Abstract
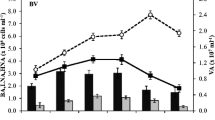
Little is known of the factors shaping sediment bacterial communities, despite their high abundance and reports of high diversity. Two factors hypothesized to shape bacterial communities in the water column are nutrient (resource) availability and virus infection. The role these factors play in benthic bacterial diversity was assessed in oligotrophic carbonate–based sediments of Florida Bay (USA). Sediment–water mesocosm enclosures were made from 1-m diameter clear polycarbonate cylinders which were pushed into sediments to ˜201 cm sediment depth enclosing ˜80 L of water. Mesocosms were amended each day for 14 d with 10 µM NH +4 and 1 µM PO 3−4 . In a second experiment, viruses from a benthic flocculent layer were concentrated and added back to flocculent layer samples which were collected near the mesocosm enclosures. Photosynthesis by microalgae in virus-amended incubations was monitored by pulse-amplitude modulated (PAM) fluorescence. In both experiments, bacterial diversity was estimated using automated rRNA intergenic spacer analysis (ARISA), a high-resolution fingerprinting approach. Initial sediment bacterial operational taxonomic unit (OTU) richness (236 ± 3) was higher than in the water column (148 ± 9), where an OTU was detectable when its amplified DNA represented >0.09% of the total amplified DNA. Effects on bacterial diversity and operational taxonomic unit (OTU) richness in nutrient-amended mesocosms may have been masked by the effects of containment, which stimulated OTU richness in the water column, but depressed OTU richness and diversity in sediments. Nutrient addition significantly elevated virus abundance and the ratio of viruses to bacteria (p < 0.05 for both) in the sediments, concomitant with elevated bacterial diversity. However, water column bacterial diversity (in unamended controls) was not affected by nutrient amendments, which may be due to rapid nutrient uptake by sediment organisms or adsorption of P to carbonate sediments. Addition of live viruses to benthic flocculent layer samples increased bacterial OTU diversity and richness compared with heat-killed controls; however, cluster analyses showed that the community structure in the virus-amended mesocosms varied greatly between replicates. Despite the strong effects upon eubacterial communities, photosynthesis of co-occurring protists and cyanobacteria was not significantly altered by the presence of virus concentrates. This study supports the hypothesis that nutrient availability plays a key role in shaping sediment bacterial communities, and also that viruses may regulate the abundance of the dominant competitors and allow less dominant organisms to maintain or increase their abundance in a community due to decreased competition for resources.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
EG Abal WC Dennison (1996) ArticleTitleSeagrass depth range and water quality in southern Moreton Bay, Queensland, Australia. Mar Freshwat Res 47 763–771 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmvFSmtrk%3D
HW Ackermann MS DuBow (1987) General Properties of Bacteriophages, 1st ed, vol 1. CRC Press Boca Raton, FL
K Anger (1975) ArticleTitleOn the influence of sewage pollution on inshore benthic communities in the South of Kiel Bay. Part 2. Quantitative studies on community structure. Helgol Wiss Meeresunters 27 408–438
E AvanissAghajani K Jones D Chapman C Brunk (1994) ArticleTitleA molecular technique for identification of bacteria using small subunit ribosomal RNA sequences. Biotechniques 17 144–149 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXitlOrsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle7946297
O Bergh KY Borsheim G Bratbak M Heldal (1989) ArticleTitleHigh abundance of viruses found in aquatic environments. Nature 340 467–468 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaA3s%2FlvFU%3D Occurrence Handle2755508
DF Bird SK Juniper M RicciardiRigault P Martineu YT Prairie SE Calvert (2001) ArticleTitleSubsurface viruses and bacteria in Holocene/Late Pleistocene sediments of Saanich Inlet, BC: ODP Holes 1033B and 1034B, Leg 169S. Mar Geol 174 227–239 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0025-3227(00)00152-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjtFegtrc%3D
