Abstract
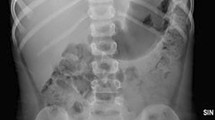
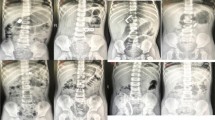
Foreign body ingestion is a common problem in the pediatric population and a frequent cause for emergency room visits. Magnets are common household objects that when ingested can bring about severe, possibly fatal gastrointestinal complications. Radiography is an integral component of the management of these children. Pediatric and emergency radiologists alike must be aware of imaging manifestations of magnet ingestion, as their identification drives decision-making for consulting surgeons and gastroenterologists. Radiology can thus substantially augment the clinical history and physical exam, facilitating appropriate management. This manuscript sequentially presents cases of magnet ingestion featuring imaging findings coupled with surgical and pathological correlation. Each case is presented to highlight ways in which the radiologist can make impactful contributions to diagnosis and management. Clinical overview with pitfalls of magnet ingestion imaging and an imaging decision tree will also be presented.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oestreich AE (2009) Worldwide survey of damage from swallowing multiple magnets. Pediatr Radiol 39:142–147
(CDC) CfDCaP (2006) Gastrointestinal injuries from magnet ingestion in children–United States, 2003–2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 55:1296–1300
Bronstein AC, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR et al (2011) 2010 annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 28th annual report. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 49:910–941
Ikenberry SO, Jue TL, Anderson MA et al (2011) Management of ingested foreign bodies and food impactions. Gastrointest Endosc 73:1085–1091
Cheng W, Tam PK (1999) Foreign-body ingestion in children: experience with 1,265 cases. J Pediatr Surg 34:1472–1476
Wishart DE (1928) The fate of foreign bodies swallowed by children. Can Med Assoc J 18:415–418
Brown JC, Murray KF, Javid PJ (2012) Hidden attraction: a menacing meal of magnets and batteries. J Emerg Med 43:266–269
Oestreich AE (2007) The usefulness of magnification in postgastric magnetopathy. Pediatr Radiol 37:1268–1269
McCormick S, Brennan P, Yassa J et al (2002) Children and mini-magnets: an almost fatal attraction. Emerg Med J 19:71–73
Nui A, Hirama T, Katsuramaki T et al (2005) An intestinal volvulus caused by multiple magnet ingestion: an unexpected risk in children. J Pediatr Surg 40:e9–e11
Ilçe Z, Samsum H, Mammadov E et al (2007) Intestinal volvulus and perforation caused by multiple magnet ingestion: report of a case. Surg Today 37:50–52
Oestreich AE (2004) Multiple magnet ingestion alert. Radiology 233:615
Chung S, Forte V, Campisi P (2010) A review of pediatric foreign body ingestion and management. Clin Pediatr Emerg Med 11:6
Butterworth J, Feltis B (2007) Toy magnet ingestion in children: revising the algorithm. J Pediatr Surg 42:e3–e5
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge several of their colleagues at Seattle Children’s Hospital for their assistance with this manuscript. These include Drs. Kathy Patterson of pathology, Jeffrey Avansino and Matthew Harting of surgery, and Anthony Woodward and Russ Migita of emergency medicine.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otjen, J.P., Rohrmann, C.A. & Iyer, R.S. Imaging pediatric magnet ingestion with surgical-pathological correlation. Pediatr Radiol 43, 851–859 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2549-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2549-1