Abstract
Background
Analysis of the middle ear with fetal MRI has not been previously reported.
Objective
To show the contribution of fetal MRI to middle ear imaging.
Materials and methods
The tympanic cavity was evaluated in 108 fetal cerebral MRI examinations (facial and/or cerebral malformation excluded) and in two cases, one of Treacher Collins syndrome (case 1) and the other of oculo-auriculo-vertebral (OUV) spectrum (case 2) with middle ear hypoplasia identified by MRI at 27 and 36 weeks’ gestation, respectively.
Results
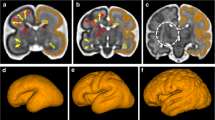
In all 108 fetuses (mean gestational age 32.5 weeks), the tympanic cavity and T2 hypointensity related to the ossicles were well visualised on both sides. Case 1 had micro/retrognathia and bilateral external ear deformity and case 2 had retrognathism with a left low-set and deformed ear. MRI made it possible to recognize the marked hypoplasia of the tympanic cavity, which was bilateral in case 1 and unilateral in case 2. Both syndromes are characterized by craniofacial abnormalities including middle ear hypoplasia, which cannot be diagnosed with US.
Conclusion
The middle ear cavity can be visualized with fetal MRI. We emphasize the use of this imaging modality in the diagnosis of middle ear hypoplasia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tilea B, Garel C, Menez F et al (2006) Contribution of fetal MRI to the diagnosis of inner ear abnormalities: report of two cases. Pediatr Radiol 36:149–154
Nemzek WR, Brodie HA, Chong BW et al (1996) Imaging findings of the developing temporal bone in fetal specimens. AJNR 17:1467–1477
Fryer A (2003) Syndromes associated with hereditary deafness. In: King SJ, Boothroyd AG (eds) Pediatric ENT radiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 35–54
Edwards SJ, Gladwin AJ, Dixon MJ (1997) The mutational spectrum in Treacher Collins syndrome reveals a predominance of mutations that create a premature-termination codon. Am J Hum Genet 60:515–524
Marszalek B, Wojcicki P, Kobus K et al (2002) Clinical features, treatment and genetic background of Treacher Collins syndrome. J Appl Genet 43:223–233
Burglen L, Soupre V, Diner PA et al (2001) Oto-mandibular dysplasias: genetics and nomenclature of syndromes. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 46:400–409
Dixon J, Trainor P, Dixon MJ (2007) Treacher Collins syndrome. Orthod Craniofac Res 10:88–95
Cohen J, Ghezzi F, Goncalves L et al (1995) Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of Treacher Collins syndrome: a case and review of the literature. Am J Perinatol 12:416–419
Crane JP, Beaver HA (1986) Midtrimester sonographic diagnosis of mandibulofacial dysostosis. Am J Med Genet 25:251–255
Meizner I, Carmi R, Katz M (1991) Prenatal ultrasonic diagnosis of mandibulofacial dysostosis (Treacher Collins syndrome). J Clin Ultrasound 19:124–127
Milligan DA, Harlass FE, Duff P et al (1994) Recurrence of Treacher Collins’ syndrome with sonographic findings. Mil Med 159:250–252
Ochi H, Matsubara K, Ito M et al (1998) Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of Treacher Collins syndrome. Obstet Gynecol 91:862
Shih JC, Shyu MK, Lee CN et al (1998) Antenatal depiction of the fetal ear with three-dimensional ultrasonography. Obstet Gynecol 91:500–505
Tanaka Y, Kanenishi K, Tanaka H et al (2002) Antenatal three-dimensional sonographic features of Treacher Collins syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 19:414–415
Vento AR, LaBrie RA, Mulliken JB (1991) The O.M.E.N.S. classification of hemifacial microsomia. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 28:68–76, discussion 77
Castori M, Brancati F, Rinaldi R et al (2006) Antenatal presentation of the oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum (OAVS). Am J Med Genet A 140:1573–1579
De Catte L, Laubach M, Legein J et al (1996) Early prenatal diagnosis of oculoauriculovertebral dysplasia or the Goldenhar syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 8:422–424
Bisdas S, Lenarz M, Lenarz T et al (2005) Inner ear abnormalities in patients with Goldenhar syndrome. Otol Neurotol 26:398–404
Martinelli P, Maruotti GM, Agangi A et al (2004) Prenatal diagnosis of hemifacial microsomia and ipsilateral cerebellar hypoplasia in a fetus with oculoauriculovertebral spectrum. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 24:199–201
Volpe P, Gentile M (2004) Three-dimensional diagnosis of Goldenhar syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 24:798–800
Hattori Y, Tanaka M, Matsumoto T et al (2005) Prenatal diagnosis of hemifacial microsomia by magnetic resonance imaging. J Perinat Med 33:69–71
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katorza, E., Nahama-Allouche, C., Castaigne, V. et al. Prenatal evaluation of the middle ear and diagnosis of middle ear hypoplasia using MRI. Pediatr Radiol 41, 652–657 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-010-1913-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-010-1913-2