J Borneman EW Triplett (1997) ArticleTitleMolecular microbial diversity in soils from eastern Amazonia: Evidence for unusual microorganisms and microbial population shifts associated with deforestation. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 2647–2653 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktlektLg%3D Occurrence Handle9212415
G Bratbak M Heldal TF Thingstad P Tuomi (1996) ArticleTitleDynamics of virus abundance in coastal seawater. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 19 263–269 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-6496(96)00023-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjsV2ms7o%3D
A Chao (1987) ArticleTitleNon-parametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Statist 11 265–270
A Cifuentes J Anton S Bentloch A Donnelly RA Herbert F Rodriguez-Valera (2000) ArticleTitleProkaryotic diversity in Zostera noltii–colonized marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 66 1715–1719 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.4.1715-1719.2000 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXisVWlsLk%3D Occurrence Handle10742267
JH Connell (1972) ArticleTitleCommunity interactions on marine rocky intertidal shores. Ann Rev Ecol Systematics 3 169–192 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.es.03.110172.001125
JB Cotner RH Sada H Bootsma T Johengen JF Cavaletto WS Gardner (2000) ArticleTitleNutrient limitation of heterotrophic bacteria in Florida Bay. Estuaries 23 611–620 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkvV2ntQ%3D%3D
R Danovaro A DellÁnno A Trucco M Serresi S Vanucci (2001) ArticleTitleDetermination of virus abundance in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 67 1384–1387 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.67.3.1384-1387.2001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhslSjtrc%3D Occurrence Handle11229937
R Danovaro E Manini A DellÁnno (2002) ArticleTitleHigher abundance of bacteria than of viruses in deep Mediterranean sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68 1468–1472 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.3.1468-1472.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitFSjsbY%3D Occurrence Handle11872504
R Danovaro M Serresi (2000) ArticleTitleViral density and virus-to-bacterium ratio in deep-sea sediments of the eastern mediterranean. Appl Environ Microbiol 66 1857–1861 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.5.1857-1861.2000 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjtV2lt70%3D Occurrence Handle10788350
MM Fisher EW Triplett (1999) ArticleTitleAutomated approach for ribsomal intergenic spacer analysis of microbial diversity and its application to freshwater bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 65 4630–4836
JA Fuhrman (1999) ArticleTitleMarine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological effects. Nature 399 541–548 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjvFeiurk%3D Occurrence Handle10376593
JA Fuhrman DE Comeau A Hagstrom AM Chan (1988) ArticleTitleExtraction of DNA suitable for molecular biological studies from natural planktonic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 54 1426–1429 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXktlCkt70%3D
JA Fuhrman CA Suttle (1993) ArticleTitleViruses in marine planktonic systems. Oceanography 6 51–63
J Garcia-Martinez SG Acinas AI Antón F Rodriguez-Valera (1999) ArticleTitleUse of the 16S-23S ribosomal genes spacer region in studies of prokaryotic diversity. J Microbiol Methods 36 55–64 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00011-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjs1Kgu74%3D Occurrence Handle10353800
SJ Giovannoni TB Britschgi CL Moyer KG Field (1990) ArticleTitleGenetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature 345 60–63 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXktFymu7s%3D Occurrence Handle2330053
JM Gonzales R Simó R Massana JS Covert EO Casamayor C Pedrós-Alió MA Moran (2000) ArticleTitleBacterial community structure associated with a dimethylsulfoniopropionate-producing North Atlantic algal bloom. Appl Environ Microbiol 66 4237–4246 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.10.4237-4246.2000 Occurrence Handle11010865
M Graco L Farías V Molina D Gutiérrez LP Nielsen (2001) ArticleTitleMassive developments of microbial mats following phytoplankton blooms in a naturally eutrophic bay: Implications for nitrogen cycling. Limnology Oceanogr 46 821–832 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkvFeksrw%3D
