Abstract
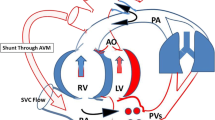
Herein we report the case of a neonate with a prenatally diagnosed large pulmonary arteriovenous malformation, managed with minimally invasive hemodynamic monitoring in our Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. The combination of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Pressure Recording Analytical Method could guide neonatal management of critical cases of vascular anomalies: immediate data are offered to clinicians, from which therapeutic decisions such as timing of surgical resection are made to achieve a positive outcome. We also systemically collected and summarized information on patients’ characteristics of previous cases reported in literature to data, and we compared them to our case.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Majumdar S, McWilliams JP (2020) Approach to pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: a comprehensive update. J Clin Med 9:1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061927
Gossage JR, Kanj G (1998) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. A state of the art review. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158:643–661
Gludovacz K, Vlasselaer J, Mesens T, Van Holsbeke C, Van Robays J, Gyselaers W (2012) Early neonatal complications from pulmonary arteriovenous malformations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: case report and review of the literature. J Matern Neonatal Med 25:1494–1498. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2011.629250
Romagnoli S, Franchi F, Ricci Z, Scolletta S, Payen D (2017) The pressure recording analytical method (PRAM): technical concepts and systematic review. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 31:1460–1470. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2016.09.004
Favia I, Rizza A, Garisto C, Haiberger R, Di Chiara L, Romagnoli S et al (2016) Cardiac index assessment by the pressure recording analytical method in infants after paediatric cardiac surgery: a pilot retrospective study. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 23:919–923. https://doi.org/10.1093/icvts/ivw251
Giliberti P, Mondì V, Conforti A, Lombardi MH, Sgrò S, Bozza P et al (2011) Near infrared spectroscopy in newborns with surgical disease. J Matern Neonatal Med 24:56–58. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2011.607673
Bailey SM, Hendricks-Munoz KD, Mally P (2014) Cerebral, renal, and splanchnic tissue oxygen saturation values in healthy term newborns. Am J Perinatol 31:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1349894
Bernal NP, Hoffman GM, Ghanayem NS, Arca MJ (2010) Cerebral and somatic near-infrared spectroscopy in normal newborns. J Pediatr Surg 45:1306–1310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2010.02.110
White RI, Pollak JS, Wirth JA (1996) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: diagnosis and transcatheter embolotherapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol 7:787–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1051-0443(96)70851-5
Hall RJ, Nelson WP, Blake HA, Geiger JP (1965) Massive pulmonary arteriovenous fistula in the newborn: a correctable form of “cyanotic heart disease;” an additional cause of cyanosis with left axis deviation. Ciculation 31:762–767. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.31.5.762
Crosby IK, Tompkins DG, Carpenter MA (1975) Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula and patent ductus arteriosus in the newborn infant. J Pediatr 86:986–987
Clarke C, Goh T, Blackwood A, Venables A (1976) Massive pulmonary arteriovenous fistula in the newborn. Br Heart J 38:1092–1095
Fried R, Amberson JB, Loughlin JEO, Cruz SB, Sniderman KW, Firpo AB et al (1982) Congenital pulmonary arteriovenous fistula producing pulmonary arterial steal syndrome. Pediatr Cardiol 2:313–318
Pierce RN, Dunn L, Knisely AS (1992) Consumptive coagulopathy in utero associated with multiple vascular malformations. Pediatr Pathol 12:67–71
Allen SW, Whitfield JM, Clarke DR, Sujansky E, Wiggins JW (1993) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation in the newborn: a familial case. Pediatr Cardiol 14:58–61
Grady RM, Sharkey AM, Bridges ND (1994) Transcatheter coil embolisation of a pulmonary arteriovenous malformation in a neonate. Br Heart J 71:370–371
Trivedi K, Sreeram N (1996) Neonatal pulmonary arteriovenous malformation. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 74(1):F80. https://doi.org/10.1136/fn.74.1.f80
Russell MW, Gomez C, Nugent C, Christiansen J (2002) Large fetal pulmonary arteriovenous fistula: impact on pulmonary development. Pediatr Cardiol 23:454–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-002-0127-2
Bennhagen RG, Holje G, Laurin S, Pesonen E (2002) Coil embolization of a neonatal pulmonary arteriovenous malformation newborn. Pediatr Cardiol 23:235–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-001-0056-5
Heling K-S, Tennstedt C, Goldner B, Bollmann R (2002) Prenatal diagnosis of intrapulmonary arteriovenous malformation: sonographic and pathomorphological findings. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 19:514–517. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-0705.2002.00702.x
Ravasse P, Maragnes P, Petit T, Laloum D (2003) Total pneumonectomy as a salvage procedure for pulmonary arteriovenous malformation in a newborn: report of one case. J Pediatr Surg 38:254–255. https://doi.org/10.1053/jpsu.2003.50057
Boudjemline Y, Ladouceur M, Bonnet D (2006) Neonatal transcatheter closure of a large pulmonary arteriovenous fistula. Cardiol Young 16:593–595. https://doi.org/10.1017/S104795110600062X
Borsellino A, Giorlandino C, Malena S, Trucchi A, Cilio R, Bagolan P (2006) Early neurologic complications of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation in a newborn: an indication for surgical resection. J Pediatr Surg 41:453–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.11.043
Jenny DP, Tsai-Goodman B, Martin RP, Tulloh RM (2007) Antenatal diagnosis and postnatal treatment of intrapulmonary arteriovenous malformation. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 92:F366. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2006.104315
Curie A, Lesca G, Cottin V, Edery P, Bellon G, Faughnan ME et al (2007) Long-term follow-up in 12 children with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: confirmation of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in all cases. J Pediatr 151:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.03.021
