Abstract
Candidates for the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) are screened using an electrocardiogram (S-ECG) tool to measure appropriate detection. We sought to define the S-ICD candidacy of congenital heart disease patients using the S-ECG tool. We also analyzed the reliability of the (S-ECG) tool between measurers in this population. Patients above the age of 12 and with a diagnosis associated with either a higher incidence of cardiac arrest or vascular access challenges were asked to undergo screening. S-ECGs were then analyzed by a pediatric electrophysiologist, an S-ICD device engineer, and an S-ICD clinical representative for candidacy. Results were compared for interobserver variability and S-ECGs were analyzed by t test to determine variables that differ among passing and failing leads. Thirty-one patients underwent screening. Two of the 31 (6.5%) patients failed S-ICD screening. Analysis of the screening leads demonstrated the highest passing rates using lead III at a 5 mm/mV amplitude setting with 71 and 62% pass rate in the supine and standing positions, respectively. Interobserver analysis correlated well among the three measurers. There was a higher amplitude difference between QRS and T waves among passing versus failing S-ECG. Congenital heart disease patients have acceptable passage rates utilizing the S-ECG algorithm. Interobserver measurements were well correlated and these data suggest that the proximal coil to device (lead III) vector would be best utilized in this patient population. A larger difference between QRS and T wave amplitudes was associated with a higher S-ECG passing rate.

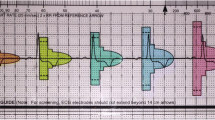
(Courtesy of Boston Scientific)

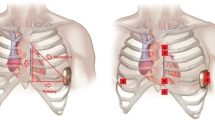
(Courtesy of Cameron Health/Boston Scientific)