JN Guthrie DJW Moriarty LL Blackall (2000) ArticleTitleDNA extraction from coral reef sediment bacteria for the polymerase chain reaction. Microbiol Methods 43 73–80 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXot1yjurk%3D Occurrence Handle11121605
G Hardin (1960) ArticleTitleThe competitive exclusion principle. Science 131 1292–1297 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CC%2BC2M3jt1Q%3D
P Hartig K Wolfstein S Lippemeier F Colijn (1998) ArticleTitlePhotosynthetic activity of natural microphytobentos populations measured by fluorescence (PAM) and 14C-tracer methods: A comparison. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 166 53–62
I Hewson JA Fuhrman (2002) ArticleTitleViriobenthos abundance and production in neritic and basin sediments of Southern California. Eos 83 OS31C–29
I Hewson JM O′Neil WC Dennison (2001) ArticleTitleVirus-like particles associated with Lyngbya majuscula (Cyanophyta; Oscillatoriacea) bloom decline in Moreton Bay, Australia. Aquat Microb Ecol 25 207–213
I Hewson JM O′Neil JA Fuhrman WC Dennison (2001) ArticleTitleVirus-like particle distribution and abundance in sediments and overlying waters along eutrophication gradients in two subtropical estuaries. Limnol Oceanogr 47 1734–1746
I Hewson JM O’Neil CA Heil G Bratbak WC Dennison (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of concentrated natural viral communities on photosynthesis and community composition of co-occurring benthic microalgae and phytoplankton. Aquat Microb Ecol 25 1–10
JB Hughes JJ Hellmann TH Rocketts BJM Bohannan (2001) ArticleTitleCounting the uncountable: Statistical approaches to estimating microbial diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 67 4399–4406 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.67.10.4399-4406.2001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXns1Wisro%3D Occurrence Handle11571135
J Huisman FJ Weissing (1999) ArticleTitleBiodiversity of plankton by species oscillations and chaos. Nature 402 407–410 Occurrence Handle10.1038/46540
GE Hutchinson (1961) ArticleTitleThe paradox of the plankton. Am Naturalist 95 137–146 Occurrence Handle10.1086/282171
SC Jiang JH Paul (1998) ArticleTitleGene transfer by transduction in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 64 2780–2787 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsVKhsrw%3D Occurrence Handle9687430
JL Klappenbach JM Dunbar TM Schmidt (2000) ArticleTitlerRNA operon copy number reflects ecological strategies of bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 66 1328–1333 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.4.1328-1333.2000 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXisVWntLc%3D Occurrence Handle10742207
K Koop D Booth A Broadbent J Brodie D Bucher D Capone J Coll WC Dennison M Erdmann P Harrison O HoeghGuldberg P Hutchings G Jones AWD Larkum JM O′Neil A Steven T Tentori S Ward J Williamson D Yellowlees (2001) ArticleTitleENCORE: The effect of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs. Synthesis of results and conclusions. Mar Pollut Bull 42 91–120
C Lassen NP Revsbech O Pedersen (1997) ArticleTitleMacrophyte development and resuspension regulate the photosynthesis and production of benthic microalgae. Hydrobiologia 350 1–11 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003052226202 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXntlKlu7g%3D
AM Laverman AGCL Speksnijder M Braster GA Kowalchuk HA Verhof HW vanVerseveld (2001) ArticleTitleSpatiotemporal stability of ammonia-oxidizing community in a nitrogen-saturated forest soil. Microb Ecol 42 35–45 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmsF2it7w%3D Occurrence Handle12035079
LN Li C Kato K Horikoshi (1999) ArticleTitleBacterial diversity in deep sea sediments form different depths. Biodiversity Conservation 8 650–667
WT Liu TL Marsh H Cheng LJ Forney (1997) ArticleTitleCharacterization of microbial diversity by determining terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 4516–4522 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnt12ntbs%3D Occurrence Handle9361437
VM Madrid JY Aller RC Aller AY Christoserdov (2001) ArticleTitleHigh prokaryote diversity and analysis of community structure in mobile mud deposits off French Guiana: Identification of two new bacterial candidate divisions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37 197–209 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(01)00165-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXovVCju70%3D