Sinkovskaya E, Berkley E, Bogdan D, Sclater A, Abuhamad A (2009) The role of echocardiography in prenatal diagnosis of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation. Prenat Diagn 29:634–636. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.2261
Ruf B, Eicken A, Schreiber C, Hess J (2010) Clinical improvement after banding of a pulmonary branch artery in a symptomatic patient with Osler–Rendu–Weber syndrome. Pediatr Cardiol 31:136–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-009-9553-8
Diaz G, Marquez A, Gentile J (2012) Right pulmonary artery to left atrial fistula: a description of two cases, emphasising a diagnostic approach. Cardiol Young 22:279–284. https://doi.org/10.1017/S104795111100182X
Hellmund A, Berg C, Bryan C, Schneider M, Hraška V, Gembruch U (2014) Large fetal pulmonary arteriovenous malformation detected at midtrimester scan with subsequent high cardiac output syndrome and favorable postnatal outcome. Fetal Diagn Ther 35:133–136. https://doi.org/10.1159/000353913
Ostras O, Kurkevych A, Bohuta L, Yalynska T, Raad T, Lewin M et al (2015) Prenatal diagnosis of left pulmonary artery-to-pulmonary vein fistula and its successful surgical repair in a neonate. Tex Hear Inst J 42:169–171. https://doi.org/10.14503/THIJ-13-3960
Devanagondi R, Tapio JB, Grifka RG (2015) Transcatheter occlusion of large pulmonary arteriovenous malformations using multiple devices in a neonate. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 85(3):430–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccd.25561
Loureiro P, Laranjo S, Lage MJ, Trigo C, Pinto FF, Martins JDF (2017) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation closure in a preterm newborn. Port J Cardiol 36:779–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repc.2016.12.017
Yakut K, Varan B, Ozkan M (2018) A rare cause of cyanosis in newborns: arteriovenous fistula between the right pulmonary artery and the left atrium and its treatment. Cardiol Young 28:605–607. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1047951117002669
Lin Y, Hogan W, Stillwell K, Moore P, Peyvandi S, Amin E et al (2020) Giant neonatal pulmonary arteriovenous malformation: an imaging and management challenge. Cardiovasc Imaging Case Reports 4:526–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.case.2020.08.008
Wałdoch A, Sabiniewicz R, Kwiatkowska J (2020) A rare cause of newborn central cyanosis. Echocardiography 37(9):1524–1525. https://doi.org/10.1111/echo.14809
Contegiacomo A, Del Ciello A, Rella R, Attempati N, Coppolino D, Larici AR, Di Stasi C, Marano G, Manfredi R (2019) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: what the interventional radiologist needs to know. Radiol Med 124(10):973–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-019-01051-7
Dokumcu Z, Ozcan C, Alper H, Erdener A (2015) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation in children. Pediatr Int 57(4):708–711. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.12564
Barile L, Landoni G, Pieri M, Ruggeri L, Maj G, Neto CN et al (2013) Cardiac index assessment by the pressure recording analytic method in critically ill unstable patients after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 27:1108–1113. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2013.02.016
Carsetti A, Cecconi M, Rhodes A (2015) Fluid bolus therapy: monitoring and predicting fluid responsiveness. Curr Opin Crit Care 21:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCC.0000000000000240
Marik PE, Cavallazzi R, Vasu T, Hirani A (2009) Dynamic changes in arterial waveform derived variables and fluid responsiveness in mechanically ventilated patients: a systematic review of the literature*. Crit Care Med 37:2642–2647. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a590da
Han D, Pan S, Li H, Meng L, Luo Y, Ou-Yang C (2020) Prognostic value of cardiac cycle efficiency in children undergoing cardiac surgery: a prospective observational study. Br J Anaesth 125:321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2020.05.042
Walsh TS, McArdle F, McLellan SA, Maciver C, Maginnis M, Prescott RJ et al (2004) Does the storage time of transfused red blood cells influence regional or global indexes of tissue oxygenation in anemic critically ill patients? Crit Care Med 32:364–371. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000108878.23703.E0
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Dr. Ee Win Khoo (MD, RANZCR, consultant radiologist at the Queen Elizabeth Hospital Woodville South, Adelaide, South Australia) and Dr. Luca Borro (3D Biomedical Specialist, Clinical Management and Technological Innovations Area, Department of Imaging, Bambino Gesù Children's Hospital, Rome, Italy) for their support.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PG and DUDR conceptualized and designed the study, drafted the initial manuscript, participated to the case management, collected data, performed literature search, carried out the initial analyses and reviewed and revised the manuscript. FL, CC, FP, ASa performed literature search, collected and interpreted data, and revised the manuscript. AC and PBa performed surgical repair, and critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. ASe, LC and AT performed imaging (computed tomography, prenatal ultrasound and echocardiography, respectively), and revised the manuscript. AN performed genetic analysis and revised the manuscript. PF performed histopathological studies and revised the manuscript. PBo, NC and FS participated to the case management and revised the manuscript. AD and IC coordinated and supervised data collection, and critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Considering the nature of the analysis, this study reported only a retrospective analysis of data available through the Institutional Database. Personal data were restricted to essential information and were treated in order to guarantee the respect of privacy of the involved patients, as specifically stated by Italian Law D.Lgs n.196 of 2003 about personal data protection. Therefore, the study did not require preliminary evaluation by the local Ethical Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giliberti, P., De Rose, D.U., Landolfo, F. et al. Hemodynamic Assessment of a Large Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformation in a Neonate: Case Report and Review of Literature. Pediatr Cardiol 43, 1383–1391 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-022-02862-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-022-02862-8