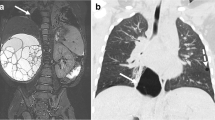
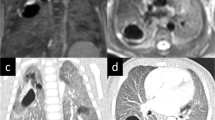
Abstract
Background
The contribution of MRI in the prenatal evaluation of congenital lung abnormalities (CLA) has not been extensively investigated.
Objective
(1) To compare diagnostic accuracy and assessment of prognostic factors between US and MRI in CLA and (2) to assess the diagnosis agreement between prenatal imaging and postnatal diagnosis.
Materials and methods
We included 23 consecutive fetuses who underwent concomitant US and MRI during gestation as well as postnatal CT and surgery (n = 22).
Results
US-MRI sets were performed at median gestational age of 26 (n = 16) and 34 (n = 22) weeks. Postnatal diagnoses were 11 congenital pulmonary airway malformations (CPAM), 4 bronchopulmonary sequestrations (BPS), 6 hybrid lesions and 2 cysts. US and MRI agreement was significantly better during the second trimester than during the third one (P = 0.02). Disagreements were related to missed cysts (n = 5), mediastinal shift (n = 6) and vessels (n = 5). US and MRI diagnosis agreement was present in 20 cases, including 5 cases of misdiagnosis. US and MRI were concordant with postnatal diagnosis in 17 and 16 cases, respectively.
Conclusion
In our series, no clear superiority of MRI over US in the prenatal evaluation of CLA was demonstrated, but US better demonstrated systemic feeding vessels and MRI cysts and normal lung adjacent to the lesion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azizkhan RG, Crombleholme TM (2008) Congenital cystic lung disease: contemporary antenatal and postnatal management. Pediatr Surg Int 24:643–657
Illanes S, Hunter A, Evans M et al (2005) Prenatal diagnosis of echogenic lung: evolution and outcome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 26:145–149
Cavoretto P, Molina F, Poggi S et al (2008) Prenatal diagnosis and outcome of echogenic fetal lung lesions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 32:769–783
Farrugia MK, Raza SA, Gould S et al (2008) Congenital lung lesions: classification and concordance of radiological appearance and surgical pathology. Pediatr Surg Int 24:987–991
Hadchouel A, Benachi A, Revillon Y et al (2011) Factors associated with partial and complete regression of fetal lung lesions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 38:88–93
Adzick NS (2009) Management of fetal lung lesions. Clin Perinatol 36:363–376
Hubbard AM, Adzick NS, Crombleholme TM et al (1999) Congenital chest lesions: diagnosis and characterization with prenatal MR imaging. Radiology 212:43–48
Olutoye OO, Coleman BG, Hubbard AM et al (2000) Prenatal diagnosis and management of congenital lobar emphysema. J Pediatr Surg 35:792–795
Chen CP, Liu YP, Lin SP et al (2005) Prenatal magnetic resonance imaging demonstration of the systemic feeding artery of a pulmonary sequestration associated with in utero regression. Prenat Diagn 25:721–723
Dhingsa R, Coakley FV, Albanese CT et al (2003) Prenatal sonography and MR imaging of pulmonary sequestration. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:433–437
Kawamura M, Itoh H, Yamada S et al (2005) Spontaneous regression of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung: longitudinal examinations by magnetic resonance imaging. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 45:157–160
Levine D, Jennings R, Barnewolt C et al (2001) Progressive fetal bronchial obstruction caused by a bronchogenic cyst diagnosed using prenatal MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:49–52
Liu YP, Shih SL (2008) Congenital lobar emphysema: appearance on fetal MRI. Pediatr Radiol 38:1264
Quinn TM, Hubbard AM, Adzick NS (1998) Prenatal magnetic resonance imaging enhances fetal diagnosis. J Pediatr Surg 33:553–558
Levine D, Barnewolt CE, Mehta TS et al (2003) Fetal thoracic abnormalities: MR imaging. Radiology 228:379–388
Liu YP, Chen CP, Shih SL et al (2010) Fetal cystic lung lesions: evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Pulmonol 45:592–600
Adzick NS, Harrison MR, Glick PL et al (1985) Fetal cystic adenomatoid malformation: prenatal diagnosis and natural history. J Pediatr Surg 20:483–488
Crombleholme TM, Coleman B, Hedrick H et al (2002) Cystic adenomatoid malformation volume ratio predicts outcome in prenatally diagnosed cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung. J Pediatr Surg 37:331–338
Stocker JT, Madewell JE, Drake RM (1977) Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung. Classification and morphologic spectrum. Hum Pathol 8:155–171
Griffin N, Devaraj A, Goldstraw P et al (2008) CT and histopathological correlation of congenital cystic pulmonary lesions: a common pathogenesis? Clin Radiol 63:995–1005
Correia-Pinto J, Gonzaga S, Huang Y et al (2010) Congenital lung lesions—underlying molecular mechanisms. Semin Pediatr Surg 19:171–179
Stanton M, de-Njere I, de-Ajayi N et al (2009) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the postnatal management of congenital cystic lung lesions. J Pediatr Surg 44:1027–1033
Aziz D, Langer JC, Tuuha SE et al (2004) Perinatally diagnosed asymptomatic congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation: to resect or not? J Pediatr Surg 39:329–334
Fitzgerald DA (2007) Congenital cyst adenomatoid malformations: resect some and observe all? Paediatr Respir Rev 8:67–76
Calvert JK, Lakhoo K (2007) Antenatally suspected congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung: postnatal investigation and timing of surgery. J Pediatr Surg 42:411–414
Tsai AY, Liechty KW, Hedrick HL et al (2008) Outcomes after postnatal resection of prenatally diagnosed asymptomatic cystic lung lesions. J Pediatr Surg 43:513–517
Conforti A, Aloi I, Trucchi A et al (2009) Asymptomatic congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung: is it time to operate? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 138:826–830
Davenport M, Warne SA, Cacciaguerra S et al (2004) Current outcome of antenally diagnosed cystic lung disease. J Pediatr Surg 39:549–556
Sauvat F, Michel JL, Benachi A et al (2003) Management of asymptomatic neonatal cystic adenomatoid malformations. J Pediatr Surg 38:548–552
Achiron R, Strauss S, Seidman DS et al (1995) Fetal lung hyperechogenicity: prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis, natural history and neonatal outcome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 6:40–42
Yong PJ, Von Dadelszen P, Carpara D et al (2012) Prediction of pediatric outcome after prenatal diagnosis and expectant antenatal management of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation. Fetal Diagn Ther 31:94–102
Biyyam DR, Chapman T, Ferguson MR et al (2010) Congenital lung abnormalities: embryologic features, prenatal diagnosis, and postnatal radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 30:1721–1738
Newman B (2006) Congenital bronchopulmonary foregut malformations: concepts and controversies. Pediatr Radiol 36:773–791
Dietrich RB, Cohen I (2006) Fetal MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 14:503–522
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beydon, N., Larroquet, M., Coulomb, A. et al. Comparison between US and MRI in the prenatal assessment of lung malformations. Pediatr Radiol 43, 685–696 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2596-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2596-7