Abstract
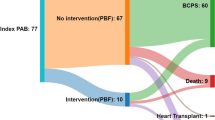
We investigated the effects of intraoperative parameters measured during pulmonary artery banding operations and pre-discharge parameters on the completion of Fontan procedures. Fifty consecutive patients with single-ventricle anomalies and unrestricted pulmonary blood flow who underwent a PAB operation in and were discharged from our hospital were retrospectively analyzed. Patients who underwent a Fontan operation, a Glenn shunt operation, or who were eligible for a Fontan procedure were defined as the “successful group.” Patients who needed rebanding prior to a bidirectional Glenn shunt, patients who were not eligible for a Glenn shunt, and those underwent a takedown due to high pulmonary arterial pressure after implantation of a Glenn shunt were defined as the “failure-to-progress group.” The successful group included 34 (68%) patients and the failure-to-progress group included 16 (32%) patients. The median age was 2 months (IQR 1–4 months). There was a statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of systolic pulmonary arterial pressure, mean pulmonary arterial pressure, and pulmonary arterial pressure/systemic arterial pressure after PAB (P = 0.01, 0.03, and 0.03, respectively). While the median gradient before discharge was 60 mm Hg (IQR 50–70 mm Hg) in the successful group, it was 47.5 mm Hg (IQR 45–63.7 mm Hg) in the failure-to-progress group (P = 0.05). Mortality was observed in one (2.9%) patient in the successful group and five (31.2%) patients in the failure-to-progress group (P = 0.04). Successful pulmonary arterial banding increases long-term survival. Adequate targets should be determined, efforts should be made to achieve these targets, and patients should be followed up closely in terms of rebanding when the targets are not reached.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trusler GA, Mustard WT (1972) A method of banding the pulmonary artery for large isolated ventricular septal defect with and without transposition of the great arteries. Ann Thorac Surg 13:351–355
Albus RA, Trusler GA, Izakawa T, Williams W (1984) Pulmonary artery banding. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 88:645–653
Valente AS, Mesquita F, Mejia AC, Maia IC, Maior MS, Branco CK et al (2009) Pulmonary artery banding: a simple procedure? a critical analysis at a tertiary center. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc 24:327–333
Baslaim G (2009) Modification of Trusler’s formula for the pulmonary artery banding. Heart Lung Circ 18:353–357
Kajihara N, Asou T, Takeda Y, Kosaka Y, Onakatomi Y, Nagafuchi H, Yasui S (2010) Pulmonary artery banding for functionally single ventricles: ımpact of tighter banding in staged fontan era. Ann Thorac Surg 89(1):174–179
Wernovsky G, Bove EL (1998) Single ventricle lesions. In: Chang AC, Hanley FL, Wernovsky G, Wessel DL (eds) Pediatric cardiac intensive care. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 275–276
Kotani Y, Coles M, Desai ND, Honjo O, Caldarone CA, Coles JG, et al (2015) The utility of aortic blood flow measurements in the prediction of pulmonary artery banding outcome. Ann Thorac Surg 99(6):2096–2100
Liu C, Pei Cheng P, Liu A, Li B et al (2019) Reverse remodeling of pulmonary arterioles after pulmonary artery banding in patients ≥ 2 years old with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension and congenital heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol 40(5):958–964
Sasikumar N, Ramanan S, Manohar K, Rema S, Subramanyan R, Kumar RS et al (2014) Pulmonary artery banding for univentricular heart beyond the neonatal period. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 22(6):660–666
Talwar S, Kamat NA, Choudhary SK, Ramakrishnan S, Saxena A, Juneja R et al (2016) Mid-term outcomes of patients undergoing adjustable pulmonary artery banding. Indian Heart J 68(1):72–76
Bonnet D, Corno AF, Sidi D, Sekarski N, Beghetti M, Schulze-Neick I et al (2004) Early clinical results of the telemetric adjustable pulmonary artery banding FloWatch-PAB. Circulation 110(11 Suppl 1):158–163
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SE: Conception or design of the work, Drafting the work, Final approval of the version to be published, any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. EÇ: Drafting the work, Final approval of the version to be published, any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. SBG: Conception or design of the work, Revising the work, Final approval of the version to be published, any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. OY: Acquisition and analysis, Final approval of the version to be published, any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. İCT, İSO, YE, AG, SH: Revising the work, Final approval of the version to be published, any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee (140920-2020/39, 09.06.2020) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was not obtained from the individual participants included in the study as it was a retrospective study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ergün, S., Çilsal, E., Genç, S.B. et al. Univentricular Pulmonary Artery Banding: How Tight is Tight Enough for Successful Progress?. Pediatr Cardiol 42, 840–848 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-021-02548-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-021-02548-7