetic and phenotypic diversity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)-degrading bacteria isolated from 2,4-D-treated field soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 60 1106–1115 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXis1Gmsbs%3D Occurrence Handle8017907
JO Ka WE Holben JM Tiedje (1994) ArticleTitleUse of gene probe to aid in recovery and identification of functionally dominant 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading populations in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 60 1116–1120 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXis1Gmsbg%3D Occurrence Handle8017908
Y Kamagata RR Fulthorpe K Tamura H Takami LJ Forney JM Tiedje (1997) ArticleTitlePristine environments harbor a new group of oligotrophic 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acid-degrading bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 2266–2272 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjsFCltbg%3D Occurrence Handle9172346
W Kitagawa S Takami K Miyauchi E Masai Y Kamagata JM Tiedje M Fukuda (2002) ArticleTitleNovel 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation genes from oligotrophic Bradyrhizobium sp. strain HW13 isolated from a pristine environment. J Bacteriol 184 509–518 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JB.184.2.509-518.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjtVyrug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11751829
S Kurata T Kanagawa K Yamada M Torimura Y Kamagata T Yokomaku K Kurane (2001) ArticleTitleFluorescent quenching-based quantitative detection of specific DNA/RNA using a BODIPY FL-labeled probe or primer. Nucleic Acids Res 29 e34 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/29.6.e34 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M3ks1Omuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11239011
OV Maltseva C McGowan R Fulthorpe PJ Oriel (1996) ArticleTitleDegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by haloalkaliphilic bacteria. Microbiology 142 1115–1122 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjtFyisr8%3D Occurrence Handle8704953
C McGowan R Fulthorpe A Wright JM Tiedje (1998) ArticleTitleEvidence for interspecies gene transfer in the evolution of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degraders. Appl Environ Microbiol 64 4089–4092 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXms1emsrY%3D Occurrence Handle9758850
G Muyzer C Ellen DE Waal AG Uitterlinden (1993) ArticleTitleProfiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction–amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59 695–700 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXit1Kktrk%3D Occurrence Handle7683183
CH Nakatsu R Korona RE Lenski FJ De Bruijn TL Marsh L Forney (1998) ArticleTitleParallel and divergent genotypic evolution in experimental population of Ralstonia sp. J Bacteriol 180 4325–4331 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlvVCmtb0%3D Occurrence Handle9721265
MH Rogoff JJ Reid (1956) ArticleTitleBacterial decomposition of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. J Bacteriol 71 303–307 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG28XltlSgtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle13306699
GL Silton LT Fan LE Erickson SM Lee (1986) ArticleTitleBiodegradation of 2,4-D and related xenobiotic compounds. Enzyme Microb Technol 8 395–403 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0141-0229(86)90145-6
Y Suwa AD Wright F Fukumori KA Nummy RP Hausinger WE Hollben LJ Forney (1996) ArticleTitleCharacterization of a chromosomally encoded 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid/α-ketoglutarate dioxygenase from Burkholderia sp. strain RASC. Appl Environ Microbiol 62 2464–2469 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjvFGnu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle8779585
JD Thompson DG Higgins TJ Gibson (1996) ArticleTitleClustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22 4673–4680
JM Tiedje M Alexander (1969) ArticleTitleEnzymatic cleavage of the ether bond of 2,4-dichlorophnoxyacetate. J Agric Food Chem 17 1080–1084 Occurrence Handle10.1021/jf60165a012 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1MXkvFymsr8%3D
TR Vallaeys R Futhorpe AM Wright G Soulas (1996) ArticleTitleThe metabolic pathway of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation involves different families of tfdA and tfdB genes according to PCR-RFLP analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 20 163–172 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-6496(96)00027-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjvFGhtLs%3D
WG Weisbrug SM Barns DA Pelletier DJ Lane (1991) ArticleTitle16S Ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173 697–703 Occurrence Handle1987160
Acknowledgment
The Japanese Society for the Promotion of Science supported this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, T., Kurata, S., Nakatsu, C. et al. Molecular Analysis of Bacterial Community Based on 16S rDNA and Functional Genes in Activated Sludge Enriched with 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid (2,4-D) under Different Cultural Conditions. Microb Ecol 49, 151–162 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-1035-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-1035-6