P Maranger DF Bird (1996) ArticleTitleHigh concentrations of viruses in the sediments of Lake Gilbert, Quebec. Microb Ecol 31 141–151
JR Marchesi AJ Weightman BA Crag RJ Parkes JC Fry (2001) ArticleTitleMethanogen and bacterial diversity and distribution in deep sea hydrate sediments from the Cascadia Margin as revealed by 16s rRNA molecular analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 34 221–228
RT Noble JA Fuhrman (1998) ArticleTitleUse of SYBR Green I rapid epifluoresence counts of marine viruses and bacteria. Aquat Microb Ecol 14 113–118
JH Paul JB Rose SC Jiang CA Kellogg L Dickson (1993) ArticleTitleDistribution of viral abundance in the reef environment of Key Largo, Florida. Appl Environ Microbiol 59 718–724 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB2cznt1M%3D Occurrence Handle8480998
LM Proctor JA Fuhrman (1992) ArticleTitleMortality of marine bacteria in response to enrichments of the virus size fraction from seawater. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 87 283–293
LM Proctor JA Fuhrman (1990) ArticleTitleViral mortality of marine bacteria and cyanobacteria. Nature 343 60–61 Occurrence Handle10.1038/343060a0
JV Robinson CD Sandgren (1983) ArticleTitleThe effect of temporal environmental heterogeneity on community structure: a replicated experimental study. Oecologia (Berlin) 57 98–102
G Rocap DL Distel JB Waterbury SW Chisolm (2002) ArticleTitleResolution of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus ecotypes by using 16S-23S ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 68 1180–1191 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.3.1180-1191.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitFSjsr4%3D Occurrence Handle11872466
F Rohwer A Segall G Steward V Seguritan M Breitbart F Wolven F Azam (2000) ArticleTitleThe complete genomic sequence of the marine phage Roseophage SI01 shares homology with nonmarine phages. Limnol Oceanogr 45 408–418 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXitVKrtL8%3D
KG Sellner (1997) ArticleTitlePhysiology, ecology and toxic properties of marine cyanobacterial blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 42 1089–1104
K Simek J Pernthaler MG Weinbauer K Hornák JR Dolan J Nedoma M Masín R Amann (2001) ArticleTitleChanges in bacterial community composition and dynamics and viral mortality rates associated with enhanced flagellate grazing in a mesoeutrophic reservoir. Appl Environ Microbiol 67 2723–2733 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.67.6.2723-2733.2001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkt1Cit7c%3D Occurrence Handle11375187
RR Sokal FJ Rohlf (1995) Biometry. The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, vol 3. Freeman New York
CA Suttle (1992) ArticleTitleInhibition of photosynthesis in phytoplankton by the submicron size fraction concentrated from seawater. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 87 105–112
CA Suttle AM Chan (1993) ArticleTitleMarine cyanophages infecting oceanic and coastal strains of Synechococcus: Abundance, morphology, cross-infectivity and growth characteristics. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 92 99–109
CA Suttle AM Chan MT Cottrell (1990) ArticleTitleInfection of phytoplankton by viruses and reduction of primary productivity. Nature 347 467–469 Occurrence Handle10.1038/347467a0
CA Suttle AM Chan MT Cottrell (1991) ArticleTitleUse of ultrafiltration to isolate viruses from seawater which are pathogens of marine phytoplankton. Appl Environ Microbiol 57 721–726
MT Suzuki MS Rappe ZW Haimberger H Winfield N Adair J Stroebel SJ Giovannoni (1997) ArticleTitleBacterial diversity among small-subunit rRNA gene clones and cellular isolates from the same seawater sample. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 983–989 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhsV2ku7k%3D Occurrence Handle9055415
TF Thingstad M Heldal G Bratbak I Dundas (1993) ArticleTitleAre viruses important partners in pelagic food webs? Trends Evolutionary Ecol 8 209–213 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0169-5347(93)90101-T
JR Todorov AY Christoserdov JY Aller (2000) ArticleTitleMolecular analysis of microbial communities in mobile deltaic muds of Southeastern Papua New Guinea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 33 147–155 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(00)00055-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtVCru78%3D Occurrence Handle10967214
