Abstract
Background
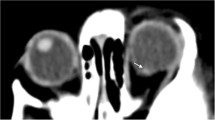
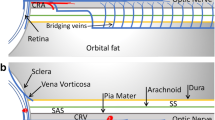
Retinal hemorrhages are one of the most important supportive evidences for abusive head trauma (AHT). Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) is highly suited to identify various forms of intracranial hemorrhage in AHT. However its utility in imaging retinal hemorrhage is not well established.
Objective
SWI is a sensitive sequence for identifying retinal hemorrhage on MRI.
Materials and methods
In this retrospective analysis, 26 consecutive infants and young children with a suspected admission diagnosis of AHT underwent indirect ophthalmoscopy and brain MRI protocol for AHT along with SWI. Brain susceptibility-weighted images of 14 age-matched children were used as controls. For detecting retinal hemorrhage, susceptibility-weighted images of patients and controls were reviewed randomly and independently by two neuroradiologists who were blinded to the history and ophthalmology findings. A pediatric ophthalmologist graded the indirect ophthalmoscopy images.
Results
A diagnosis of AHT was confirmed in all 26 cases from a multidisciplinary meeting. Indirect ophthalmoscopy images were available in 21 cases. Ophthalmoscopy was positive for retinal hemorrhage in the right eye in 18 cases (85.7%) and in the left eye in 16 cases (76.2%). On SWI, retinal hemorrhage was identified in the right eye in 9/21 cases (42.8%) and in the left eye in 8/21 cases (38.1%) of AHT. Analysis of SWI in 21 cases of AHT demonstrated a sensitivity of 50%, specificity of 100%, positive predictive value of 100% and negative predictive value of 32% for detecting retinal hemorrhage.
Conclusion
SWI is moderately sensitive and highly specific for identifying retinal hemorrhage in AHT. Further studies are needed to identify steps to improve the efficiency of SWI in detecting retinal hemorrhage.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cowley LE, Morris CB, Maguire SA et al (2015) Validation of a prediction tool for abusive head trauma. Pediatrics 136:290–298
Leventhal JM, Asnes AG, Pavlovic L, Moles RL (2014) Diagnosing abusive head trauma: the challenges faced by clinicians. Pediatr Radiol 44:S537–S542
Bhardwaj G, Chowdhury V, Jacobs MB et al (2010) A systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of ocular signs in pediatric abusive head trauma. Ophthalmology 117(983–992):e917
Piteau SJ, Ward MG, Barrowman NJ, Plint AC (2012) Clinical and radiographic characteristics associated with abusive and nonabusive head trauma: a systematic review. Pediatrics 130:315–323
Vinchon M, de Foort-Dhellemmes S, Desurmont M, Delestret I (2010) Confessed abuse versus witnessed accidents in infants: comparison of clinical, radiological, and ophthalmological data in corroborated cases. Childs Nerv Syst 26:637–645
Levin AV (2010) Retinal hemorrhage in abusive head trauma. Pediatrics 126:961–970
Zuccoli G, Panigrahy A, Haldipur A et al (2013) Susceptibility weighted imaging depicts retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma. Neuroradiology 55:889–893
Zuccoli G, Khan AS, Panigrahy A, Tamber MS (2017) In vivo demonstration of traumatic rupture of the bridging veins in abusive head trauma. Pediatr Neurol 72:31–35
Beavers AJ, Stagner AM, Allbery SM et al (2015) MR detection of retinal hemorrhages: correlation with graded ophthalmologic exam. Pediatr Radiol 45:1363–1371
Beauchamp MH, Ditchfield M, Babl FE et al (2011) Detecting traumatic brain lesions in children: CT versus MRI versus susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). J Neurotrauma 28:915–927
Jenny C, Hymel KP, Ritzen A et al (1999) Analysis of missed cases of abusive head trauma. JAMA 281:621–626
Maguire SA, Watts PO, Shaw AD et al (2013) Retinal haemorrhages and related findings in abusive and non-abusive head trauma: a systematic review. Eye 27:28–36
Hsieh KL, Zimmerman RA, Kao HW, Chen CY (2015) Revisiting neuroimaging of abusive head trauma in infants and young children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 204:944–952
Tong KA, Ashwal S, Obenaus A et al (2008) Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging: a review of clinical applications in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:9–17
Tong KA, Ashwal S, Holshouser BA et al (2003) Hemorrhagic shearing lesions in children and adolescents with posttraumatic diffuse axonal injury: improved detection and initial results. Radiology 227:332–339
Altinok D, Saleem S, Zhang Z et al (2009) MR imaging findings of retinal hemorrhage in a case of nonaccidental trauma. Pediatr Radiol 39:290–292
Polan RM, Poretti A, Scheller JM et al (2015) Retinal hemorrhages in nonaccidental trauma: look at susceptibility-weighted imaging on pediatric MRI. Pediatr Neurol 52:464–465
Binenbaum G, Forbes BJ (2014) The eye in child abuse: key points on retinal hemorrhages and abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol 44:S571–S577
Acknowledgments
We thank Eric Gagnon, Ph.D., data scientist, Department of Radiology, Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, for data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thamburaj, K., Soni, A., Frasier, L.D. et al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging of retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma. Pediatr Radiol 49, 210–216 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4292-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-018-4292-8