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khairy P (2016) Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in adults with congenital heart disease. Heart 102:1703–1709
Silka MJ, Hardy BG, Menashe VD, Morris CD (1998) A population-based prospective evaluation of risk of sudden cardiac death after operation for common congenital heart defects. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:245–251
Khairy P, Fernandes SM, Mayer JE Jr, Triedman JK, Walsh EP, Lock JE, Landzberg MJ (2008) Long-term survival, modes of death, and predictors of mortality in patients with Fontan surgery. Circulation 117:85–92
Khairy P, Harris L, Landzberg MJ, Fernandes SM, Barlow A, Mercier LA, Viswanathan S, Chetaille P, Gordon E, Dore A, Cecchin F (2008) Sudden death and defibrillators in transposition of the great arteries with intra-atrial baffles: a multicenter study. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 1:250–257
Groh CA, Sharma S, Pelchovitz DJ, Bhave PD, Rhyner J, Verma N, Arora R, Chicos AB, Kim SS, Lin AC, Passman RS, Knight BP (2014) Use of an electrocardiographic screening tool to determine candidacy for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm 11:1361–1366
Aziz S, Leon AR, El-Chami MF (2014) The subcutaneous defibrillator: a review of the literature. J Am Coll Cardiol 63:1473–1479
Burke MC, Gold MR, Knight BP, Barr CS, Theuns DA, Boersma LV, Knops RE, Weiss R, Leon AR, Herre JM, Husby M, Stein KM, Lambiase PD (2015) Safety and efficacy of the totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: 2-year results from a pooled analysis of the IDE study and EFFORTLESS registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 65:1605–1615
De Maria E, Olaru A, Cappelli S (2015) The entirely subcutaneous defibrillator (S-ICD): state of the art and selection of the ideal candidate. Curr Cardiol Rev 11:180–186
Bordachar P, Marquie C, Pospiech T, Pasquie JL, Jalal Z, Haissaguerre M, Thambo JB (2016) Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillators in children, young adults and patients with congenital heart disease. Int J Cardiol 203:251–258
Bongiorni MG, Viani S, Zucchelli G, Di Cori A, Segreti L, Paperini L, Levorato D, Boem A, Branchitta G, Andreini D, Soldati E (2015) Subcutaneous implantable cardiac defibrillators: indications and limitations. Curr Heart Fail Rep 12:79–86
Pedersen SS, Mastenbroek MH, Carter N, Barr C, Neuzil P, Scholten M, Lambiase PD, Boersma L, Johansen JB, Theuns DA (2016) A comparison of the quality of life of patients with an entirely subcutaneous implantable defibrillator system versus a transvenous system (from the EFFORTLESS S-ICD quality of life substudy). Am J Cardiol 118:520–526
Tjong FVY, Brouwer TF, Smeding L, Kooiman KM, de Groot JR, Ligon D, Sanghera R, Schalij MJ, Wilde AAM, Knops RE (2016) Combined leadless pacemaker and subcutaneous implantable defibrillator therapy: feasibility, safety, and performance. Europace 18:1740–1747
Kuschyk J, Stach K, Tulumen E, Rudic B, Liebe V, Schimpf R, Borggrefe M, Roger S (2015) Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: first single-center experience with other cardiac implantable electronic devices. Heart Rhythm 12:2230–2238
Pettit SJ, McLean A, Colquhoun I, Connelly D, McLeod K (2013) Clinical experience of subcutaneous and transvenous implantable cardioverter defibrillators in children and teenagers. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 36:1532–1538
Jarman JW, Lascelles K, Wong T, Markides V, Clague JR, Till J (2012) Clinical experience of entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in children and adults: cause for caution. Eur Heart J 33:1351–1359
Bettin M, Lascelles F, Rath B, Kobe J, Eckardt L (2015) Recent advances in the entirely subcutaneous ICD system. F1000Prime Rep 7:46 eCollection 2015
Zeb M, Curzen N, Veldtman G, Yue A, Roberts P, Wilson D, Morgan J (2015) Potential eligibility of congenital heart disease patients for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator based on surface electrocardiogram mapping. Europace 17:1059–1067
Zeb M, Curzen N, Allavatam V, Wilson D, Yue A, Roberts P, Morgan J (2015) Sensitivity and specificity of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator pre-implant screening tool. Int J Cardiol 195:205–209
Francia P, Adduci C, Palano F, Semprini L, Serdoz A, Montesanti D, Santini D, Musumeci B, Salvati A, Volpe M, Autore C (2015) Eligibility for the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 26:893–899
Chan NY, Yuen HC, Mok NS (2015) Right parasternal electrode configuration converts a failed electrocardiographic screening to a pass for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation. Heart Lung Circ 24:e203–e205
Wilson DG, Zeb M, Veldtman G, Dimitrov BD, Morgan JM (2016) Left and right parasternal sensing for the S-ICD in adult congenital heart disease patients and normal controls. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 39:282–290
Randles DA, Hawkins NM, Shaw M, Patwala AY, Pettit SJ, Wright DJ (2014) How many patients fulfil the surface electrocardiogram criteria for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation? Europace 16:1015–1021
Frommeyer G, Dechering DG, Zumhagen S, Loher A, Kobe J, Eckardt L, Reinke F (2016) Long-term follow-up of subcutaneous ICD systems in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a single-center experience. Clin Res Cardiol 105:89–93
Maurizi N, Olivotto I, Olde Nordkamp LR, Baldini K, Fumagalli C, Brouwer TF, Knops RE, Cecchi F (2015) Prevalence of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator candidacy based on template ECG screening in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm 13:457–463
Lambiase PD, Gold MR, Hood M, Boersma L, Theuns DA, Burke MC, Weiss R, Russo AM, Kaab S, Knight BP (2016) Evaluation of subcutaneous ICD early performance in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy from the pooled EFFORTLESS and IDE cohorts. Heart Rhythm 13:1066–1074
Olde Nordkamp LR, Brouwer TF, Barr C, Theuns DA, Boersma LV, Johansen JB, Neuzil P, Wilde AA, Carter N, Husby M, Lambiase PD, Knops RE (2015) Inappropriate shocks in the subcutaneous ICD: incidence, predictors and management. Int J Cardiol 195:126–133
El-Chami MF, Harbieh B, Levy M, Leon AR, Merchant FM (2016) Clinical and electrocardiographic predictors of T wave oversensing in patients with subcutaneous ICD. J Arrhythm 32:181–185
Olde Nordkamp LR, Warnaars JL, Kooiman KM, de Groot JR, Rosenmoller BR, Wilde AA, Knops RE (2014) Which patients are not suitable for a subcutaneous ICD: incidence and predictors of failed QRS-T-wave morphology screening. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 25:494–499
Brisben AJ, Burke MC, Knight BP, Hahn SJ, Herrmann KL, Allavatam V, Mahajan D, Sanghera R, Gold MR (2015) A new algorithm to reduce inappropriate therapy in the S-ICD system. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 26:417–423
Ziacchi M, Corzani A, Diemberger I, Martignani C, Marziali A, Mazzotti A, Massaro G, Rapezzi C, Biffi M, Boriani G (2016) Electrocardiographic eligibility for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator: evaluation during bicycle exercise. Heart Lung Circ 25:476–483
Kooiman KM, Knops RE, Olde Nordkamp L, Wilde AA, de Groot JR (2014) Inappropriate subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator shocks due to T-wave oversensing can be prevented: implications for management. Heart Rhythm 11:426–434
Gold MR, Weiss R, Theuns DA, Smith W, Leon A, Knight BP, Carter N, Husby M, Burke MC (2014) Use of a discrimination algorithm to reduce inappropriate shocks with a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm 11:1352–1358
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Shelby Kutty, MD, Ling Li, MD, and Valerie K. Shostrom, M.S. for statistical work and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept/design: VCT, HR, AJ. Data collection, analysis/interpretation: VCT, MP, MM, AJ, HR, AR. Drafting article: VCT, AJ. Critical revision of article: VCT, AR, AJ, MM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Mark Peterson and Martin McDaniel are contracted employees of Boston Scientific. All other authors have no disclosures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, V.C., Peterson, M., McDaniel, M. et al. Analysis of Screening Electrocardiogram for the Subcutaneous Defibrillator in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 38, 1162–1168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1635-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-017-1635-4