P Tuomi KM Fagerbakke G Bratbak M Heldal (1995) ArticleTitleNutritional enrichment of a microbial community: The effects on activity, elemental composition, community structure and virus production. FEMS Microbiol Ecol l6 123–134 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-6496(94)00076-9
I Valiela J McClelland J Hauxwell PJ Behr D Hersh K Foreman (1997) ArticleTitleMacroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: Controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnol Oceanog 42 1105–1118
DM Ward R Weller MM Bateson (1990) ArticleTitlerRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature 345 63–65 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXktlOltbo%3D Occurrence Handle1691827
MG Weinbauer D Fuks P Peduzzi (1993) ArticleTitleDistribution of viruses and dissolved DNA along a coastal trophic gradient in the northern Adriatic Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 59 4074–4082 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmtFKqsA%3D%3D
MG Weinbauer P Peduzzi (1995) ArticleTitleEffect of virus-rich high molecular weight concentrates of seawater on the dynamics of dissolved amino acids and carbohydrates. Mar Ecol Prog 127 245–253 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xmt1aktQ%3D%3D
SJ Williamson LA Houchin L McDaniel JH Paul (2002) ArticleTitleSeasonal variation in lysogeny as depicted by prophage induction in Tampa Bay, Florida. Appl Environ Microbiol 68 4307–4314 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.9.4307-4314.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmvVequrY%3D Occurrence Handle12200280
WH Wilson NG Carr NH Mann (1996) ArticleTitleThe effect of phosphate status on the kinetics of cyanophage infection in the oceanic cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH7803. J Phycol 32 506–516 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XlvVWisb8%3D
WH Wilson IR Joint NG Carr NH Mann (1993) ArticleTitleIsolation and molecular characterization of five marine cyanophages propagated on Synechococcus sp. strain WH7803. Appl Environ Microbiol 59 3736–3743 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXislWjtA%3D%3D
WH Wilson S Turner NH Mann (1998) ArticleTitlePopulation dynamics of phytoplankton and viruses in a phosphate-limited mesocosm and their effects on DMSP and DMS production. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sci 46 49–59 Occurrence Handle10.1006/ecss.1998.0333 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitFOjtbo%3D
JP Xu M Noble SL Eittreim LK Rosenfeld FB Schwing CH Pilskaln (2002) ArticleTitleDistribution and transport of suspended particulate matter in Monterey Canyon, California. Mar Geol 181 215–234 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00268-7
JH Zar (1984) Biostatistical Analyses, 2nd ed. Prentice-Hall New York
Y Zhong F Chen SW Wilhelm L Poorvin RE Hodson (2002) ArticleTitlePhylogenetic diversity of marine cyanophage isolated and natural virus communities as revealed by sequences of viral capsid assembly proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol 68 1576–1584 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.68.4.1576-1584.2002 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivFGltrg%3D Occurrence Handle11916671
Acknowledgements
The authors thank C. Heil, D. Ault, M.B. Neely, S. Murasko (USF), G. Hitchcock, J. Jurado (UMiami, RSMAS), L. Gilbane, M.S. Schwalbach, J. Steele (USC), J. Burns (UMD), and two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript. We thank the entire staff and vessel operators at the FIO/FMRI Keys Marine Laboratory, Layton, Florida, for their assistance in this study. I.H. was supported by a USC Seagrant Traineeship while conducting this study. This work was supported by NSF grants OCE9906989, OCE0084231, and OCE9705523 awarded to J.A.F and NOAA/COP/SFERPM2000 Award No. NAO60PO519 to G.A.V. (G. Hitchcock, UM/RSMAS, co-PI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hewson, I., Vargo, G. & Fuhrman, J. Bacterial Diversity in Shallow Oligotrophic Marine Benthos and Overlying Waters: Effects of Virus Infection, Containment, and Nutrient Enrichment . Microb Ecol 46, 322–336 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-002-1067-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-002-1067-3